Abstract
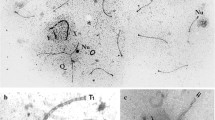
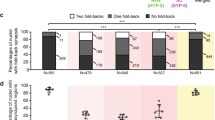
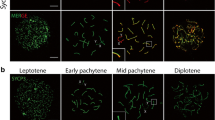
Homologous chromosome synapsis in inversion heterozygotes results in the formation of inversion loops. These loops might be transformed into straight, non-homologously paired bivalents via synaptic adjustment. Synaptic adjustment was discovered 30 years ago; however, its relationship with recombination has remained unclear. We analysed this relationship in female mouse embryos heterozygous for large paracentric inversion In(1)1Rk using immunolocalisation of the synaptonemal complex (SYCP3) and mature recombination nodules (MLH1) proteins. The frequency of cells containing bivalents with inversion loops decreased from 69 % to 28 % during pachytene. If an MLH1 focus was present in the non-homologously paired inverted region of the straight bivalent, it was always located in the middle of the inversion. Most of the small, incompletely adjusted loops contained MLH1 foci near the points at which pairing partners were switched. This observation indicates that the degree of synaptic adjustment depended on the crossover position. Complete synaptic adjustment was only possible if a crossover (CO) was located exactly in the middle of the inversion. If a CO was located at any other site, this interrupted synaptic adjustment and resulted in inversion loops of different sizes with an MLH1 focus at or near the edge of the remaining loop.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CO:
-
Crossover
- Cy3:
-
Orange fluorescing cyanine
- DAPI:
-
4′-6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DSB:
-
Double-strand break
- DOP-PCR:
-
Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed polymerase chain reaction
- dpc:
-
Days post-conception
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- MLH1:
-
MutL Homolog 1
- NCO:
-
Non-crossover
- SC:
-
Synaptonemal complex
- SYCP3:
-
Synaptonemal complex protein 3
- TAMRA:
-
Carboxytetramethylrhodamine
References
Agulnik SI, Borodin PM, Gorlov IP et al (1990) The origin of a double insertion of homogeneously staining regions in the house mouse (Mus musculus musculus). Heredity 65:265–267
Anderson LK, Reeves A (1998) Re-examining a mouse paracentric inversion heterozygote. The Society for Experimental Biology, Annual Meeting, 23–27 March, York, England, pp 55–56
Anderson LK, Stack SM, Sherman JD (1988) Spreading synaptonemal complexes from Zea mays. I. No synaptic adjustment of inversion loops during pachytene. Chromosoma 96(4):295–305
Anderson LK, Reeves A, Webb LM, Ashley T (1999) Distribution of crossing over on mouse synaptonemal complexes using immunofluorescent localization of MLH1 protein. Genetics 151(4):1569–1579
Ashley T, Moses MJ, Solari AJ (1981) Fine structure and behaviour of a pericentric inversion in the sand rat, Psammomys obesus. J Cell Sci 50:105–119
Ashley T, Cacheiro NL, Russell LB, Ward DC (1993) Molecular characterization of a pericentric inversion in mouse chromosome 8 implicates telomeres as promoters of meiotic recombination. Chromosoma 102(2):112–120
Ashley T, Gaeth AP, Creemers LB et al (2004) Correlation of meiotic events in testis sections and microspreads of mouse spermatocytes relative to the mid-pachytene checkpoint. Chromosoma 113(3):126–136
Baker SM, Plug AW, Prolla TA et al (1996) Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat Genet 13(3):336–342
Bardhan A, Sharma T (2000) Sequential meiotic prophase development in the pubertal Indian pygmy field mouse: synaptic progression of the XY chromosomes, autosomal heterochromatin, and pericentric inversions. Genome 43(1):172–180
Barlow AL, Hulten MA (1998) Crossing over analysis at pachytene in man. Eur J Hum Genet 6(4):350–358
Barlow AL, Benson FE, West SC, Hulten MA (1997) Distribution of the Rad51 recombinase in human and mouse spermatocytes. EMBO J 16(17):5207–5215
Batanian J, Hulten MA (1987) Electron microscopic investigations of synaptonemal complexes in an infertile human male carrier of a pericentric inversion inv(1)(p32q42). Regular loop formation but defective synapsis including a possible interchromosomal effect. Hum Genet 76(1):81–89
Berchowitz LE, Copenhaver GP (2010) Genetic interference: don’t stand so close to me. Curr Genomics 11(2):91–102
Bojko M (1990) Synaptic adjustment of inversion loops in Neurospora crassa. Genetics 124(3):593–598
Borodin PM, Gorlov IP, Ladygina T (1990a) Double insertion of homogeneously staining regions in chromosome 1 of wild Mus musculus musculus: effects on chromosome pairing and recombination. J Hered 81(2):91–95
Borodin PM, Gorlov IP, Ladygina T (1990b) Synapsis in single and double heterozygotes for partially overlapping inversions in chromosome 1 of the house mouse. Chromosoma 99(5):365–370
Borodin PM, Ladygina TY, Rodionova MI et al (2005) Genetic control of chromosome synapsis in mice heterozygous for a paracentric inversion. Russ J Genet 41(6):602–607
Burgoyne PS, Mahadevaiah SK, Turner JM (2009) The consequences of asynapsis for mammalian meiosis. Nat Rev Genet 10(3):207–216
Chandley AC (1982) A pachytene analysis of two male-fertile paracentric inversions in chromosome 1 of the mouse and in the male-sterile double heterozygote. Chromosoma 85(1):127–135
Chandley AC, McBeath S, Speed RM et al (1987) Pericentric inversion in human chromosome 1 and the risk for male sterility. J Med Genet 24(6):325–334
Cheng EY, Chen YJ, Disteche CM, Gartler SM (1999) Analysis of a paracentric inversion in human oocytes: nonhomologous pairing in pachytene. Hum Genet 105(3):191–196
Davisson MT, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Moses MJ (1981) A pericentric inversion in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 30(2):70–76
Gabriel-Robez O, Ratomponirina C, Rumpler Y et al (1986) Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in an infertile human male heterozygous for a pericentric inversion in chromosome 1. Hum Genet 72(2):148–152
Gabriel-Robez O, Ratomponirina C, Croquette M et al (1988) Synaptonemal complexes in a subfertile man with a pericentric inversion in chromosome 21. Heterosynapsis without previous homosynapsis. Cytogenet Cell Genet 48(2):84–87
Goldfarb T, Lichten M (2010) Frequent and efficient use of the sister chromatid for DNA double-strand break repair during budding yeast meiosis. PLoS Biol 8(10):e1000520
Greenbaum IF, Reed MJ (1984) Evidence for heterosynaptic pairing of the inverted segment in pericentric inversion heterozygotes of the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus). Cytogenet Cell Genet 38(2):106–111
Guichaoua MR, Delafontaine D, Taurelle R et al (1986) Loop formation and synaptic adjustment in a human male heterozygous for two pericentric inversions. Chromosoma 93(4):313–320
Handel MA, Schimenti JC (2010) Genetics of mammalian meiosis: regulation, dynamics and impact on fertility. Nat Rev Genet 11(2):124–136
Kaelbling M, Fechheimer NS (1985) Synaptonemal complex analysis of a pericentric inversion in chromosome 2 of domestic fowl, Gallus domesticus. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39(2):82–86
Kleckner N, Zickler D, Jones GH et al (2004) A mechanical basis for chromosome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(34):12592–12597
Koehler KE, Millie EA, Cherry JP et al (2004) Meiotic exchange and segregation in female mice heterozygous for paracentric inversions. Genetics 166(3):1199–1214
Li XC, Bolcun-Filas E, Schimenti JC (2011) Genetic evidence that synaptonemal complex axial elements govern recombination pathway choice in mice. Genetics 189(1):71–82
Massip K, Yerle M, Billon Y et al (2010) Studies of male and female meiosis in inv(4)(p1.4;q2.3) pig carriers. Chromosome Res 18(8):925–938
Moens PB, Chen DJ, Shen Z et al (1997) Rad51 immunocytology in rat and mouse spermatocytes and oocytes. Chromosoma 106(4):207–215
Moses MJ, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Davisson MT (1982) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. IV. Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma 84:457–474.
Peters AH, Plug AW, van Vugt MJ, de Boer P (1997) A drying-down technique for the spreading of mammalian meiocytes from the male and female germline. Chromosome Res 5(1):66–68
Plug AW, Peters AH, Keegan KS et al (1998) Changes in protein composition of meiotic nodules during mammalian meiosis. J Cell Sci 111:413–423
Reeves A (2001) MicroMeasure: a new computer program for the collection and analysis of cytogenetic data. Genome 44(3):439–443
Saadallah N, Hulten M (1986) EM investigations of surface spread synaptonemal complexes in a human male carrier of a pericentric inversion inv(13)(p12q14): the role of heterosynapsis for spermatocyte survival. Ann Hum Genet 50:369–383
Scherthan H (2007) Telomere attachment and clustering during meiosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(2):117–124
Schwacha A, Kleckner N (1997) Interhomolog bias during meiotic recombination: meiotic functions promote a highly differentiated interhomolog-only pathway. Cell 90(6):1123–1135
Speed RM, Chandley AC (1983) Meiosis in the foetal mouse ovary. II. Oocyte development and age-related aneuploidy. Does a production line exist. Chromosoma 88(3):184–189
Tease C, Fisher G (1986) Further examination of the production-line hypothesis in mouse foetal oocytes. I. Inversion heterozygotes. Chromosoma 93(5):447–452
Youds JL, Boulton SJ (2011) The choice in meiosis—defining the factors that influence crossover or non-crossover formation. J Cell Sci 124:501–513
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mrs. Antonina Zhelezova and Mrs. Marina Rodionova for their help in breeding mice and SC spread preparation. We thank the Microscopy Center of the Siberian Department of Russian Academy of Sciences for granting access to their equipment. This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the Biodiversity Program of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Beth A. Sullivan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torgasheva, A.A., Rubtsov, N.B. & Borodin, P.M. Recombination and synaptic adjustment in oocytes of mice heterozygous for a large paracentric inversion. Chromosome Res 21, 37–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-012-9336-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-012-9336-6