Abstract
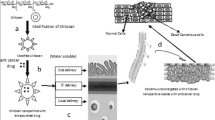
Melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer. Brain metastasis is the worst scenario in metastatic melanoma and the treatment options for these patients are limited. Temozolomide (TMZ) is a chemotherapy agent used to treat primary central nervous system tumors. Our objective was to develop chitosan-coated nanoemulsion containing temozolomide (CNE-TMZ) for nasal route administration to melanoma brain metastasis treatment. A preclinical model of metastatic brain melanoma was standardized, and the efficiency of the developed formulation was further determined in vitro and in vivo. The nanoemulsion was done by spontaneous emulsification method and the formulation was characterized by size, pH, polydispersity index, and zeta potential. Culture assessments to determine cell viability were done in the A375 human melanoma cell line. To determine the safety of formulation, healthy C57/BL6 mice were treated with a nanoemulsion without TMZ. The model in vivo used B16-F10 cells implanted by stereotaxic surgery in C57/BL6 mice brains. The results demonstrate that the preclinical model used showed to be useful to analyze the efficiency of new candidate drugs to treat melanoma brain metastasis. The chitosan-coated nanoemulsions with TMZ showed the expected physicochemical characteristics and demonstrated safety and efficacy, reducing around 70% the tumor size compared to control mice, and presenting a tendency in mitotic index reduction, becoming an interesting approach to treat melanoma brain metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Adnet T et al (2020) Pharmacotechnical development of a nasal drug delivery composite nanosystem intended for alzheimer’s disease treatment. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030251
Azambuja JH et al (2020) Nasal administration of cationic nanoemulsions as CD73-siRNA delivery system for glioblastoma treatment: a new therapeutical approach. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01730-6
Azimi F et al (2012) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.37.8539
Baldrick P (2010) The safety of chitosan as a pharmaceutical excipient. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2009.09.015
Bobek V et al (2010) A clinically relevant, syngeneic model of spontaneous, highly metastatic B16 mouse melanoma. Antiancer Res 30(12):4799–4803
Bogunovic D et al (2009) Immune profile and mitotic index of metastatic melanoma lesions enhance clinical staging in predicting patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905139106
Bruinsmann FA et al (2019) Nasal drug delivery of anticancer drugs for the treatment of glioblastoma: preclinical and clinical trials. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234312
Calderó G, García-Celma M, Solans C (2010) Formation of polymeric nano-emulsions by a low-energy method and their use for nanoparticle preparation. J Colloid Interface Sci 353:406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.09.073
Chiarion-Sileni V et al (2011) Central nervous system failure in melanoma patients: Results of a randomised, multicentre phase 3 study of temozolomide- and dacarbazine-based regimens. Br J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.178
Clemente N et al (2018) ‘Solid lipid nanoparticles carrying temozolomide for melanoma treatment. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020255
Davies MA et al (2011) Prognostic factors for survival in melanoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25634
De Matteis L et al (2016) Controlling properties and cytotoxicity of chitosan nanocapsules by chemical grafting. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14100175
Dianzani C, Monge C, Miglio G, Serpe L, Martina K, Cangemi L, Ferraris C, Mioletti S, Osella S, Gigliotti CL, Boggio E, Clemente N, Dianzani U, Battaglia L (2020) Nanoemulsions as delivery systems for poly-chemotherapy aiming at melanoma treatment. Cancers (Basel) 12(5):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051198
Erdei E, Torres SM (2010) A new understanding in the epidemiology of melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10(11):1811–1823. https://doi.org/10.1586/era.10.170
Fachel FNS et al (2018) Box-Behnken design optimization of mucoadhesive chitosan-coated nanoemulsions for rosmarinic acid nasal delivery—in vitro studies. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.054
Fachel FNS, Michels LR, Azambuja JH, Lenz GS, Gelsleichter NE, Endres M, Scholl JN, Schuh RS, Barschak AG, Figueiró F, Bassani VL, Henriques AT, Koester LS, Teixeira HF, Braganhol E (2020) Chitosan-coated rosmarinic acid nanoemulsion nasal administration protects against LPS-induced memory deficit, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Neurochem Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104875
Fan Y et al (2018) Updated Progress of Nanocarrier-Based Intranasal Drug Delivery Systems for Treatment of Brain Diseases. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 35(5):433–467. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2018024697
Ferraro MG et al (2020) Breast cancer chemotherapeutic options: a general overview on the preclinical validation of a multi-target Ruthenium(III) complex lodged in nucleolipid nanosystems. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061412
Ho BN, Pfeffer CM, Singh ATK (2017) Update on Nanotechnology-based Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Treatment 5981:5975–5981. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12044
In GK, Poorman K, Saul M, O’Day S, Farma JM, Olszanski AJ, Gordon MS, Thomas JS, Eisenberg B, Flaherty L, Weise A, Daveluy S, Gibney G, Atkins MB, Vanderwalde A (2020) Molecular profiling of melanoma brain metastases compared to primary cutaneous melanoma and to extracranial metastases. Oncotarget 11(33):3118–3128. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27686.=
Intakhab Alam M et al (2011) Nanostructured lipid carrier containing CNS acting drug: formulation, optimization and evaluation. Curr Nanosci 7(6):1014–1027. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573413711107061014
Ishak RAH et al (2013) A comparative study of chitosan shielding effect on nano-carriers hydrophilicity and biodistribution. Carbohyd Polym 94(1):669–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.072
Jiang G et al (2017) Formulation of temozolomide-loaded nanoparticles and their targeting potential to melanoma cells. Oncol Rep 37(2):995–1001. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5342
Khan A et al (2016) Brain targeting of temozolomide via the intranasal route using lipid-based nanoparticles: brain pharmacokinetic and scintigraphic analyses. Mol Pharm 13(11):3773–3782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00586
Kim SS et al (2015) Encapsulation of temozolomide in a tumor-targeting nanocomplex enhances anti-cancer efficacy and reduces toxicity in a mouse model of glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.08.022
Kim YS, Shin S, Yin JH, Park J, Jung SH, Chung YJ (2022) Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the existence of pro-metastatic subpopulation within a parental B16 murine melanoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 12(613):120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.05.003
Kircher DA et al (2016) Melanoma brain metastasis: mechanisms, models, and medicine. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091468
Kong L et al (2011) Melanoma in a murine model 16(9):2550–2561. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0279.Inhibition
Korn EL et al (2008) Meta-analysis of phase II cooperative group trials in metastatic stage IV melanoma to determine progression-free and overall survival benchmarks for future phase II trials. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.12.7837
Lebre F et al (2016) Intranasal Administration of Novel Chitosan nanoparticle/DNA complexes induces antibody response to Hepatitis B surface antigen in Mice. Mol Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00707
Lee JYK et al (2000) Brain surgery with image guidance: current recommendations based on a 20-year assessment. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1159/000048381
Li R-H et al (2015) Temozolomide for treating malignant melanoma. J Coll Phys Surg Pak 25(9): 680–688. 09.2015/JCPSP.680688
Linos E et al (2009) Increasing burden of melanoma in the United States. J Investig Dermatol 129(7):1666–1674. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.423
Matica A, Menghiu G, Ostafe V (2017) Biodegradability of chitosan based products. New Front Chem 26:75–86
McDonald MA et al (2018) Unmasking of intracranial metastatic melanoma during ipilimumab/nivolumab therapy: case report and literature review. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4470-y
Michels LR, Fachel FNS, Azambuja JH, Gelsleichter NE, Braganhol E, Teixeira HF (2019) HPLC–UV method for temozolomide determination in complex biological matrices: application for in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo studies. Biomed Chromatogr. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4615
Michels LR, Fachel FNS, Schuh RS, Azambuja JH, de Souza PO, Gelsleichter NE, Lenz GS, Visioli F, Braganhol E, Teixeira HF (2023) Nasal administration of a temozolomide-loaded thermoresponsive nanoemulsion reduces tumor growth in a preclinical glioblastoma model. J Control Release 355:343–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.070
Miyake MM, Bleier BS (2015) The blood-brain barrier and nasal drug delivery to the central nervous system. Am J Rhinol Allergy 29(2):124–127. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4149
Pantshwa JM et al (2020) Nanodrug delivery systems for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010213
Portnow J, Badie B, Chen M, Liu A, Blanchard S, Synold TW (2009) The neuropharmacokinetics of temozolomide in patients with resectable brain tumors: potential implications for the current approach to chemoradiation. Clin Cancer Res 15(22):7092–7098. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1349
Prego C et al (2005) Transmucosal macromolecular drug delivery. J Controll Release. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.07.030
Propet B (1994) Laboratory methods in histotechnology. laboratory manuals: manual of histologic staining methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. American Registry of Pathology, Washington, D.C. [viii, 279 p. : ill. (some col.) ; 26 cm]
Riss TL et al (2004) Cell viability assays, assay guidance manual. In: Assay guidance manual. Bethesda (MD): Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23805433
Sabit H, Kaliyadan F, Menezes R (2020) Malignant melanoma: underlying epigenetic mechanisms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijdvl.ijdvl_791_19
Soni V, Adhikari M, Simonyan H, Lin L, Sherman JH, Young CN, Keidar M (2021) In vitro and in vivo enhancement of Temozolomide effect in human glioblastoma by non-invasive application of cold atmospheric plasma. Cancers 13:4485. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174485
Suri SS, Fenniri H, Singh B (2007) Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems. J Occup Med Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-2-16
Tas F (2012) Metastatic behavior in melanoma: timing, pattern, survival, and influencing factors. J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/647684
Tapola NS et al (2008) Safety aspects and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of chitosan tablets. J Am Coll Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2008.10719671
Teimouri F, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M (2013) Efficacy and side effects of dacarbazine in comparison with temozolomide in the treatment of malignant melanoma: a meta-analysis consisting of 1314 patients. Melanoma Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/CMR.0b013e3283649a97
Timmons JJ, Cohessy S, Wong ET (2016) (2016) ‘Injection of syngeneic murine melanoma cells to determine their metastatic potential in the lungs.’ J vis Exp 111:4–7. https://doi.org/10.3791/54039
Trinh VA, Patel SP, Hwu WJ (2009) The safety of temozolomide in the treatment of malignancies. Expert Opin Drug Saf 8(4):493–499. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740330902918281
World Health Organization (2020) ‘No Title’. https://www.who.int/uv/resources/FAQ/skincancer/en/index2.html
Young GJ et al (2017) Management of intracranial melanomas in the era of precision medicine. Oncotarget. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19223
Zhu W et al (2014) Temozolomide for treatment of brain metastases: A review of 21 clinical trials. World J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v5.i1.19
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Brazilian agencies: Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq—Processo 422298/2016-6; 310846/2014-5), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES- processo 001), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS—Processo 16/2551-0000265-7; PRONEX—Processo 16/2551-0000473-0); NE Gelsleichter, PO de Souza, GN Debom, GS Lenz, GG Roliano, LR Michels, FNS Fachel, JH Azambuja were recipients of UFCSPA, FAPERGS, CAPES or CNPq fellowships. We would like to ackonowlegde G. Rizzotto for technical support on IHC experiments.
Funding
Universidade Federal de Ciências da Saúde de Porto Alegre,Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior,001,001,001,001,Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico,422298/2016-6; 310846/2014-5,422298/2016-6; 310846/2014-5,Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul,16/2551-0000265-7; 16/2551-0000473-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by NEG, POS, FCT, GND, GSL, GGR, RCS, FV, FNSF, LRM, JHA, HFT, and EB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NEG and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gelsleichter, N.E., de Souza, P.O., Teixeira, F.C. et al. Metastatic Melanoma: A Preclinical Model Standardization and Development of a Chitosan-Coated Nanoemulsion Containing Temozolomide to Treat Brain Metastasis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 2939–2951 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01338-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01338-4