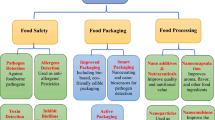
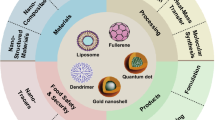
Abstract
In the modern world where packaged food and beverages are becoming more and more common, the necessity to research an alternative packaging technique with reduced health hazards is the need of the hour. Food packaging is increasingly focusing on using natural, biodegradable, and bioavailable polymers due to their environmentally friendly characteristics. UV protection is crucial in maintaining the integrity and quality of food products, ensuring they reach consumers with their intended characteristics intact. To enhance the UV protection characteristics of packaging materials, small additions of biocompatible materials with high light absorption can be incorporated. Cellulose and its derivatives, from natural sources, are widely used in the packaging sector for their affordability and versatility. Cellulose is a popular choice for integrating UV protection into packaging materials, mitigating the potential impact of UV radiation on chemical and physical attributes. Compounds like flavonoids and related phenylpropanoids exhibit exceptional UV radiation absorption capabilities, serving as a primary defense mechanism employed by plants to endure stressful conditions induced by the accumulation of harmful solar radiation. The synergistic combination of cellulose and flavonoids creates innovative packaging materials that are biodegradable, non-toxic and possess inherent radiation-shielding capabilities. This integration aligns with sustainable and eco-friendly practices, contributing to the development of effective and environmentally friendly packaging solutions.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Abdul Khalil HPS, Tye YY, Leh CP, Saurabh CK, Ariffin F, Mohammad Fizree H, Mohamed A, Suriani AB (2017) Cellulose reinforced biodegradable polymer composite film for packaging applications. Springer International Publishing, In bionanocomposites for packaging applications, pp 49–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67319-6_3
Adeyeye OA, Sadiku ER, Babu Reddy A, Ndamase AS, Makgatho G, Sellamuthu PS, Perumal AB, Nambiar RB, Fasiku VO, Ibrahim ID, Agboola O (2019) The use of biopolymers in food packaging. Green biopolymers and their nanocomposites 137–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8063-1_6
Agarwal D, Hewson L, Foster TJ (2018) A comparison of the sensory and rheological properties of different cellulosic fibres for food. Food Funct 9:1144–1151. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo01495c
Agati G, Azzarello E, Pollastri S, Tattini M (2012) Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: Location and functional significance. Plant Sci 196:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLANTSCI.2012.07.014
Ahmad H (2021) Celluloses as support materials for antibacterial agents: a review. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03703-2
Ahmed A, Adak B, Bansala T, Mukhopadhyay S (2020) Green Solvent Processed Cellulose/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Films with Superior Mechanical, Thermal, and Ultraviolet Shielding Properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:1687–1697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b19686
Ahn S, Halake K, Lee J (2017) Antioxidant and ion-induced gelation functions of pectins enabled by polyphenol conjugation. Int J Biol Macromol 101:776–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.173
Al-Hadeethi Y, Sayyed MI, Nune M (2021) Radiation shielding study of WO3–ZnO–PbO–B2O3 glasses using Geant4 and Phys-X: A comparative study. Ceram Int 47:3988–3993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.263
Al-Malaika S, Ashley H, Issenhuth S (1994) The antioxidant role of α-tocopherol in polymers. I. The nature of transformation products of α‐tocopherol formed during melt processing of LDPE. J Pol Sci Part A: Pol Chem 32(16):3099–3113. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.1994.080321610
Almisned G, Tekin HO, Ene A, Issa SAM, Kilic G, Zakaly HMH (2021) A closer look on nuclear radiation shielding properties of eu3+ doped heavy metal oxide glasses: Impact of al2 o3 /pbo substitution. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185334
Annegowda HV, Bhat R, Min-Tze L, Karim AA, Mansor SM (2012) Influence of sonication treatments and extraction solvents on the phenolics and antioxidants in star fruits. J Food Sci Technol 49:510–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0435-8
Aoki T, Akashi T, Ayabe S-I (2000) Flavonoids of Leguminous Plants: Structure, Biological Activity, and Biosynthesis. J Plant Res 113:475–488
Arrigo R, Tz Dintcheva N, Guenzi M, Gambarotti C, Filippone G, Coiai S, Carroccio S (2015) Thermo-oxidative resistant nanocomposites containing novel hybrid-nanoparticles based on natural polyphenol and carbon nanotubes. Polym Degrad Stab 115:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.POLYMDEGRADSTAB.2015.02.014
Arts ICW, van de Putte B, Hollman PCH (2000) Catechin contents of foods commonly consumed in The Netherlands. 1. Fruits, vegetables, staple foods, and processed foods. J Agric Food Chem 48:1746–1751. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF000025H
Avena-Bustillos RJ, Krochta JM (1993) Water vapor permeability of caseinate‐based edible films as affected by pH, calcium crosslinking and lipid content. J Food Sci 58(4):904–907. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1993.tb09388.x
Avior Y, Bomze D, Ramon O, Nahmias Y (2013) Flavonoids as dietary regulators of nuclear receptor activity. Royal Society of Chemistry, Food and Function. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3fo60063g
Awan F, Islam MS, Ma Y, Yang C, Shi Z, Berry RM, Tam KC (2018) Cellulose Nanocrystal-ZnO Nanohybrids for Controlling Photocatalytic Activity and UV Protection in Cosmetic Formulation. ACS Omega 3:12403–12411. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01881
Aziz T, Farid A, Haq F, Kiran M, Ullah A, Zhang K, Li C et al (2022) A Review on the Modification of Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153206
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M (2021) Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Balasubramanian AI, Rosenberg LE, Yam K, Chikindas ML (2009) Antimicrobial packaging: potential vs. reality—a review. J Appl Packag Res 3(4):193–221
Bandurska H, Niedziela J, Chadzinikolau T (2013) Separate and combined responses to water deficit and UV-B radiation. Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.003
Barnes PW, Flint SD, Slusser JR, Gao W, Ryel RJ (2008) Diurnal changes in epidermal UV transmittance of plants in naturally high UV environments. Physiol Plant 133:363–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1399-3054.2008.01084.X
Barnes PW, Tobler MA, Keefover-Ring K, Flint SD, Barkley AE, Ryel RJ, Lindroth RL (2016) Rapid modulation of ultraviolet shielding in plants is influenced by solar ultraviolet radiation and linked to alterations in flavonoids. Plant, Cell Environ 39:222–230. https://doi.org/10.1111/PCE.12609
Batista RA, Espitia PJP, de Souza J, Quintans S, Freitas MM, Cerqueira MÂ, Teixeira JA, Cardoso JC (2019) Hydrogel as an alternative structure for food packaging systems. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.006
Bedane AH, Eić M, Farmahini-Farahani M, Xiao H (2015) Water vapor transport properties of regenerated cellulose and nanofibrillated cellulose films. J Membr Sci 493:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.06.009
Bidel LPR, Meyer S, Goulas Y, Cadot Y, Cerovic ZG (2007) Responses of epidermal phenolic compounds to light acclimation: In vivo qualitative and quantitative assessment using chlorophyll fluorescence excitation spectra in leaves of three woody species. J Photochem Photobiol, B 88:163–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2007.06.002
Bornman JF, Barnes PW, Robinson SA, Ballaré CL, Flint SD, Caldwell MM (2015) Solar ultraviolet radiation and ozone depletion-driven climate change: Effects on terrestrial ecosystems. Photochem Photobiol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4pp90034k
Bravo L (1998) Polyphenols: Chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev 56:317–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1753-4887.1998.TB01670.X
Brunetti C, di Ferdinando M, Fini A, Pollastri S, Tattini M (2013) Flavonoids as Antioxidants and Developmental Regulators: Relative Significance in Plants and Humans. Int J Mol Sci 14:3540–3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS14023540
Burford N, Eelman MD, Groom K (2005) Identification of complexes containing glutathione with As(III), Sb(III), Cd(II), Hg(II), Tl(I), Pb(II) or Bi(III) by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Inorg Biochem 99:1992–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.06.019
Caldwell MM, Robberecht R, Flint SD (1983) Internal filters: prospects for UV‐acclimation in higher plants. Physiol Plant 58(3):445–450. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1983.tb04206.x
Callemien D, Collin S (2010) Structure, organoleptic properties, quantification methods, and stability of phenolic compounds in beer-A review. Food Rev Intl 26:1–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559120903157954
Cao WT, Chen FF, Zhu YJ, Zhang YG, Jiang YY, Ma MG, Chen F (2018) Binary Strengthening and Toughening of MXene/Cellulose Nanofiber Composite Paper with Nacre-Inspired Structure and Superior Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties. ACS Nano 12:4583–4593. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00997
Carrillo-Inungaray ML, Trejo-Ramirez JA, Reyes-Munguia A, Carranza-Alvarez C (2018) Use of Nanoparticles in the Food Industry: Advances and Perspectives. In Impact of Nanoscience in the Food Industry. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811441-4.00015-7
Cartelat A, Cerovic ZG, Goulas Y, Meyer S, Lelarge C, Prioul JL, Barbottin A et al (2005) Optically assessed contents of leaf polyphenolics and chlorophyll as indicators of nitrogen deficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crop Res 91:35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCR.2004.05.002
Casati P, Zhang X, Burlingame AL, Walbot V (2005) Analysis of leaf proteome after UV-B irradiation in maize lines differing in sensitivity. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:1673–1685. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M500173-MCP200
Cerruti P, Santagata G, Gomez D’Ayala G, Ambrogi V, Carfagna C, Malinconico M, Persico P (2011) Effect of a natural polyphenolic extract on the properties of a biodegradable starch-based polymer. Polym Degrad Stab 96:839–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.02.003
Chandran GU, Parappanal AS, Hema S, Sambhudevan S, Shankar B (2022) A critical review on cellulose nano structures based polymer nanocomposites for packaging applications. Taylor and Francis Ltd., Polymer-Plastics Technology and Materials. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2022.2086813
Chaudhary P, Fatima F, Kumar A (2020) Relevance of Nanomaterials in Food Packaging and its Advanced Future Prospects. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:5180–5192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01674-8
Chaudhuri S, Basu K, Sengupta B, Banerjee A, Sengupta PK (2008) Ground- and excited-state proton transfer and antioxidant activity of 3-hydroxyflavone in egg yolk phosphatidylcholine liposomes: Absorption and fluorescence spectroscopic studies. Luminescence 23:397–403. https://doi.org/10.1002/BIO.1052
Chaves JO, de Souza MC, da Silva LC, Lachos-Perez D, Torres-Mayanga PC, da Fonseca Machado AP, Forster-Carneiro T et al (2020) Extraction of Flavonoids From Natural Sources Using Modern Techniques. Front Chem 8:864. https://doi.org/10.3389/FCHEM.2020.507887/BIBTEX
Cockell CS, Knowland J (1999) Ultraviolet radiation screening compounds. Biological Rev Cambridge Philosophical Soc 74:311–345. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0006323199005356
Correa-Pacheco ZN, Black-Solís JD, Ortega-Gudiño P, Sabino-Gutiérrez MA, Benítez-Jiménez JJ, Barajas-Cervantes A, Bautista-Baños S, Hurtado-Colmenares LB (2020) Preparation and characterization of bio-based PLA/PBAT and cinnamon essential oil polymer fibers and life-cycle assessment from hydrolytic degradation. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12010038
Curcio M, Puoci F, Iemma F, Parisi OI, Cirillo G, Spizzirri UG, Picci N (2009) Covalent insertion of antioxidant molecules on chitosan by a free radical grafting procedure. J Agric Food Chem 57:5933–5938. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF900778U/ASSET/IMAGES/LARGE/JF-2009-00778U_0006.JPEG
Cutter CN (2006) Opportunities for bio-based packaging technologies to improve the quality and safety of fresh and further processed muscle foods. Meat Sci 74:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2006.04.023
Cvetković D, Marković D, Cvetković D, Radovanović B (2011) Effects of continuous UV-irradiation on the antioxidant activities of quercetin and rutin in solution in the presence of lecithin as the protective target. J Serbian Chem Soc 76:973–985. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC101123089C
Das S, Kumar S, Samal SK, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2018) A review on superhydrophobic polymer nanocoatings: recent development and applications. Indust Eng Chem Res 57(8):2727–2745. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b04887
Dasgupta N, Ranjan S, Gandhi M (2019) Nanoemulsion ingredients and components. Environment Chem Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-00849-7
David G, Gontard N, Angellier-Coussy H (2019) Mitigating the impact of cellulose particles on the performance of biopolyester-based composites by gas-phase esterification. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020200
Day TA, Vogelmann TC, DeLucia EH (1992) Are some plant life forms more effective than others in screening out ultraviolet-B radiation?. Oecologia 92:513–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317843
Devcich DA, Pedersen IK, Petrie KJ (2007) You eat what you are: Modern health worries and the acceptance of natural and synthetic additives in functional foods. Appetite 48:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2006.09.014
Dias DA, Smith TA, Ghiggino KP, Scollary GR (2012) The role of light, temperature and wine bottle colour on pigment enhancement in white wine. Food Chem 135:2934–2941. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2012.07.068
Dixon RA, Ferreira D (2002) Genistein. Phytochemistry 60:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00116-4
Dobroslavić E, Garofulić IE, Šeparović J, Zorić Z, Pedisić S, Dragović-Uzelac V (2022) Pressurized Liquid Extraction as a Novel Technique for the Isolation of Laurus nobilis L. Leaf Polyphenols Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165099
Dobson CC, Mottawea W, Rodrigue A, Pereira BLB, Hammami R, Power KA, Bordenave N (2019) Impact of molecular interactions with phenolic compounds on food polysaccharides functionality. Adv Food Nutri Res 90:135–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/BS.AFNR.2019.02.010
Edible films and coatings: a review. 2023. https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US8836195. Accessed January 27.
Elalaily NA, Abou-Hussien EM, Saad EA (2016) Bismuth silicate glass containing heavy metal oxide as a promising radiation shielding material. Radiat Eff Defects Solids 171:840–854. https://doi.org/10.1080/10420150.2016.1250093
Esposto BS, Jauregi P, Tapia-Blácido DR, Martelli-Tosi M (2021) Liposomes vs. chitosomes: encapsulating food bioactives. Trends in Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.12.003
Ezati P, Khan A, Priyadarshi R, Bhattacharya T, Tammina SK, Rhim JW (2023) Biopolymer-based UV protection functional films for food packaging. Food Hydrocolloids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108771
Fahlman BM, Krol EdS (2009) Inhibition of UVA and UVB radiation-induced lipid oxidation by quercetin. J Agric Food Chem 57:5301–5305. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF900344D
Farris S, Schaich KM, Liu LS, Piergiovanni L, Yam KL (2009) Development of polyion-complex hydrogels as an alternative approach for the production of bio-based polymers for food packaging applications: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2009.04.003
Flamini R, Mattivi F, de Rosso M, Arapitsas P, Bavaresco L (2013) Advanced knowledge of three important classes of grape phenolics: anthocyanins, stilbenes and flavonols. Int J Mol Sci 14:19651–19669. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS141019651
Flint SD, Searles PS, Caldwell MM (2004) Field testing of biological spectral weighting functions for induction of UV-absorbing compounds in higher plants†¶. Photochem Photobiol 79(5):399–403. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-1097.2004.tb00026.x
Gabor D, Tita O (2012) Biopolymers used in food packaging: a review. Acta Universitatis Cinbinesis, Series E: Food Technology 16(2)
Gan PG, Sam ST, Abdullah MFB, Omar MF (2020) Thermal properties of nanocellulose-reinforced composites: A review. J Appl Poly Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48544
Garazd MM, Garazd YL, Khilya VP (2003) Neoflavones. 1. Natural distribution and spectral and biological properties. Chem Nat Compounds 39:54–121. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024140915526
Gennadios A, Hanna MA, Kurth LB (1997) Application of edible coatings on meats, poultry and seafoods: a review. LWT-Food Sci Technol 30(4):337–350. https://doi.org/10.1006/fstl.1996.0202
Giusti MM, Wrolstad RE (2003) Acylated anthocyanins from edible sources and their applications in food systems. Biochem Engineering Journal 14:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(02)00221-8
Gol NB, Patel PR, Ramana Rao TV (2013) Improvement of quality and shelf-life of strawberries with edible coatings enriched with chitosan. Postharvest Biol Technol 85:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.06.008
Gorjanc M, Jazbec K, Šala M, Zaplotnik R, Vesel A, Mozetič M (2014) Creating cellulose fibres with excellent UV protective properties using moist CF4 plasma and ZnO nanoparticles. Cellulose 21:3007–3021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0284-5
Guidi L, Degl’Innocenti E, Remorini D, Biricolti S, Fini A, Ferrini F, Nicese FP, Tattini M (2011) The impact of UV-radiation on the physiology and biochemistry of Ligustrum vulgare exposed to different visible-light irradiance. Environ Exp Bot 70:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.08.005
Guzman-Puyol S, Hierrezuelo J, Benítez JJ, Tedeschi G, Porras-Vázquez JM, Heredia A, Athanassiou A, Romero D, Heredia-Guerrero JA (2022) Transparent, UV-blocking, and high barrier cellulose-based bioplastics with naringin as active food packaging materials. Int J Biological Macromolecules 209:1985–1994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.177
He J, Kunitake T, Nakao A (2003) Facile In Situ Synthesis of Noble Metal Nanoparticles in Porous Cellulose Fibers. Chem Mater 15:4401–4406. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm034720r
Hertog MG, Hollman PC, Van de Putte B (1993) Content of potentially anticarcinogenic flavonoids of tea infusions, wines, and fruit juices. J Agricul Food Chem 41(8):1242–1246. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00032a015
Hubbe MA, Pruszynski P (2020) Greaseproof paper products: a review emphasizing ecofriendly approaches. BioResources 15(1):1978–2004
Huvaere K, Skibsted LH (2015) Flavonoids protecting food and beverages against light. J Sci Food Agricul. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6796
Ibrahim NA, Refai R, Youssef MA, Ahmed AF (2005) Proper finishing treatments for sun-protective cotton-containing fabrics. J Appl Polym Sci 97:1024–1032. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.21840
Iinuma M, Tanaka T, Hamada K, Mizuno M, Asai F, Reher G, Kraus L (1987) Revised structure of neoflavone in Coutarea hexandra. Phytochemistry 26:3096–3097. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)84609-9
Islam SUl, Mohammad F (2015) Natural colorants in the presence of anchors so-called mordants as promising coloring and antimicrobial agents for textile materials. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00537
Islam MT, Repon MR, Liman MLR, Hossain MM, al Mamun MA (2021) Functional modification of cellulose by chitosan and gamma radiation for higher grafting of UV protective natural chromophores. Radiation Phys Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2021.109426
Islam MT, Liman MLR, Roy MN, Hossain MM, Repon MR, MA al Mamun. (2022) Cotton dyeing performance enhancing mechanism of mangiferin enriched bio-waste by transition metals chelation. J Text Inst 113:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2021.1892337
Ismayati M, Fatah NAN, Ernawati EE, Juliandri WBK, Lubis MAR, Fatriasari W et al (2024) Antioxidant and UV-blocking activity of PVA/tannin-based bioplastics in food packaging application. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128332
Iwashina T (2013) Flavonoid Properties of five Families newly Incorporated into the Order Caryophyllales (Review). Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Ser B 39:25–51
Jenkins GI (2014) The UV-B photoreceptor UVR8: From structure to physiology. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.119446
Jiang G, Li Yu, Zhang M, Wang F, Zhang S (2020) Poly(propylene carbonate)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-based bionanocomposites reinforced with cellulose nanocrystal for potential application as a packaging material. Poly Adv Technol 31:853–863. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4820
Jipa IM, Stroescu M, Stoica-Guzun A, Dobre T, Jinga S, Zaharescu T (2012) Effect of gamma irradiation on biopolymer composite films of poly(vinyl alcohol) and bacterial cellulose. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect B 278:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2012.02.024
Jorgensen R (1993) The origin of land plants: a union of alga and fungus advanced by flavonoids? BioSystems 31:193–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0303-2647(93)90049-I
Julkunen-Tiitto R, Nenadis N, Neugart S, Robson M, Agati G, Vepsäläinen J, Zipoli G, Nybakken L, Winkler B, Jansen MAK (2015) Assessing the response of plant flavonoids to UV radiation: an overview of appropriate techniques. Phytochem Rev 14:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11101-014-9362-4
Kamthai S, Magaraphan R (2017) Mechanical and barrier properties of spray dried carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) film from bleached bagasse pulp. Ind Crops Prod 109:753–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.09.040
Kaur P, Singh D, Singh T (2016) Heavy metal oxide glasses as gamma rays shielding material. Nucl Eng Des. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2016.07.029
Kim SH, Choi KC (2013) Anti-cancer effect and underlying mechanism(s) of Kaempferol, a phytoestrogen, on the regulation of apoptosis in diverse cancer cell models. Toxicological Research 29:229–234. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2013.29.4.229/METRICS
Kim HS, Kim YJ, Seo YR (2015) An Overview of Carcinogenic Heavy Metal: Molecular Toxicity Mechanism and Prevention. Journal of Cancer Prevention 20:232–240. https://doi.org/10.15430/jcp.2015.20.4.232
Kotilainen T, Tegelberg R, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Lindfors A, O’Hara RB, Aphalo PJ (2010) Seasonal fluctuations in leaf phenolic composition under UV manipulations reflect contrasting strategies of alder and birch trees. Physiol Plant 140:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1399-3054.2010.01398.X
Kroon-Batenburg LMJ, Kroon J (1997) The crystal and molecular structures of cellulose I and II. Glycoconjugate J 14:677–690. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018509231331
Kubow S (1992) Routes of formation and toxic consequences of lipid oxidation products in foods. Free Radical Biol Medi 12(1):63–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(92)90059-P
Kumar S, Pandey AK (2013) Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/162750
Lachos-Perez D, Baseggio AM, Mayanga-Torres PC, Maróstica MR, Rostagno MA, Martínez J, Forster-Carneiro T (2018) Subcritical water extraction of flavanones from defatted orange peel. J Supercritical Fluids 138:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SUPFLU.2018.03.015
Lagarón JM, López-Rubio A, Fabra MJ (2016) Bio-based packaging. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42971
Laine C, Harlin A, Hartman J, Hyvärinen S, Kammiovirta K, Krogerus B, Pajari H et al (2013) Hydroxyalkylated xylans - Their synthesis and application in coatings for packaging and paper. Ind Crops Prod 44:692–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.08.033
Laitinen ML, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Rousi M (2002) Foliar phenolic composition of European white birch during bud unfolding and leaf development. Physiol Plant 114:450–460. https://doi.org/10.1034/J.1399-3054.2002.1140315.X
Lao F, Sigurdson GT, Mónica Giusti M (2017) Health Benefits of Purple Corn (Zea mays L.) Phenolic Compounds. Comprehen Rev Food Sci Food Safety 16:234–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12249
Lautenschlager-Fleury D, Lautenschlager-Fleury E (1994) Spalierweiden. In: Die Weiden von Mittel- und Nordeuropa. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-5623-2_4
Li W, Wang S, Wang W, Qin C, Min W (2019) Facile preparation of reactive hydrophobic cellulose nanofibril film for reducing water vapor permeability (WVP) in packaging applications. Cellulose 26:3271–3284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02270-x
Li D, Liu X, Li W, Lin Z, Zhu B, Li Z, Li J et al (2021) Scalable and hierarchically designed polymer film as a selective thermal emitter for high-performance all-day radiative cooling. Nat Nanotechnol 16:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-00800-4
Liang K, Bae KH, Lee F, Keming X, Chung JE, Gao SJ, Kurisawa M (2016) Self-assembled ternary complexes stabilized with hyaluronic acid-green tea catechin conjugates for targeted gene delivery. J Controlled Release 226:205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCONREL.2016.02.004
Liman MLR, Islam MT, Hossain MM, Sarker P (2020) Sustainable Dyeing Mechanism of Polyester with Natural Dye Extracted from Watermelon and Their UV Protective Characteristics. Fibers and Polymers 21(2301):2313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-1135-7
Liman MLR, Islam MT, Hossain MM, Sarker P, Dabnath S (2021) Coloration of cotton fabric using watermelon extract: mechanism of dye-fiber bonding and chromophore absorption. J Textile Inst 112:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/00405000.2020.1738036
Liman MR, Luthfar MT, Islam MRR, Hossain MM, Sarker P (2021) Comparative dyeing behavior and UV protective characteristics of cotton fabric treated with polyphenols enriched banana and watermelon biowaste. Sustainable Chem Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100417
Lipton J, Weng GM, Rӧhr JA, Wang H, Taylor AD (2020) Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Two-Dimensional Materials: Meticulous Control on the Nanoscale. Cell Press, Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.03.012
Liu J, Wang C, Wang Z, Zhang C, Shuang Lu, Liu J (2011) The antioxidant and free-radical scavenging activities of extract and fractions from corn silk (Zea mays L.) and related flavone glycosides. Food Chem 126:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.014
Liu J, Meng CG, Yan YH, Ya na Shan J, Kan CHJ (2016) Protocatechuic acid grafted onto chitosan: Characterization and antioxidant activity. Int J Biol Macromol 89(518):526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.089
Liu W, Lee SW, Lin D, Shi F, Wang S, Sendek AD, Cui Y (2017) Enhancing ionic conductivity in composite polymer electrolytes with well-aligned ceramic nanowires. Nat Energy. https://doi.org/10.1038/nenergy.2017.35
Liu Z, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Wang Y (2017) 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.08.018
Liu J, Meng CG, Liu S, Kan J, Jin CH (2017) Preparation and characterization of protocatechuic acid grafted chitosan films with antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocolloids 63(457):466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.09.035
Liu J, Wang X, Yong H, Kan J, Jin C (2018a) Recent advances in flavonoid-grafted polysaccharides: Synthesis, structural characterization, bioactivities and potential applications. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.149
Liu Y, Wang S, Lan W (2018b) Fabrication of antibacterial chitosan-PVA blended film using electrospray technique for food packaging applications. Int J Biol Macromol 107:848–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.09.044
Liu X, Le Bourvellec C, Catherine MGC, Renard. (2020) Interactions between cell wall polysaccharides and polyphenols: Effect of molecular internal structure. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 19:3574–3617. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12632
Liu Y, Ahmed S, Sameen DE, Wang Y, Rui L, Dai J, Li S, Qin W (2021) A review of cellulose and its derivatives in biopolymer-based for food packaging application. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.04.016
Lopez-Lazaro M (2008) Distribution and Biological Activities of the Flavonoid Luteolin. Mini-Rev Med Chem 9:31–59. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955709787001712
Louis J, Meyer S, Maunoury-Danger F, Fresneau C, Meudec E, Cerovic ZG, Louis J et al (2009) Seasonal changes in optically assessed epidermal phenolic compounds and chlorophyll contents in leaves of sessile oak (Quercus petraea): towards signatures of phenological stage. Funct Plant Biol 36:732–741. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP09010
Luo H, Dong J, Yao F, Yang Z, Li W, Wang J, Xinhua Xu, Jian Hu, Wan Y (2018) Layer-by-layer assembled bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide hydrogels with extremely enhanced mechanical properties. Nano-Micro Letters. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-018-0195-3
Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Rémésy C, Jiménez L (2004) Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutri 79:727–747. https://doi.org/10.1093/AJCN/79.5.727
Martino E, Collina S, Rossi D, Bazzoni D, Gaggeri R, Bracco F, Azzolina O (2008) Influence of the extraction mode on the yield of hyperoside, vitexin and vitexin-2-O-rhamnoside from Crataegus monogyna Jacq. (Hawthorn). Phytochem Anal 19:534–540. https://doi.org/10.1002/PCA.1081
Masek A (2015) Flavonoids as natural stabilizers and color indicators of ageing for polymeric materials. Polymers 7:1125–1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7061125
Matthies A, Clavel T, Gütschow M, Engst W, Haller D, Blaut M, Braune A (2008) Conversion of daidzein and genistein by an anaerobic bacterium newly isolated from the mouse intestine. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4847–4852. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00555-08/ASSET/91D00969-C690-4F6C-A9D2-6FFF3DAC4E99/ASSETS/GRAPHIC/ZAM0150890800004.JPEG
Mazza CA, Boccalandro HE, Giordano CV, Battista D, Scopel AL, Ballaré CL (2000) Functional significance and induction by solar radiation of ultraviolet-absorbing sunscreens in field-grown soybean crops. Plant Physiol 122(1):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.1.117
Methods in Plant Biochemistry Volume 1 - P. M. Dey - Google Books. 2023. https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=6UbRS4p56coC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=+Harborne+JB,+General+procedures+and+measurement+of+total+pheno%3Flics,+in+Methods+in+Plant+Biochemistry.+Vol.+1.+Plant+Phenolics,+ed.+by+Dey+PM+and+Harborne+JB,+Academic+Press+Ltd,+London,+pp.+1%E2%80%9328+(1989)&ots=qLKPC9WFHn&sig=gZUobHXGn90V_cgoHsEACgUJ_YQ&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed January 28.
Mewis I, Schreiner M, Nguyen CN, Krumbein A, Ulrichs C, Lohse M, Zrenner R (2012) UV-B irradiation changes specifically the secondary metabolite profile in broccoli sprouts: Induced signaling overlaps with defense response to biotic stressors. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1546–1560. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs096
Micard V, Belamri R, Morel MH, Guilbert S (2000) Properties of chemically and physically treated wheat gluten films. J Agric Food Chem 48:2948–2953. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0001785
Mierziak J, Kostyn K, Kulma A (2014) Flavonoids as important molecules of plant interactions with the environment. Molecules 19:16240–16265. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES191016240
Mikyška A, Hrabák M, Hašková D, Šrogl J (2002) The role of malt and hop polyphenols in beer quality, flavour and haze stability. J Inst Brew 108:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/J.2050-0416.2002.TB00128.X
Morales LO, Tegelberg R, Brosché M, Lindfors A, Siipola S, Aphalo PJ (2011) Temporal variation in epidermal flavonoids due to altered solar UV radiation is moderated by the leaf position in Betula pendula. Physiol Plant 143:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1399-3054.2011.01511.X
Morales LO, Brosché M, Vainonen J, Jenkins GI, Wargent JJ, Sipari N, Strid Å, Anders v. Lindfors, Riitta Tegelberg, and Pedro J. Aphalo. (2013) Multiple roles for UV RESISTANCE LOCUS8 in regulating gene expression and metabolite accumulation in arabidopsis under solar ultraviolet radiation. Plant Physiol 161:744–759. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.211375
Moreno MA, Orqueda ME, Gómez-Mascaraque LG, Isla MI, López-Rubio A (2019) Crosslinked electrospun zein-based food packaging coatings containing bioactive chilto fruit extracts. Food Hydrocolloids 95:496–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.05.001
Moreno-Vásquez MJ, Buitimea-Valenzuela EL, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Encinas-Encinas JC, Rodríguez-Félix F, Sánchez-Valdes S, Rosas-Burgos EC, Ocaño-Higuera VM, Graciano-Verdugo AZ (2017) Functionalization of chitosan by a free radical reaction: Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial potential. Carbohyd Polym 155:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2016.08.056
Moridani MY, Pourahmad J, Bui H, Siraki A, O’Brien PJ (2003) Dietary flavonoid iron complexes as cytoprotective superoxide radical scavengers. Free Radical Biol Med 34:243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01241-8
Naşcu-Briciu RD, Cobzac SC, Baciu S (2011) Optimum Ultrasound Assisted Extraction Conditions of Some Flavonoids from Green Tea Leaves. Control Quality of Green Tea Product by TLC Fingerprinting. Anal Lett 44:2865–2875. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2011.582549
Nemazifard M, Kavoosi G, Marzban Z, Ezedi N (2017) Physical, mechanical, water binding, and antioxidant properties of cellulose dispersions and cellulose film incorporated with pomegranate seed extract. Int J Food Properties 20:1501–1514. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1219369
Neo YP, Ray S, Jin J, Gizdavic-Nikolaidis M, Nieuwoudt MK, Liu D, Quek SY (2013) Encapsulation of food grade antioxidant in natural biopolymer by electrospinning technique: a physicochemical study based on zein-gallic acid system. Food Chem 136:1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.010
Nijveldt RJ, van Nood E, van Hoorn DEC, Boelens PG, van Norren K, van Leeuwen PAM (2001) Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am J Clin Nutr 74:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/AJCN/74.4.418
Nishimura S, Taki M, Takaishi S, Iijima Y, Akiyama T (2000) Structures of 4-Aryl-coumarin (Neoflavone) Dimers Isolated from Pistacia chinensis BUNGE and Their Estrogen-like Activity. Chem Pharm Bulletin 48:505–508. https://doi.org/10.1248/CPB.48.505
Nishiyama Y, Langan P, Chanzy H (2002) Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124:9074–9082. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0257319
Nishiyama Y, Sugiyama J, Chanzy H, Langan P (2003) Crystal structure and hydrogen bonding system in cellulose iα from synchrotron x-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 125:14300–14306. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja037055w
Niu X, Liu Y, Fang G, Huang C, Rojas OJ, Pan H (2018) Highly Transparent, Strong, and Flexible Films with Modified Cellulose Nanofiber Bearing UV Shielding Property. Biomacromol 19:4565–4575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b01252
Oda H (2011) Development of UV absorbers for sun protective fabrics. SAGE Publications. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517511416277
Oh YS, Jang ES, Bock JY, Yoon SH, Jung MY (2006) Singlet oxygen quenching activities of various fruit and vegetable juices and protective effects of apple and pear juices against hematolysis and protein oxidation induced by methylene blue photosensitization. J Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00014.x
Ohkatsu Y, Sakurai T, Sato T (2010) Relationship between Chemical Structure and Antioxidant Function of Flavonoids. J Japan Petrol Inst 53:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1627/JPI.53.213
Ohkawa K (2015) Nanofibers of cellulose and its derivatives fabricated using direct electrospinning. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20059139
Oishi Y, Nakaya M, Matsui E, Hotta A (2015) Structural and mechanical properties of cellulose composites made of isolated cellulose nanofibers and poly(vinyl alcohol). Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 73:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.02.026
Orsat V, Routray W (2017) Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Flavonoids. Water Extraction of Bioactive Compounds: from Plants to Drug Development. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809380-1.00008-5
Ozdemir M, Kemerli T (2016) Innovative applications of micro and nanoencapsulation in food packaging. Encapsulat Control Release Technol Food Syst 333–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118946893.ch12
Pan G, Guoyong Yu, Zhu C, Qiao J (2012) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of flavonoids compounds (FC) from hawthorn seed (HS). Ultrason Sonochem 19:486–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2011.11.006
Pan M-H, Lai C-S, Ho C-T (2023) Anti-inflammatory activity of natural dietary flavonoids. Food Funct. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0fo00103a
Panchal P, Ogunsona E, Mekonnen T (2019) Trends in advanced functional material applications of nanocellulose. Processes. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7010010
Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR (2016) Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of Nutritional Science 5:e47. https://doi.org/10.1017/JNS.2016.41
Park HJ, Weller CL, Vergano PJ, Testin RF (1993) Permeability and mechanical properties of cellulose‐based edible films. J Food Sci 58(6):1361–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1993.tb06183.x
Peelman N, Ragaert P, de Meulenaer B, Adons D, Peeters R, Cardon L, van Impe F, Devlieghere F (2013) Application of bioplastics for food packaging. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2013.06.003
Pellicer E, Nikolic D, Sort J, Baró MD, Zivic F, Grujovic N, Grujic R, Pelemis S (2017) Advances in applications of industrial biomaterials. Advances in Applications of Industrial Biomaterials. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62767-0
Photoprotection of natural flavonoids. 2023. https://japsonline.com/admin/php/uploads/1063_pdf.pdf. Accessed June 9.
Piñeros-Hernandez D, Medina-Jaramillo C, López-Córdoba A, Goyanes S (2017) Edible cassava starch films carrying rosemary antioxidant extracts for potential use as active food packaging. Food Hydrocolloids 63:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODHYD.2016.09.034
Plant Breeding Reviews, Volume 25 - Google Books. 2023. https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=NQinOSRh9f0C&oi=fnd&pg=PA89&dq=Griesbach+R+(2005)+Biochemistry+and+genetics+of+flower+color.+Plant+Breed+Rev+25,+89%E2%80%93114.&ots=Z66bRu5drT&sig=g46GPa2T9KnX1L8vgvDgMb5J078&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed January 28.
Plant Secondary Metabolites: Occurrence, Structure and Role in the Human Diet - Google Books. 2023. https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=mvJmDW7CVTMC&oi=fnd&pg=PP2&dq=Crozier+A,+Jaganath+IB,+Clifford+MN+(2006)+Phenols,+poly%3Fphenols+and+tannins:+an+overview.+In:+Crozier+A,+Clifford+MN,+Ashihara+H+(eds)+Plant+secondary+metabolites:+occurrence,+structure+and+role+in+the+human+diet.+Blackwell+Publishing+Ltd,+Oxford,+pp+1%E2%80%93&ots=oM553VKzMq&sig=i2rDH1GxLTqh-jPUb1ctY-yoI-U&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed January 28.
Pollastri S, Tattini M (2011) Flavonols: old compounds for old roles. Ann Bot 108:1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1093/AOB/MCR234
Pooresmaeil M, Behzadi Nia S, Namazi H (2019) Green encapsulation of LDH(Zn/Al)-5-Fu with carboxymethyl cellulose biopolymer; new nanovehicle for oral colorectal cancer treatment. Int J Biol Macromol 139:994–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.060
Popović SZ, Lazić VL, Hromiš NM, Šuput DZ, Bulut SN (2018) Biopolymer packaging materials for food shelf-life prolongation. In: Biopolymers for food design. Academic Press, pp 223–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811449-0.00008-6
Potters G, Pasternak TP, Guisez Y, Palme KJ, Jansen MAK (2007) Stress-induced morphogenic responses: growing out of trouble? Trends Plant Sci 12:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TPLANTS.2007.01.004
Rajala, Satu, Tuomo Siponkoski, Essi Sarlin, Marja Mettänen, Maija Vuoriluoto, Arno Pammo, Jari Juuti, Orlando J Rojas, Sami Franssila, and Sampo Tuukkanen. Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material.
Randriamanana TR, Nissinen K, Moilanen J, Nybakken L, Julkunen-Tiitto R (2015) Long-term UV-B and temperature enhancements suggest that females of Salix myrsinifolia plants are more tolerant to UV-B than males. Environ Exp Bot 109:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.06.007
Rehan F, Ahemad N, Gupta M (2019) Casein nanomicelle as an emerging biomaterial—A comprehensive review. Colloids Surf, B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.03.051
Rhim JW (2004) Physical and mechanical properties of water resistant sodium alginate films. LWT 37:323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2003.09.008
Rhim JW, Ng PKW (2007) Natural biopolymer-based nanocomposite films for packaging applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47:411–433. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390600846366
Rhim JW, Gennadios A, Handa A, Weller CL, Hanna MA (2000) Solubility, tensile, and color properties of modified soy protein isolate films. J Agric Food Chem 48:4937–4941. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0005418
Risch SJ (2009) Food Packaging History and Innovations. J Agric Food Chem 57:8089–8092. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900040r
Roberts MR, Paul ND (2006) Seduced by the dark side: integrating molecular and ecological perspectives on the influence of light on plant defence against pests and pathogens. New Phytol 170:677–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1469-8137.2006.01707.X
Robertson GL (2009) Food packaging and shelf life: a practical guide. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420078459
Rojas-Lema S, Quiles-Carrillo L, Garcia-Garcia D, Melendez-Rodriguez B, Balart R, Torres-Giner S (2020) Tailoring the properties of thermo-compressed polylactide films for food packaging applications by individual and combined additions of lactic acid oligomer and halloysite nanotubes. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081976
Rouf TB, Kokini JL (2017) Natural biopolymer-based nanocomposite films for packaging applications. Bionanocomposites Packaging Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67319-6_8/FIGURES/12
Roy S, Kim HC, Panicker PS, Rhim JW, Kim J (2021) Cellulose nanofiber-based nanocomposite films reinforced with zinc oxide nanorods and grapefruit seed extract. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040877
Saha T, Hoque ME, Mahbub T (2020) Biopolymers for Sustainable Packaging in Food, Cosmetics, and Pharmaceuticals. In Advanced Processing, Properties, and Applications of Starch and Other Bio-Based Polymers, Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819661-8.00013-5
Santosa B (2021) Water infusion of IR-Bagendit rice leaves from various locations in central java as a candidate material to prevent a heavy metal exposure. J Hunan Univ Nat Sci 48(7)
Satyanarayana KG, Arizaga GGC, Wypych F (2009) Biodegradable composites based on lignocellulosic fibers-An overview. Progress in Polymer Science (oxford). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.12.002
Savadekar NR, Mhaske ST (2012) Synthesis of nano cellulose fibers and effect on thermoplastics starch based films. Carbohyd Polym 89:146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.063
Scalia S, Mezzena M (2009) Incorporation of quercetin in lipid microparticles: Effect on photo- and chemical-stability. J Pharm Biomed Anal 49:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPBA.2008.10.011
Scheirs J, Camino G, Tumiatti W (2001) Overview of water evolution during the thermal degradation of cellulose. Eur Poly J 37(5):933–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-3057(00)00211-1
Schreiner M, Mewis I, Huyskens-Keil S, Jansen MAK, Zrenner R, Winkler JB, O’Brien N, Krumbein A (2012) UV-B-induced secondary plant metabolites - potential benefits for plant and human health. Crit Rev Plant Sci 31:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2012.664979
Searles PS, Flint SD, Caldwell MM (2001) A meta-analysis of plant field studies simulating stratospheric ozone depletion. Oecologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420000592
Sessini V, Navarro-Baena I, Arrieta MP, Dominici F, López D, Torre L, Kenny JM, Dubois P, Raquez JM, Peponi L (2018) Effect of the addition of polyester-grafted-cellulose nanocrystals on the shape memory properties of biodegradable PLA/PCL nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 152:126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.04.012
Sharma A, Thakur M, Bhattacharya M, Mandal T, Goswami S (2019) Commercial application of cellulose nano-composites – A review. Biotechnology Reports. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00316
Shen Y, Seidi F, Ahmad M, Liu Y, Saeb MR, Akbari A, Xiao H (2023) recent advances in functional cellulose-based films with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties for food packaging. Cite This: J Agric Food Chem 71:16469–16487. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06004
Shirsath SR, Sonawane SH, Gogate PR (2012) Intensification of extraction of natural products using ultrasonic irradiations-A review of current status. Chem Eng Process 53:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEP.2012.01.003
Sims RJ, Rojas LA, Beck D, Bonasio R, Schüller R, Drury WJ, Eick D, Reinberg D (2011) The C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II is modified by site-specific methylation. Science 332:99–103. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1202663
Singh VP, Badiger NM, Kaewkhao J (2014) Radiation shielding competence of silicate and borate heavy metal oxide glasses: Comparative study. J Non-Cryst Solids 404:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.08.003
Snell KRS, Kokubun T, Griffiths H, Convey P, Hodgson DA, Newsham KK (2009) Quantifying the metabolic cost to an Antarctic liverwort of responding to an abrupt increase in UVB radiation exposure. Glob Change Biol 15:2563–2573. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.01929.x
Sousa F, Guebitz GM, Kokol V (2009) Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan enzymatically functionalized with flavonoids. Process Biochem 44:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2009.03.009
Sousa do N, Dantas S, SantiagoMaia RGDAS, Silva de EO, Vieira RS, Bastos-Neto M (2020) Ethylene adsorption on chitosan/zeolite composite films for packaging applications. Food Packag Shelf Life. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100584
Souza BWS, Cerqueira MA, Martins JT, Casariego A, Teixeira JA, Vicente AA (2010) Influence of electric fields on the structure of chitosan edible coatings. Food Hydrocolloids 24:330–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2009.10.011
Souza de HJB, Fernandes de RVB, Borges SV, Felix PHC, Viana LC, Lago AMT, Botrel DA (2018) utility of blended polymeric formulations containing cellulose nanofibrils for encapsulation and controlled release of sweet orange essential oil. Food Bioprocess Technol 11:1188–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2082-9
Sperandeo P, Bosco F, Clerici F, Polissi A, Gelmi ML, Romanelli A (2020) Covalent grafting of antimicrobial peptides onto microcrystalline cellulose. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:4895–4901. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00412
Edible and biodegradable polymer films: challenges and opportunities. 2023. https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US9729236. Accessed January 27.
Stafford HA (1991) Flavonoid evolution: an enzymic approach. Plant Physiol 96:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1104/PP.96.3.680
Stobiecki M, Kachlicki P (2006) Isolation and identification of flavonoids. The Science of Flavonoids. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-28822-2_2/COVER
Suganya V, Anuradha V (2017) Microencapsulation and nanoencapsulation a review. Int J Pharm Clin Res. https://doi.org/10.25258/ijpcr.v9i3.8324
Szkudelska K, Nogowski L (2007) Genistein-A dietary compound inducing hormonal and metabolic changes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 105:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSBMB.2007.01.005
Takahashi A, Ohnishi T, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T (2004) The Significance of the Study about the Biological Effects of Solar Ultraviolet Radiation using the Exposed Facility on the International Space Station. Biol Sci Space 18:255–260. https://doi.org/10.2187/BSS.18.255
Tănase EE, Râpă M, Popa O (2014) Biopolymers based on renewable resources-a review. Biotechnologies, Vol. XVIII, ISSN 2285-1364188-195
Tang XZ, Kumar P, Alavi S, Sandeep KP (2012) Recent Advances in Biopolymers and Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites for Food Packaging Materials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2010.500508
Taniguchi M, LaRocca CA, Bernat JD, Lindsey JS (2022) Digital Database of Absorption Spectra of Diverse Flavonoids Enables Structural Comparisons and Quantitative Evaluations. J Nat Prod. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00720
Tharanathan RN (2003) Biodegradable films and composite coatings: Past, present and future. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2244(02)00280-7
Thennarasu P, Prabunathan P, Senthilkumar M (2018) Development of biomass-derived functionalized activated carbon-coated and polyaniline-grafted cotton fabric with enhanced ultraviolet resistance. J Ind Text 47:1609–1625. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083717702008
Tolstoguzov V (2003) Some thermodynamic considerations in food formulation. Food Hydrocol 17(1):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0268-005X(01)00111-4
Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC (2001) Phenolic compounds and related enzymes as determinants of quality in fruits and vegetables. J Sci Food Agri 81:853–876. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.885
Tomé LC, Gonalves CMB, Boaventura M, Brandão L, Mendes AM, Silvestre AJD, Neto CP, Gandini A, Freire CSR, Marrucho IM (2011) Preparation and evaluation of the barrier properties of cellophane membranes modified with fatty acids. Carbohyd Polym 83:836–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.060
Tomimatsu Y, Suetsugu H, Yoshimura Y, Shimizu A (2019) The solubility of cellulose in binary mixtures of ionic liquids and dimethyl sulfoxide: Influence of the anion. J Mol Liq 279:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.01.093
Trache D, Hazwan Hussin M, Chuin CTH, Sumiyyah Sabar MR, Fazita N, Taiwo OFA, Hassan TM, Mohamad Haafiz MK (2016) Microcrystalline cellulose: Isolation, characterization and bio-composites application—A review. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.056
Tumwesigye KS, Oliveira JC, Sousa-Gallagher MJ (2016) New sustainable approach to reduce cassava borne environmental waste and develop biodegradable materials for food packaging applications. Food Packag Shelf Life 7:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FPSL.2015.12.001
Tyagi P, Hubbe MA, Lucia L, Pal L (2018) High performance nanocellulose-based composite coatings for oil and grease resistance. Cellulose 25:3377–3391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1810-7
Vartiainen J, Shen Y, Kaljunen T, Malm T, Vähä-Nissi M, Putkonen M, Harlin A (2016) Bio-based multilayer barrier films by extrusion, dispersion coating and atomic layer deposition. J Appl Poly Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.42260
Vedove TMARD, Maniglia BC, Tadini CC (2021) Production of sustainable smart packaging based on cassava starch and anthocyanin by an extrusion process. J Food Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110274
Veit M, Bilger W, Mühlbauer T, Brummet W, Winter K (1996) Diurnal changes in flavonoids. J Plant Physiol 148:478–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(96)80282-3
Velikovi DT, Nikolova MT, S v Ivancheva JB, Stojanovi VBV (2007) Extraction of flavonoids from garden (Salvia officinalis L.) and glutinous (Salvia glutinosa L.) sage by ultrasonic and classical maceration. J Serb Chem Soc 72:73–80. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0701073V
Vidal S, Francis L, Noble A, Kwiatkowski M, Cheynier V, Waters E (2004) Taste and mouth-feel properties of different types of tannin-like polyphenolic compounds and anthocyanins in wine. In Analytica Chimica Acta 513:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2003.10.017
Vieira MG, Adeodato MA, da Silva L, dos Santos O, Beppu MM (2011) Natural-based plasticizers and biopolymer films: A review. Eur Polymer J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.12.011
Vinodhini P, Angelin KS, Gomathi Thandapani PN, Sudha VJ, Sukumaran A (2017) FTIR, XRD and DSC studies of nanochitosan, cellulose acetate and polyethylene glycol blend ultrafiltration membranes. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1721–1729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.122
Virgili F, Marino M (2008) Regulation of cellular signals from nutritional molecules: a specific role for phytochemicals, beyond antioxidant activity. Free Radical Biol Med 45:1205–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FREERADBIOMED.2008.08.001
Wang L, Weller CL (2006) Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2005.12.004
Wang H, Gurau G, Rogers RD (2012) Ionic liquid processing of cellulose. Chem Soc Rev 41:1519–1537. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15311d
Wang X, Yong H, Gao Li, Li L, Jin M, Liu J (2019) Preparation and characterization of antioxidant and pH-sensitive films based on chitosan and black soybean seed coat extract. Food Hydrocolloids 89:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.10.019
Wang W, Zhang B, Jiang S, Bai H, Zhang S (2019) Use of CeO2 nanoparticles to enhance UV-shielding of transparent regenerated cellulose films. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030458
Wang H, Ding F, Ma L, Zhang Y (2021a) Edible films from chitosan-gelatin: Physical properties and food packaging application. Elsevier Ltd., Food Bioscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100871
Wang W, Feng Gu, Deng Z, Zhu Y, Zhu J, Guo T, Song J, Xiao H (2021b) Multilayer surface construction for enhancing barrier properties of cellulose-based packaging. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117431
Webster JB, Duncan SE, Marcy JE, O’Keefe SF (2009) Controlling light oxidation flavor in milk by blocking riboflavin excitation wavelengths by interference. J Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01336.x
Xie S, Zhao J, Zhang B, Wang Z, Ma H, Chuhong Yu, Ming Yu, Li L, Li J (2015) Graphene Oxide Transparent Hybrid Film and Its Ultraviolet Shielding Property. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:17558–17564. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04231
Xu A, Wang J, Wang H (2010) Effects of anionic structure and lithium salts addition on the dissolution of cellulose in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium-based ionic liquid solvent systems. Green Chem 12:268–327. https://doi.org/10.1039/b916882f
Yan N, Chai XS (2021) Rapid determination of the content of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium in aqueous solution by a color indicator-assisted spectroscopy. Polym Test. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106990
You J, Gao S, Jin H, Li W, Zhang H, Aimin Yu (2010) On-line continuous flow ultrasonic extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatographic separation for determination of the flavonoids from root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. J Chromatogr A 1217:1875–1881. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHROMA.2010.01.050
Yrjänheikki J, Keinänen R, Pellikka M, Hökfelt T, Koistinaho J (1998) Tetracyclines inhibit microglial activation and are neuroprotective in global brain ischemia. PNAS 95:15769–15774. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.95.26.15769
Zavala JA, Mazza CA, Dillon FM, Chludil HD, Ballaré CL (2015) Soybean resistance to stink bugs (Nezara viridula and Piezodorus guildinii) increases with exposure to solar UV-B radiation and correlates with isoflavonoid content in pods under field conditions. Plant Cell Environ 38:920–928. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12368
Zhang WJ, Björn LO (2009) The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the accumulation of medicinal compounds in plants. Fitoterapia 80:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FITOTE.2009.02.006
Zhang N, Bi F, Fengfeng Xu, Yong H, Bao Y, Jin C, Liu J (2020a) Structure and functional properties of active packaging films prepared by incorporating different flavonols into chitosan based matrix. Int J Biol Macromol 165:625–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.209
Zhang XF, Song L, Wang Z, Wang Y, Wan L, Yao J (2020b) Highly transparent graphene oxide/cellulose composite film bearing ultraviolet shielding property. Int J Biol Macromol 145:663–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.241
Zhao G, Jun Du, Chen W, Pan M, Chen D (2019) Preparation and thermostability of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils from two sources of biomass: rice straw and poplar wood. Cellulose 26:8625–8643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02683-8
Zhu F (2021) Polysaccharide based films and coatings for food packaging: Effect of added polyphenols. Food Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129871
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the Director, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Amritapuri, Kerala, India for providing all requisite support.
Funding
The authors did not receive any financial support from any sources for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the idea for the article. The literature search, data analysis and drafting of manuscript were performed by Greeshma U Chandran and Avani Anil Kumar. All authors critically revised the work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This review paper involves the synthesis and analysis of previously published research studies. As such, it does not directly involve human subjects, animals, or any other ethical considerations. All efforts have been made to ensure the accurate reporting and synthesis of information from the selected studies, and proper citation practices have been followed.
Consent for publication
Authors have acquired requisite copyright consent for the external data used.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandran, G.U., Kumar, A.A., Menon, S.K. et al. The potential role of flavonoids in cellulose-based biopolymeric food packaging materials for UV radiation protection. Cellulose 31, 4733–4773 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05838-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05838-4