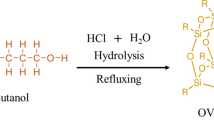
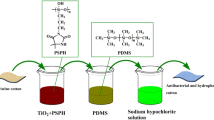
Abstract
The problem of functional integration is a significant challenge for the preparation of multifunctional cotton fabrics. Herein, silver@titanium dioxide (Ag@TiO2) Janus nanoparticles were synthesized by Pickering emulsion polymerization, and then the Janus nanoparticles were finished on the epoxy modified cotton fabric to obtain a multifunctional cotton fabric. The Ag@TiO2 Janus nanoparticles possessed an asymmetric structure. The one side of the Janus nanoparticles was the silane with hydrophilic amino group, which was covalently bonded with the epoxy group on the cotton fabric fibers. The other side was silane with hydrophobic long-chain alkane, which was faced the environment. The structure endowed the cotton fabric with durably superhydrophobic, UV resistance, and antibacterial. The multifunctional cotton fabric had a water contact angle of 160°, and the contact angle could still reach 152° at the damaged part of the multifunctional cotton fabric after 50 abrasion cycles, indicating the superhydrophobic of the multifunctional cotton fabric. The antibacterial rate of the multifunctional cotton fabric against Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Streptococcus Urealyticus (S. aureus) were more than 95%, and the antibacterial rate of the multifunctional cotton fabric still maintained more than 70%, after 10 cycles of laundering treatment, exhibiting the antibacterial property of the multifunctional cotton fabric. The Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) value of the multifunctional cotton fabric was 34.3, which indicated the multifunctional cotton fabric had excellent ultraviolet resistance. This study provided a new method for multi-functional finishing of fabrics, allowing new functions to be given without damage.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal N, Tan JSJ, Low PS et al (2019) Green synthesis of robust superhydrophobic antibacterial and UV-blocking cotton fabric by a dual‐stage silanization approach. Adv Mater Interfaces 6(11):1900032. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201900032
Ama B, Nbsa B, Ab A et al (2020) Plasmonic hybrid platinum-titania nanocomposites as highly active photocatalysts: self-cleaning of cotton fiber under solar light-science direct. J Mater Res Technol 9(2):1447–1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.11.070
Ahmad N, Rasheed S, Ahmed K et al (2022) Facile two-step functionalization of multifunctional superhydrophobic cotton fabric for UV-blocking, self cleaning, antibacterial, and oil-water separation. Sep Purif Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122626
Bartosewicz B, Liszewska M, Budner B et al (2020) Fabrication of Ag-modified hollow titania spheres via controlled silver diffusion in Ag–TiO2 core–shell nanostructures. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 11(1):141–146. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.11.12
Bhattacharjee S, Macintyre CR, Wen XY et al (2020) Nanoparticles incorporated graphene-based durable cotton fabric. Carbon 166:148–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.029
Choi K, Bang JW, Kyu Moon I et al (2020) Enhanced photoelectrochemical efficiency and stability using nitrogen-doped TiO2 on a GaAs photoanode. J Alloys Compd 843:155973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155973
Chen J, Dai S, Liu LY et al (2021) Photo-functionalized TiO2 nanotubes decorated with multifunctional ag nanoparticles for enhanced vascular biocompatibility. Bioact Mater 6(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.07.009
Cheng W, Liu WJ, Wang P et al (2022) Multifunctional coating of cotton fabric via the assembly of amino-quinone networks with polyamine biomacromolecules and dopamine quinone. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.165
Da Silva DJ, Souza AG, Ferreira GS et al (2021) Cotton fabric decorated with antimicrobial Ag-coated TiO2 nanoparticles are unable to fully and rapidly eradicate SARS-CoV-2. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4(12):12949–12956. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c03492
Gao DG, Guo SH, Zhou YY et al (2022) Hydrophobic, flexible electromagnetic interference shielding films derived from hydrolysate of waste leather scraps. J Colloid Interface Sci 613:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.01.043
Gao S, Li HQ, Zheng LZ et al (2021) Superhydrophobic and conductive polydimethylsiloxane/titanium dioxide@reduced graphene oxide coated cotton fabric for human motion detection. Cellulose 28(11):7373–7388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03951-2
Gao DG, Li XJ, Li YJ, Lyu B, Ren JJ, Ma JZ (2021) Long-acting antibacterial activity on the cotton fabric. Cellulose 28(3):1221–1240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03560-5
Hong J, Wu T, Wu HY et al (2021) Nanohybrid silver nanoparticles@halloysite nanotubes coated with polyphosphazene for effectively enhancing the fire safety of epoxy resin. Chem Eng J 407:127087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127087
Kumar S, Sharma R, Gupta A et al (2022) TiO2 based photocatalysis membranes: an efficient strategy for pharmaceutical mineralization. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157221
Liu H, Wang YD, Huang JY et al (2018) Bioinspired surfaces with superamphiphobic properties: concepts, synthesis, and applications. Adv Funct Mater 28(19):1707415. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201707415
Li XS, Chen LG, Cui D et al (2021) Preparation and application of Janus nanoparticles: recent development and prospects. Coord Chem Rev 454:0010–8545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214318
Liu ZJ, Zhang CY, Zhang XG et al (2021) Durable superhydrophobic PVDF/FEVE/GO@TiO2 composite coating with excellent anti-scaling and UV resistance properties. Chem Eng J 411:128632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128632
Li SS, Lin XH, Gong SL (2022) Waterborne polyurethane assembly multifunctional coating for hydrophobic and antibacterial fabrics. Cellulose 29(13):7397–7411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04705-4
Rong LD, Liu HC, Wang BJ et al (2019) Durable antibacterial and hydrophobic cotton fabric utilizing enamine bonds. Carbohydr Polym 211:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.103
Raeisi M, Kazerouni Y, Mohammadi A et al (2020) Superhydrophobic cotton fabric coated by chitosan and titanium dioxide nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial and UV-protecting properties. Int J Biol Macromol 171:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.220
Tan YJ, Sun LY, Wang GC et al (2022) A two-step nonthermal plasma method to fabricate Ag/N- doped TiO2/CNTs for formaldehyde removal under visible light irradiation. J Clean Prod 370:0959–6526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133507
Xia L, Dai JG, Wang XH et al (2022) Facile fabrication of multifunctional cotton fabric by AgNC@ boronate polymer/crosslinked chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 288:119384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119384
Xu P, Wu ZG, Dai W et al (2021) Synthesis of multiple ag nanoparticles loaded hollow mesoporous carbon spheres for highly efficient and recyclable catalysis. Microporours Mesoporous Mat 314:110856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110856
Yuzer B, Aydın MI, Con AH et al (2022) Photocatalytic, self-cleaning and antibacterial properties of Cu (II) doped TiO2. J Environ Manag 302:114023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114023
Zheng ZK, Huang BB, Qin XY et al (2011) Facile in situ synthesis of visible-light plasmonic photocatalysts M@TiO2 (M = au, pt, ag) and evaluation of their photocatalytic oxidation of benzene to phenol. J Mater Chem 21(25):9079–9087. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM10983A
Zhang X, Fu QR, Duan HW et al (2021) Janus nanoparticles: from fabrication to (Bio)applications. ACS Nano 15(4):6147–6191. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01146
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support for this study from the Key Project of Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (Special Support, 2023JC-XJ-12), the Shaanxi Provincial "Special Support Plan for High-level Talents, Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi (Program No. 2021TD-16).
Funding
This work was carried out with support from the Key Project of Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (Special Support, 2023JC-XJ-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DG conceived the concept, supervised the project and provided financial support and thoughts of manuscript. FW performed the experiment, prepared the samples and did the manuscript and analysis. ZZ performed the experiment and provided thought. LB provided manuscript retouching and fund support. JM provided the thought, manuscript retouching and fund
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All authors have understood and complied with the code of ethics, approved, and agreed to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, D., Wang, F., Lyu, B. et al. Multifunctional cotton fabric with durable antibacterial, superhydrophobicity, and UV resistance based on Ag@TiO2 Janus nanoparticles. Cellulose 31, 2617–2633 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05727-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05727-2