Abstract
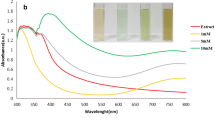
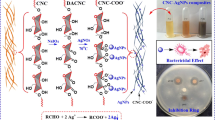
Present work deals with the extraction of nanocellulose (NC) from pistachio nut shells, which is an agro-waste. NC was extracted through acid hydrolysis and characterized with respect to particle size, and morphology. Non- agglomerated hybrid NCAg was synthesized successfully because NC can act as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The as-synthesized nanocellulose silver (NCAg) hybrid was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV–vis), high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). UV-Visible spectrum at 406 nm revealed surface plasmon resonance (SPR) caused by the spherically shaped Ag-NPs. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and HRTEM studies confirmed the FCC crystalline structure of silver in the nanocellulose matrix. The Ag-NPs were uniform and spherical, with particle size ranging from 2 to 18 nm according to the TEM micrographs. NCAg hybrid was tested for antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis bacteria. The NCAg hybrid with controlled morphology, size and good antibacterial activity has potential applications in active packaging films, wound treatment, coatings, adhesives, and anti-biofouling films with good reinforcement ability.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the presented materials and data are owned by the authors. All the data and materials will be made available if required.
References
Aadil KR, Pandey N, Mussatto SI, Jha H (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using acacia lignin, their cytotoxicity, catalytic, metal ion sensing capability and antibacterial activity. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103296
Apaydin-Varol E, Pütün E, Pütün AE (2007) Slow pyrolysis of pistachio shell. Fuel 86:1892–1899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.11.041
Arun R, Shruthy R, Preetha R, Sreejit V (2022) Biodegradable nano composite reinforced with cellulose nano fiber from coconut industry waste for replacing synthetic plastic food packaging. Chemosphere 291:132786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132786
Biswal AK, Misra PK (2020) Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles for prospective application in food packaging and biomedical fields. Mater Chem Phys 250:123014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123014
Bledzki AK, Mamun AA, Volk J (2010) Barley husk and coconut shell reinforced polypropylene composites: the effect of fibre physical, chemical and surface properties. Compos Sci Technol 70:840–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.01.022
Boluk Y, Danumah C (2014) Analysis of cellulose nanocrystal rod lengths by dynamic light scattering and electron microscopy. J Nanopart Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2174-4
Chieng BW, Lee SH, Ibrahim NA, Then YY, Loo YY (2017) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from oil palm mesocarp fiber. Polymers (Basel) 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080355
Demirbaş A (2002) Fuel characteristics of olive husk and walnut, hazelnut, sunflower, and almond shells. Energy Sources 24:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/009083102317243601
Elumalai D, Kaleena PK, Ashok K et al (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Achyranthes aspera and its larvicidal activity against three major mosquito vectors. Eng Agric Environ Food 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eaef.2015.08.002
Emam HE, El-Bisi MK (2014) Merely Ag nanoparticles using different cellulose fibers as removable reductant. Cellulose 21:4219–4230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0438-5
Errokh A, Magnin A, Putaux JL, Boufi S (2019) Hybrid nanocellulose decorated with silver nanoparticles as reinforcing filler with antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Eng C 105:110044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110044
Figueiredo P, Lintinen K, Hirvonen JT et al (2018) Properties and chemical modifications of lignin: towards lignin-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Prog Mater Sci 93:233–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.12.001
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Fukuda J, Hsieh Y, Lo (2022) Almond shell nanocellulose: characterization and self-assembling into fibers, films, and aerogels. Ind Crops Prod 186:115188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115188
Goswami M, Baruah D, Das AM (2018) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles supported on cellulose and their catalytic application in the scavenging of organic dyes. New J Chem 42:10868–10878. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj00526e
Han Y, Wu X, Zhang X et al (2016) Reductant-free synthesis of silver nanoparticles-doped cellulose microgels for catalyzing and product separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6322–6331. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00889
Harini K, Chandra Mohan C, Ramya K et al (2018) Effect of Punica granatum peel extracts on antimicrobial properties in walnut shell cellulose reinforced bio-thermoplastic starch films from cashew nut shells. Carbohydr Polym 184:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.072
Heidari H, Aliramezani F (2021) Reductant-free and in-situ green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on Fe3O4@Nanocellulose and their catalytic activity for the reduction of dyes. ChemistrySelect 6:1223–1229. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202004579
Hemmati F, Jafari SM, Kashaninejad M, Barani Motlagh M (2018) Synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals derived from walnut shell agricultural residues. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1216–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.012
Hu S, Hsieh YL (2015) Synthesis of surface bound silver nanoparticles on cellulose fibers using lignin as multi-functional agent. Carbohydr Polym 131:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.060
Hu L, Stevanovic T, Rodrigue D (2015) Unmodified and esterified Kraft lignin-filled polyethylene composites: compatibilization by free-radical grafting. J Appl Polym Sci 132:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41484
Jatoi AW, Kim IS, Ni QQ (2019) A comparative study on synthesis of AgNPs on cellulose nanofibers by thermal treatment and DMF for antibacterial activities. Mater Sci Eng C 98:1179–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.017
Javed R, Zia M, Naz S et al (2020) Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: recent trends and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnol 18:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-00704-4
Johnson PD, Watson MA, Brown J, Jefcoat IA (2002) Peanut hull pellets as a single use sorbent for the capture of Cu(II) from wastewater. Waste Manag 22:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(01)00036-8
Joshi KM, Shinde DR, Nikam LK et al (2019) Fragmented lignin-assisted synthesis of a hierarchical ZnO nanostructure for ammonia gas sensing. RSC Adv 9:2484–2492. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05874a
Kasiri N, Fathi M (2018) Production of cellulose nanocrystals from pistachio shells and their application for stabilizing pickering emulsions. Int J Biol Macromol 106:1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.112
Kvitek L, Vanickova M, Panacek A et al (2009) Initial study on the toxicity of silver nanoparticles (NPs) against Paramecium Caudatum. J Phys Chem C 113:4296–4300. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp808645e
Lagutschenkov A, Sinha RK, Maitre P, Dopfer O (2010) Structure and infrared spectrum of the Ag+-phenol ionic complex. J Phys Chem A 114:11053–11059. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp100853m
Lokanathan AR, Uddin KMA, Rojas OJ, Laine J (2014) Cellulose nanocrystal-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: role of sulfate groups in nucleation phenomena. Biomacromol 15:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm401613h
Maaloul N, Arfi R, Ben, Rendueles M et al (2017) Dialysis-free extraction and characterization of cellulose crystals from almond (Prunus dulcis) shells. J Mater Environ Sci 8:4171–4181
Maiti PK, Ghosh A, Parveen R et al (2019) Preparation of carboxy-methyl cellulose-capped nanosilver particles and their antimicrobial evaluation by an automated device. Appl Nanosci (Switz) 9:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0914-6
Movva M, Kommineni R (2017) Extraction of cellulose from pistachio shell and physical and mechanical characterisation of cellulose-based nanocomposites. Mater Res Express 4:045014. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa6863
Naduparambath S, Shaniba TVJ et al (2018) Isolation and characterisation of cellulose nanocrystals from sago seed shells. Carbohydr Polym 180:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.088
Niu Z, Li Y (2014) Removal and utilization of capping agents in nanocatalysis. Chem Mater 26:72–83. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm4022479
Ogundare SA, van Zyl WE (2018) Nanocrystalline cellulose as reducing- and stabilizing agent in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles: application as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate. Surf Interfaces 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2018.06.004
Owens B (2013) Silver makes antibiotics thousands of times more effective. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2013.13232
Phosanam A, Moreira J, Adhikari B, Adhikari A, Losso JN (2023) Stabilization of ginger essential oil pickering emulsions by pineapple cellulose nanocrystals. Curr Res Food Sci 7:100575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100575
Sadeghifar H, Venditti R, Jur J et al (2017) Cellulose-lignin biodegradable and flexible UV protection film. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02003
Sai Prasanna N, Mitra J (2020) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from cucumis sativus peels. Carbohydr Polym 247:116706
Schillinger U, Lücke FK (1989) Antibacterial activity of lactobacillus sake isolated from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1901–1906. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.55.8.1901-1906.1989
Wu J, Zheng Y, Song W et al (2014) In situ synthesis of silver-nanoparticles/bacterial cellulose composites for slow-released antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym 102:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.093
Wyckoff RWG (1963) Crystal structures, second. Interscience Publishers,New York, New York
Yang G, Xie J, Hong F et al (2012) Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticle impregnated bacterial cellulose membrane: effect of fermentation carbon sources of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 87:839–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.08.079
Zhang X, Sun H, Tan S et al (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of Ag nanoparticles on the nanocellulose and their antibacterial study. Inorg Chem Commun 100:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2018.12.012
Zhang M, Zhang K, De Gusseme B et al (2014) The antibacterial and anti-biofouling performance of biogenic silver nanoparticles by lactobacillus fermentum. Biofouling 30:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.873419
Zhong L, Fu S, Peng X et al (2012) Colloidal stability of negatively charged cellulose nanocrystalline in aqueous systems. Carbohydr Polym 90:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.05.091
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding from the funding agencies for the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JT: Data analysis, Methodology, Investigation, original draft preparation ST: Review, Editing, Suggestions RS: Conceptualiation, Editing, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Certify that the consent of publication has been taken from all authors. Authors read and understood the publishing policy, and submit this manuscript in accordance with this.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, J., Thomas, S. & Stephen, R. Nanocellulose extracted from pistachio nut shells as a template for nanosilver synthesis and its antimicrobial activity. Cellulose 31, 293–308 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05643-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05643-5