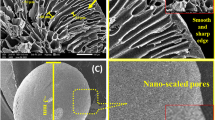
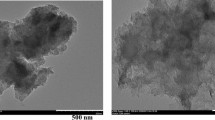
Abstract
Gas adsorption materials, such as active carbon and zeolite, are known to cause second pollution after being used, due to their non-degradability. In this study, we prepared a degradable aerogel material based on cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) and poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) with hierarchical pores and excellent CO\(_2\)-adsorption performance. The micropores, with specific area of 442 m\(^2\cdot\)g\(^{-1}\), are obtained via in-situ growing MIL-100(Fe) on CNCs and concurrently assembling those CNC particles. The resulting aggregate is further introduced into degradable PVA aerogels, who offer mesopores and macropores. The resulting degradable material has a density of 0.216 g\(\cdot\)cm\(^{-3}\) and can adsorb 0.357 mmol CO\(_2\) per gram. This makes it a promising candidate for use in the preparation of light weight CO\(_2\) collectors.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Jin Huang, upon reasonable request.
References
Abitbol T, Rivkin A, Cao Y et al (2016) Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications. Curr Opin Biotech 39:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.01.002
Azzam F, Siqueira E, Fort S et al (2016) Tunable aggregation and gelation of thermoresponsive suspensions of polymer-grafted cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromol 17(6):2112–2119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00344
Beck-Candanedo S, Roman M, Gray DG (2005) Effect of reaction conditions on the properties and behavior of wood cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromol 6(2):1048–1054. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm049300p
Brinatti C, Akhlaghi SP, Pires-Oliveira R et al (2019) Controlled coagulation and redispersion of thermoresponsive poly di(ethylene oxide) methyl ether methacrylate grafted cellulose nanocrystals. J Colloid Interf Sci 538:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.11.071
Cheng F, Liu C, Wei X et al (2017) Preparation and characterization of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized cellulose nanocrystal/alginate biodegradable composite dressing for hemostasis applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(5):3819–3828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02849
Cheng Q, Ye D, Chang C et al (2017) Facile fabrication of superhydrophilic membranes consisted of fibrous tunicate cellulose nanocrystals for highly efficient oil/water separation. J Membrane Sci 525:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.11.084
Cheng QY, Guan CS, Wang M et al (2018) Cellulose nanocrystal coated cotton fabric with superhydrophobicity for efficient oil/water separation. Carbohyd Polym 199:390–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.046
Darder M, Aranda P, Ruiz-Hitzky E (2007) Bionanocomposites: a new concept of ecological, bioinspired, and functional hybrid materials. Adv Mater 19(10):1309–1319. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200602328
De France KJ, Chan KJW, Cranston ED et al (2016) Enhanced mechanical properties in cellulose nanocrystal-poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate) injectable nanocomposite hydrogels through control of physical and chemical cross-linking. Biomacromol 17(2):649–660. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01598
de Paula EL, Roig F, Mas A et al (2016) Effect of surface-grafted cellulose nanocrystals on the thermal and mechanical properties of PLLA based nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 84:173–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.09.019
Dumanli AG, van der Kooij HM, Kamita G et al (2014) Digital color in cellulose nanocrystal films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(15):12,302-12,306. https://doi.org/10.1021/am501995e
Duran N, Paula Lemes A, Seabra BA (2012) Review of cellulose nanocrystals patents: preparation, composites and general applications. Recent Pat Nanotech 6(1):16–28. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221012798109255
Gan L, Wang Y, Zhang M et al (2019) Hierarchically spacing DNA probes on bio-based nanocrystal for spatial detection requirements. Sci Bull 64(13):934–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.05.013
Glatz H, Lizundia E, Pacifico F et al (2019) An organic cathode based dual-ion aqueous zinc battery enabled by a cellulose membrane. ACS Appl Energ Mater 2(2):1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.8b01851
Jorfi M, Foster EJ (2015) Recent advances in nanocellulose for biomedical applications. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41719
Le Gars M, Delvart A, Roger P et al (2020) Amidation of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanocrystals using aromatic aminated molecules. Colloid Polym Sci 298(6):603–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04640-5
Li D, Wang Y, Long F et al (2020) Solvation-controlled elastification and shape-recovery of cellulose nanocrystal-based aerogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(1):1549–1557. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18569
Liu S, Chen Y, Liu C et al (2019) Polydopamine-coated cellulose nanocrystals as an active ingredient in poly(vinyl alcohol) films towards intensifying packaging application potential. Cellulose 26(18):9599–9612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02749-7
Liu SY, Gong YB, Ma S et al (2020) Antistatic structural color and photoluminescent membranes from co-assembling cellulose nanocrystals and carbon nanomaterials for anti-counterfeiting. Chin J Polym Sci 38(10):1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-020-2414-x
Lizundia E, Maceiras A, Vilas J et al (2017) Magnetic cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites for the development of green functional materials. Carbohyd Polym 175:425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.024
Lizundia E, Puglia D, Nguyen TD et al (2020) Cellulose nanocrystal based multifunctional nanohybrids. Prog Mater Sci 112(100):668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100668
Maaloul N, Oulego P, Rendueles M et al (2021) Biopolymer composite from cellulose nanocrystals of almond (Prunus dulcis) shell as effective adsorbents for Cu2+ ions from aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 9(2):105–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105139
Mohammed N, Lian H, Islam MS et al (2021) Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes using functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chem Eng J 417(129):237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129237
Rescignano N, Fortunati E, Montesano S et al (2014) PVA bio-nanocomposites: a new take-off using cellulose nanocrystals and PLGA nanoparticles. Carbohyd Polym 99:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.061
Revol JF, Bradford H, Giasson J et al (1992) Helicoidal self-ordering of cellulose microfibrils in aqueous suspension. Int J Biol Macromol 14(3):170–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-8130(05)80008-X
Segal L, Creely J, Martin A et al (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Wang PX, Hamad WY, MacLachlan MJ (2016) Structure and transformation of tactoids in cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Nat Commun 7(1):11,515. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11515
Wang Y, Xie R, Zheng S et al (2021) Nonuniformly modifying high-aspect-ratio rigid cellulose nanocrystals to enhance percolation advantage in weakly compatible biomass polymer systems. Cellulose 28(8):4655–4669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03830-w
Xiang S, Ma X, Liao S et al (2019) Cellulose nanocrystal surface cationization: a new fungicide with high activity against phycomycetes capsici. Molecules 24(13):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132467
Xu J, Jia P, Wang X et al (2021) The aminosilane functionalization of cellulose nanocrystal aerogel via vapor-phase reaction and its \(\text{ CO}_{2}\) adsorption characteristics. J Appl Polym Sci 138(35):50,891. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50891
Yang X, Shi K, Zhitomirsky I et al (2015) Cellulose nanocrystal aerogels as universal 3D lightweight substrates for supercapacitor materials. Adv Mater 27(40):6104–6109. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502284
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Jiang H et al (2019) Aminosilane-grafted spherical cellulose nanocrystal aerogel with high \(\text{ CO}_{2}\) adsorption capacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(16):16,716-16,726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05068-3
Zhang T, Zhang W, Zhang Y et al (2020) Gas phase synthesis of aminated nanocellulose aerogel for carbon dioxide adsorption. Cellulose 27(6):2953–2958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03035-7
Zheng S, Liu S, Xiao B et al (2021) Integrate nanoscale assembly and plasmonic resonance to enhance photoluminescence of cellulose nanocrystals for optical information hiding and reading. Carbohyd Polym 253(117):260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117260
Zheng X, Zhang Y, Bian T et al (2019) One-step fabrication of imprinted mesoporous cellulose nanocrystals films for selective separation and recovery of Nd(III). Cellulose 26(9):5571–5582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02482-1
Zhu L, Zong L, Wu X et al (2018) Shapeable fibrous aerogels of metal-organic-frameworks templated with nanocellulose for rapid and large-capacity adsorption. ACS Nano 12(5):4462–4468. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00566
Zhu W, Ji M, Zhang Y et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of aminosilane grafted cellulose nanocrystal modified formaldehyde-free decorative paper and its \(\text{ CO}_{2}\) adsorption capacity. Polymers 11(12):2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122021
Zwawi M (2021) A review on natural fiber bio-composites, surface modifications and applications. Molecules 26(2):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020404
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Chongqing Education Committee, the Organization Department of the CPC Chongqing Committee, Chongqing human resources and Social Security Bureau, the Science & Technology Department of Sichuan Province, and Chongqing science and Technology Bureau.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (51973175); Project for Chongqing University Innovation Research Group of Chongqing Education Committee (CXQT19008); Chongqing Talent Plan for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Demonstration Team (CQYC201903243); Key R &D Project of Sichuan Province (22ZDYF3173); Technological Innovation and Application Development “Overall Rationing System” Project of Chongqing Talent Plan (cstc2021ycjh-bgzxm0307).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by SZ. Data analysis was performed by LG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LG and SZ, and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Ethics Committee approval was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee of Southwest University.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved the submission of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Materials:
The supplementary information presents 336 formula showing the major form of the H-bonds between PVA and MIL- 337 100(Fe). Meanwhile, the supplementary information includes the size distri338 bution of neat MIL-100(Fe) particles and typical SEM images of the aerogels. 339 The supplementary information also gives the specific condition of the test 340 environment for material degradation, used in the literature research of this 341 study. (pdf 11,955KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, L., Zheng, S. & Huang, J. Hierarchical pores in degradable polymer-based aerogel for CO\(_2\) adsorption. Cellulose 30, 7877–7888 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05365-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05365-8