Abstract
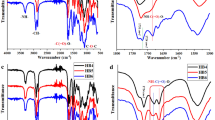
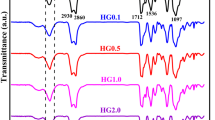
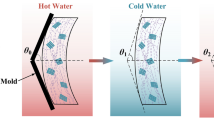
In this research work, a series of thermoset polyurethane (tPU) nanocomposites and a thermoplastic PU (TPPU) were synthesized using semi-crystalline polyols. Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL), poly(tetramethylene glycol) (PTMG), and different architecture and compositions of PCL and PTMG were used as diols. PCL was used to synthesize a TPPU (PCL-TPPU) as the control specimen. Cellulose nanowhisker (CNW), with 1.0 wt% content, was used for synthesis of the tPU nanocomposites. The aim of this research was to investigate the impact of the thermosetting using CNWs and tuning crystallization of the polyols on the shape memory performance (SMP) of PUs. The analysis of the polyols’ crystallization and crystallization of the soft segments in the PU structures was studied to evaluate the impact of structural changes on the SMP of the PUs. The results of the dynamic mechanical thermal analysis showed that the tPUs have a large elastic modulus (E′) at temperatures around ~ 25–40 °C (~ 10 MPa) and very small tanδ height (below 0.15), which was attributed to their thermoset nature and presence of CNW with high E′ value (~ 110–220 GPa). The PCL-TPPU, as the control specimen, showed E′ in the range of 200–400 kPa. The PUs have also proved to be highly biocompatible.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The experimental data will be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Argun A, Gulyuz U, Okay O (2019) Semi-crystalline, three-segmented hybrid gels with multiple shape-memory effect. Macromol Symp 385:1800164. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201800164
Barot G, Rao IJ, Rajagopal KR (2008) A thermodynamic framework for the modeling of crystallizable shape memory polymers. Int J Eng Sci 46:325–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijengsci.2007.11.008
Behrouz T, Behrooz S, Sarkhosh H, Nourany M (2022) A novel multi-functional model thermoset and PDA-coated PU nanocomposite based on graphene and an amphiphilic block copolymer. Polym Adv Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5703
Bershtein VA, David L, Egorov VM et al (2005) Structural/compositional nanoheterogeneity and glass-transition plurality in amorphous polycyanurate–poly(tetramethylene glycol) hybrid networks. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 43:3261–3272. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.20614
Bouaziz R, Roger F, Prashantha K (2017) Thermo-mechanical modeling of semi-crystalline thermoplastic shape memory polymer under large strain. Smart Mater Struct 26:55009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/aa6690
Cao F, Jana SC (2007) Nanoclay-tethered shape memory polyurethane nanocomposites. Polymer (Guildf) 48:3790–3800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.04.027
Castillo RV, Müller AJ (2009) Crystallization and morphology of biodegradable or biostable single and double crystalline block copolymers. Prog Polym Sci 34:516–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.03.002
Chen H-L, Hsiao S-C, Lin T-L et al (2001) Microdomain-tailored crystallization kinetics of block copolymers. Macromolecules 34:671–674. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma001485e
Chen S, Hu J, Zhuo H et al (2010) Study on the thermal-induced shape memory effect of pyridine containing supramolecular polyurethane. Polymer (Guildf) 51:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.11.034
Choi JT, Dao TD, Oh KM et al (2012) Shape memory polyurethane nanocomposites with functionalized graphene. Smart Mater Struct 21:75017. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/21/7/075017
Domingues RMA, Gomes ME, Reis RL (2014) The potential of cellulose nanocrystals in tissue engineering strategies. Biomacromolecules 15:2327–2346. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm500524s
Du H, Liu W, Zhang M et al (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym 209:130–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.020
Du W, Zhang Z, Yin C et al (2021) Preparation of shape memory polyurethane/modified cellulose nanocrystals composites with balanced comprehensive performances. Polym Adv Technol 32:4710–4720. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5464
Fortunati E, Luzi F, Janke A et al (2017) Reinforcement effect of cellulose nanocrystals in thermoplastic polyurethane matrices characterized by different soft/hard segment ratio. Polym Eng Sci 57:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24532
Gao Y, Liu W, Zhu S (2018) Reversible shape memory polymer from semicrystalline poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) with dynamic covalent polymer networks. Macromolecules 51:8956–8963. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b01724
Garle A, Kong S, Ojha U, Budhlall BM (2012) Thermoresponsive semicrystalline poly(ε-caprolactone) networks: exploiting cross-linking with cinnamoyl moieties to design polymers with tunable shape memory. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:645
George J, Sabapathi SN (2015) Cellulose nanocrystals: synthesis, functional properties, and applications. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 8:45–54. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSA.S64386
Goodarzi K, Rao SS (2021) Hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels to study cancer cell behaviors. J Mater Chem B 9:6103–6115. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TB00963J
Goodarzi K, Jonidi Shariatzadeh F, Solouk A et al (2020) Injectable drug loaded gelatin based scaffolds as minimally invasive approach for drug delivery system: CNC/PAMAM nanoparticles. Eur Polym J 139:109992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109992
Gupta A, Mekonnen TH (2022) Cellulose nanocrystals enabled sustainable polycaprolactone based shape memory polyurethane bionanocomposites. J Colloid Interface Sci 611:726–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.174
Ha Y, Kim Y-O, Ahn S et al (2019) Robust and stretchable self-healing polyurethane based on polycarbonate diol with different soft-segment molecular weight for flexible devices. Eur Polym J 118:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.031
He W-N, Xu J-T (2012) Crystallization assisted self-assembly of semicrystalline block copolymers. Prog Polym Sci 37:1350–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2012.05.002
Hoidy WH, Al-Mulla EAJ, Al-Janabi KW (2010) Mechanical and thermal properties of PLLA/PCL modified clay nanocomposites. J Polym Environ 18:608–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0240-x
Jafari S, Nourany M, Zakizadeh M et al (2020) The effect of controlled phase separation of PEG/PCL-2000 homopolymer polyols using their PCL500-PEG1000-PCL500 tri-block copolymer and CNCs in the final polyurethane hydrogels on their shape memory behavior. Compos Commun 19:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.03.016
Jiang S, Ji X, An L, Jiang B (2001) Crystallization behavior of PCL in hybrid confined environment. Polymer (Guildf) 42:3901–3907. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00565-6
Jiu H, Jiao H, Zhang L et al (2016) Graphene-crosslinked two-way reversible shape memory polyurethane nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27:10720–10728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5173-2
Joo Y-S, Cha J-R, Gong M-S (2018) Biodegradable shape-memory polymers using polycaprolactone and isosorbide based polyurethane blends. Mater Sci Eng C 91:426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.05.063
Kausar A (2019) Shape memory polyurethane/graphene nanocomposites: Structures, properties, and applications. J Plast Film Sheeting 36:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1177/8756087919865296
Khadivi P, Salami-Kalajahi M, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Lotfi Mayan Sofla R (2019) Fabrication of microphase-separated polyurethane/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites with irregular mechanical and shape memory properties. Appl Phys A 125:779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3082-y
Kolesov I, Dolynchuk O, Radusch HJ (2015) Shape-memory behavior of cross-linked semi-crystalline polymers and their blends. Express Polym Lett 9:255–276. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2015.24
Kumar TP, Saravanakumar S, Sankaranarayanan K (2011) Effect of annealing on the surface and band gap alignment of CdZnS thin films. Appl Surf Sci 257:1923–1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.09.027
Kumar Patel K, Purohit R (2018) Future Prospects of shape memory polymer nano-composite and epoxy based shape memory polymer—a review. Mater Today Proc 5:20193–20200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.389
Lahiji RR, Xu X, Reifenberger R et al (2010) Atomic force microscopy characterization of cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 26:4480–4488. https://doi.org/10.1021/la903111j
Landa M, Canales J, Fernández M et al (2014) Effect of MWCNTs and graphene on the crystallization of polyurethane based nanocomposites, analyzed via calorimetry, rheology and AFM microscopy. Polym Test 35:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.03.008
Li M, Guan Q, Dingemans TJ (2018) High-temperature shape memory behavior of semicrystalline polyamide thermosets. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:19106–19115. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b03658
Liu Y, Li Y, Yang G et al (2015) Multi-stimulus-responsive shape-memory polymer nanocomposite network cross-linked by cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5081056
Lu P, Hsieh Y-L (2010) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr Polym 82:329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.073
Luyt AS, Gasmi S (2016) Influence of blending and blend morphology on the thermal properties and crystallization behaviour of PLA and PCL in PLA/PCL blends. J Mater Sci 51:4670–4681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9784-z
Mariano M, El Kissi N, Dufresne A (2014) Cellulose nanocrystals and related nanocomposites: review of some properties and challenges. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 52:791–806. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.23490
Mi H-Y, Jing X, Yilmaz G et al (2018) In situ synthesis of polyurethane scaffolds with tunable properties by controlled crosslinking of tri-block copolymer and polycaprolactone triol for tissue regeneration. Chem Eng J 348:786–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.198
Mu R, Hong X, Ni Y et al (2019) Recent trends and applications of cellulose nanocrystals in food industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 93:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.09.013
Müller AJ, Balsamo V, Arnal ML et al (2002) Homogeneous nucleation and fractionated crystallization in block copolymers. Macromolecules 35:3048–3058. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma012026w
Nessi V, Falourd X, Maigret J-E et al (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals-starch nanocomposites produced by extrusion: structure and behavior in physiological conditions. Carbohydr Polym 225:115123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115123
Nojima S, Yamamoto S, Ashida T (1995) Crystallization of block copolymers IV. Molecular weight dependence of the morphology formed in ε-caprolactone–butadiene diblock copolymers. Polym J 27:673–682. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.27.673
Noormohammadi F, Nourany M, Mir Mohamad Sadeghi G et al (2021b) The role of cellulose nanowhiskers in controlling phase segregation, crystallization and thermal stimuli responsiveness in PCL-PEGx-PCL block copolymer-based PU for human tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr Polym 252:117219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117219
Nourany M, Ghelichkhani S, Sarkhosh H et al (2021) The effect of PCL/PEG ABA block lengths on the crystallization of homo/block-based polyurethane/CNW nanocomposites. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02376-y
Park SH, Oh KW, Kim SH (2013) Reinforcement effect of cellulose nanowhisker on bio-based polyurethane. Compos Sci Technol 86:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.07.006
Parnell S, Min K, Cakmak M (2003) Kinetic studies of polyurethane polymerization with Raman spectroscopy. Polymer (Guildf) 44:5137–5144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(03)00468-3
Pei Z, Yu Z, Li M et al (2021) Self-healing and toughness cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposite hydrogels for strain-sensitive wearable flexible sensor. Int J Biol Macromol 179:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.023
Prataviera R, Pollet E, Bretas RES et al (2018) Nanocomposites based on renewable thermoplastic polyurethane and chemically modified cellulose nanocrystals with improved mechanical properties. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46736. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46736
Qu Q, He J, Da Y et al (2021) High toughness polyurethane toward artificial muscles, tuned by mixing dynamic hard domains. Macromolecules 54:8243–8254. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.1c01098
Ranjbar HA, Nourany M, Mollavali M et al (2021) Stimuli-responsive polyurethane bionanocomposites of poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(ε-caprolactone) and [poly(ε-caprolactone)-grafted-] cellulose nanocrystals. Polym Adv Technol 32:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5062
Reid MS, Villalobos M, Cranston ED (2017) Benchmarking cellulose nanocrystals: from the laboratory to industrial production. Langmuir 33:1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03765
Roman M, Dong S, Hirani A, Lee YW (2009) Cellulose nanocrystals for drug delivery. In: Edgar KJ, Heinze T, Buchanan CM (eds) Polysaccharide materials: performance by design. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 4–81
Rueda L, Saralegui A, Fernández d’Arlas B et al (2013) Cellulose nanocrystals/polyurethane nanocomposites. Study from the viewpoint of microphase separated structure. Carbohydr Polym 92:751–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.093
SaifulAzry SOA, Chuah TG, Paridah MT et al (2021) Influence of cellulose II polymorph nanowhiskers on bio-based nanocomposite film from Jatropha oil polyurethane. Mater Res Express 8:15003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abc6ce
Saralegi A, Fernandes SCM, Alonso-Varona A et al (2013) Shape-memory bionanocomposites based on chitin nanocrystals and thermoplastic polyurethane with a highly crystalline soft segment. Biomacromol 14:4475–4482. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm401385c
Sarkhosh H, Nourany M, Noormohammadi F et al (2021) Development of a semi-crystalline hybrid polyurethane nanocomposites for hMSCs cell culture and evaluation of body-temperature shape memory performance and isothermal crystallization kinetics. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02522-0
Scetta G, Ju J, Selles N et al (2021) Strain induced strengthening of soft thermoplastic polyurethanes under cyclic deformation. J Polym Sci 59:685–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.20210060
Shirole A, Nicharat A, Perotto CU, Weder C (2018) Tailoring the properties of a shape-memory polyurethane via nanocomposite formation and nucleation. Macromolecules 51:1841–1849. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.7b01728
Stribeck N, Li X, Kogut I et al (2015) Morphological failure mechanisms in tensile tests of crosslinked polyurethanes with poorly developed domain structure. Macromol Mater Eng 300:699–711. https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201500007
Tang J, Sisler J, Grishkewich N, Tam KC (2017) Functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals for advanced applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:397–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.01.077
Tian D, Wang F, Yang Z et al (2019) High-performance polyurethane nanocomposites based on UPy-modified cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr Polym 219:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.029
Tingaut P, Zimmermann T, Sèbe G (2012) Cellulose nanocrystals and microfibrillated cellulose as building blocks for the design of hierarchical functional materials. J Mater Chem 22:20105–20111. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32956E
Tito NB, Creton C, Storm C, Ellenbroek WG (2019) Harnessing entropy to enhance toughness in reversibly crosslinked polymer networks. Soft Matter 15:2190–2203. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM02577K
Trache D, Hussin MH, Haafiz MKM, Thakur VK (2017) Recent progress in cellulose nanocrystals: sources and production. Nanoscale 9:1763–1786. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR09494E
Urbina L, Alonso-Varona A, Saralegi A et al (2019) Hybrid and biocompatible cellulose/polyurethane nanocomposites with water-activated shape memory properties. Carbohydr Polym 216:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.010
Vanderfleet OM, Cranston ED (2021) Production routes to tailor the performance of cellulose nanocrystals. Nat Rev Mater 6:124–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-00239-y
Vilgis T, Halperin A (1991) Aggregation of coil-crystalline block copolymers: equilibrium crystallization. Macromolecules 24:2090–2095. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00008a058
Vorov OK, Livesay DR, Jacobs DJ (2008) Conformational entropy of an ideal cross-linking polymer chain. Entropy. https://doi.org/10.3390/e10030285
Wang Y-J, Jeng U-S, Hsu S (2018a) Biodegradable water-based polyurethane shape memory elastomers for bone tissue engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:1397–1406. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00091
Wang Y, Cheng Z, Liu Z et al (2018b) Cellulose nanofibers/polyurethane shape memory composites with fast water-responsivity. J Mater Chem B 6:1668–1677. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB03069J
Wu XL, Kang SF, Xu XJ et al (2014) Effect of the crosslinking density and programming temperature on the shape fixity and shape recovery in epoxy–anhydride shape-memory polymers. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40559
Wu H, Xie H, Tian X et al (2021) Hard, tough and fast self-healing thermoplastic polyurethane. Prog Org Coat 159:106409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106409
Xiang N, Zhang X, Zheng M et al (2021) Investigation of tensile behavior and molecular structure of the thermoplastic polyurethane sheets injection molded at different mold temperatures. J Appl Polym Sci 138:50959. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50959
Xie H, Du H, Yang X, Si C (2018) Recent strategies in preparation of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils derived from raw cellulose materials. Int J Polym Sci 2018:7923068. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7923068
Yu K, Ge Q, Qi HJ (2014) Reduced time as a unified parameter determining fixity and free recovery of shape memory polymers. Nat Commun 5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4066
Zakizadeh M, Nourany M, Javadzadeh M et al (2021) Analysis of crystallization kinetics and shape memory performance of peg-pcl/mwcnt based pu nanocomposite for tissue engineering applications. Express Polym Lett 15:418–432. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2021.36
Zare M, Prabhakaran MP, Parvin N, Ramakrishna S (2019) Thermally-induced two-way shape memory polymers: mechanisms, structures, and applications. Chem Eng J 374:706–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.167
Zeng H, Sun H, Gu J (2021) Modeling the one-way and two-way shape memory effects of semi-crystalline polymers. Smart Mater Struct 30:95020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/ac179e
Zhang K, Zhao Z, Huang J et al (2019a) Self-recoverable semi-crystalline hydrogels with thermomechanics and shape memory performance. Sci China Mater 62:586–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-018-9347-5
Zhang Y, Hu J, Zhao X et al (2019b) Mechanically robust shape memory polyurethane nanocomposites for minimally invasive bone repair. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2:1056–1065. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.8b00655
Zhou J, Turner SA, Brosnan SM et al (2014) Shapeshifting: reversible shape memory in semicrystalline elastomers. Macromolecules 47:1768–1776. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma4023185
Zhuravlev E, Schmelzer JWP, Wunderlich B, Schick C (2011) Kinetics of nucleation and crystallization in poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL). Polymer (Guildf) 52:1983–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2011.03.013
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Seyed Sadi Hosseini for his insightful comments on the cytotoxicity analysis.
Funding
This work was partially funded by Amirkabir University of Technology and the grant number is not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EA: Data acquisition, data validation, formal analysis, writing the original draft; MAM, SB, FN: Data validation, formal analysis, editing the original draft; YRD: Data acquisition, formal analysis; MN: Conceptualization, data validation, writing the original draft, funding and grant acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aboueimehrizi, E., Makaremy, M.A., Bazrpash, S. et al. Synthesis of high-modulus thermoset PUs of PCL-PTMG/CNW biomaterials with different soft domain architecture and composition for high shape memory performance. Cellulose 29, 8651–8674 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04796-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04796-z