Abstract
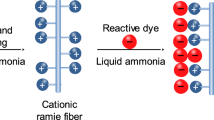
A modification procedure for ramie fiber using 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride (CHPTAC) as a cationic agent and NaOH as a catalyst was developed in this paper. The morphological and structural transformations of the fiber induced by modification were determined by XRD (XRD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and thermogravimetry analysis (TGA). XRD results show that the crystal structure of the modified fiber was still preserved although its crystallinity was decreased, which was confirmed from the TGA results. The mechanisms for the modification and dyeing of ramie fiber were analyzed, and the optimum modification conditions were determined to be the CHPTAC concentration of 30 g L−1, the NaOH concentration of 15 g L−1, the reaction temperature of 50 °C, and the reaction time of 60 min. The raw and the modified fibers were dyed with C.I. reactive red 2. The K/S values for the cationic modified fiber increased to be three times as high as the unmodified fiber. The dye uptakes increased greatly with an increase in the nitrogen contents up to 0.4% on the modified fibers.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- TGA:
-
Thermogravimetry analysis
- CHPTAC:
-
3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride
References
Brant DA, Goebel KD (1972) Evidence for the occurrence of flexible sugar ring conformers in cellulosic chains. Macromolecules 5:536–538
Broadbent AD, Thérien N, Zhao YF (1998) Comparison of the thermal fixation of reactive dyes on cotton using infrared radiation or hot air. Ind Eng Chem Res 37:1781–1785
Cai SY, Tian T (eds) (2004) Study on the technology of dyeing and finishing. Textile Press, China, pp 154–155
Chen HZ, Jin SY (2006) Effect of ethanol and yeast on cellulase activity and hydrolysis of crystalline cellulose. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:1430–1432
Goda K, Sreekala MS, Gomes A, Kaji T, Ohgi J (2006) Improvement of plant based natural fibers of toughening green composites–Efeect of load application during mercerization of ramie fibers. Composites Part A. 37:2213–2220
Hashem M, Refaie R, Hebeish A (2005) Crosslinking of partially carboxymethylated cotton fabric via cationization. J Clean Prod 13:947–954
Hill CAS, Abdul Khalil HPS, Hale MD (1998) A study of the potential of acetylation to improve the properties of plant fibers. Ind Crop Prod 8:53–63
Hu X, Wei WS, Wu WD, Zhou X (1996) A Study on cation modification of ramie (II)–modification process (in Chinese). Dyeing Finishing 22(4):5–8
Jin YA, Geng QY, Hu XM (2004) Modification of ramie fiber. Wool Text J 53–55
Koroskenyi B, McCarthy SP (2001) Synthesis of acetylated konjac glucomannan and effect of degree of acetylation on water absorbency. Biomacromolecules 2:824–826
Laguardia L, Vassallo E, Cappitelli F, Mesto E, Cremona A, Sorlini C, Bonizzoni G (2005) Investigation of the effects of plasma treatments on biodeteriorated ancient paper. Appl Surf Sci 252:1159–1166
Lei W, Lei WG, Ren C (2006) Effect of volume fraction of ramie cloth on physical and mechanical properties of ramie cloth/UP resin composite. T Nonferr Metals Soc 16:474–477
Lewis DM, Mcilroy KA (1997) Chemical modification of cellulosic fibers to enhance dyeability. Rev Prog Coloration 27:5–17
Lewis DM, Yao J (2002) The effect of various anti-setting systems in wool dyeing. Part 2: Sodium maleate based system. Coloration Technol 118:181–184
Liu FH, Liang XN, Zhang NG, Huang YS Zhang SW (2001) Effect of growth regulators on yield and fiber quality in ramie (Boemheria nivea (L.) Guad.), China grass. Field Crop Res 69:41–46
Liu SF, Zhang XL, Wang Q (2005) Cationic modification and dyeing of ramie (in Chinese). Wool Text J 12:24–28
Liu Z-T, Zhang LL, Liu Z-W, Gao ZW, Dong WS, Xiong HP, Peng YD, Tang SW (2006) Supercritical CO2 dyeing of ramie fiber with disperse dye. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:8932–8938
Mormann W, Michel U (2002) Hydrocelluloses with low degree of polymerisation from liquid ammonia treated cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 50:349–353
Petru L, Gray DG, BeMiller JN (1995) Homogeneous alkylation of cellulose in lithium chloride/dimethyl sulfoxide solvent with dimsyl sodium activation. A proposal for the mechanism of cellulose dissolution in LiCl/Me2SO. Carbohydr Res 268:319–323
Samios E, Dart RK, Dawkins JV (1997) Preparation, characterization and biodegradation studies on cellulose acetates with varying degrees of substitution. Polymer 38:3045–3054
Shin H, Ueda M, Burkinshaw SM (1999) New methods of obtaining patterned dyeing on cellulosic fibers with anionic dyes: photo-modification using a methacryloyl quaternary ammonium compound. Dyes Pigment 41:11–17
Tam KY, Smith ER, Booth J, Compton RG, Brennan CM, Atherton JH (1997) Kinetics and mechanism of dyeing processes: the dyeing of cotton fabrics with a procion blue dichlorotriazinyl reactive dye. J Colloid Interface Sci 186:387–398
Wang DJ (1999) The mechanism of chemical modification of ramie fiber (in Chinese). Bast Text Technol 22:13–16
Wu WD, Wei WS, Hu S, Zhou X (1996) A study on cationic modification of ramie (IV)-dyeing behavior of modified ramie (in Chinese). Dyeing Finishing 22 (6):5–10
Yao YY, Zhu PX, Chen M, Wu YR, Wu DC (2005) Purification of a kind of soluble dye by nanofiltration (in Chinese). J Sichuan Univ 37:67–70
Yin CY, Li JB, Xu Q, Peng Q, Liu YB, Shen XY (2006) Chemical modification of cotton cellulose in supercritical carbon dioxide: synthesis and characterization of cellulose carbamate. Carbohydr Polym 67:147–154
Zhong AH, Luo JY, Kang CZ (1998) Study on the dye property of cationic modified ramie fiber (in Chinese). GuangXi Text Sci Technol 27:14–17
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Special Project of National Grand Fundamental Research Pre-973 Program of China (Program/Grant No. 2004CCA00700). We are also appreciated the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 20473051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, ZT., Yang, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Study on the cationic modification and dyeing of ramie fiber. Cellulose 14, 337–345 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9117-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9117-0