Abstract
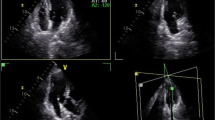
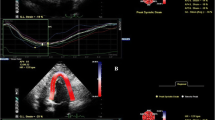
To investigate two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging (2D-STI)-based quantitative evaluation of the influences of different levels of coronary artery stenosis on left ventricular functions and its clinical diagnostic values, 120 patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) were divided into control group (30 cases), mild stenosis group (30 cases), moderate stenosis group (30 cases), and severe stenosis group (30 cases) according to coronary angiography (CAG) results. They underwent routine ultrasound examination and 2D-STI examination. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were drawn to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of different levels of coronary artery stenosis. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) of left ventricular myocardium among patients in moderate and severe stenosis groups remarkably declined (P < 0.05). Global radial strain (GRS) and global circular strain (GCS) among patients in severe stenosis group dramatically reduced (P < 0.05). ROC curves revealed that available GLS=-17.2 was the cut-off value for screening moderate coronary stenosis. The sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) amounted to 57.3%, 58.4%, and 0.573, respectively. GLS, GRS, and GCS could be used to screen severe coronary stenosis. When GLS=-16.5 was the cut-off value for screening severe coronary stenosis, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC amounted to 84.3%, 82.5%, and 0.893, respectively. With the aggravation of stenosis, left ventricular systolic function of CHD patients was impaired more significantly. 2D-STI technique could be adopted for the quantitative evaluation of left ventricular strain of patients with coronary stenosis and provided a new method for early clinical diagnosis of CHD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Y, Wang L, Song B (2022) Correlation between degenerative aortic valve Disease and severity of coronary artery damage in Coronary Heart Disease. ActaMedicaMediterrane; 1649
Wang P, Dong P, Yang X (2016) ANRIL rs2383207 polymorphism and coronary artery Disease (CAD) risk: a meta-analysis with observational studies. Cell MolBiol (Noisy-le-grand) 62(12):6–10
Cybulska B, Kłosiewicz-Latoszek L (2019) Landmark studies in coronary Heart Disease epidemiology. The Framingham Heart Study after 70 years and the Seven Countries Study after 60 years. KardiolPol 77(2):173–180
Nichols S, McGregor G, Breckon J, Ingle L (2021) Current insights into Exercise-based Cardiac Rehabilitation in patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Chronic Heart Failure. Int J Sports Med 42(1):19–26
Houston M (2018) The role of noninvasive cardiovascular testing, applied clinical nutrition and nutritional supplements in the prevention and treatment of coronary Heart Disease. TherAdvCardiovasc Dis 12(3):85–108
Lao XQ, Liu X, Deng HB, Chan TC, Ho KF, Wang F, Vermeulen R, Tam T, Wong MCS, Tse LA, Chang LY, Yeoh EK (2018) Sleep Quality, Sleep Duration, and the risk of Coronary Heart Disease: a prospective cohort study with 60,586 adults. J Clin Sleep Med 14(1):109–117
Saadatagah S, Pasha AK, Alhalabi L, Sandhyavenu H, Farwati M, Smith CY, Wood-Wentz CM, Bailey KR, Kullo IJ (2021) Coronary Heart Disease Risk Associated with primary isolated hypertriglyceridemia; a Population-based study. J Am Heart Assoc 10(11):e019343
Han X, Zhu W, Chen W (2021) Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and systolic function in patients with coronary Heart Disease by myocardial contrast echocardiography and 2-dimensional speckle tracking imaging. Zhong Nan Da XueXueBao Yi 46(11):1233–1240 English, Chinese
Xing X, Li D, Chen S, Wang L, Li Z, He L (2020) Evaluation of left ventricular systolic function in patients with different types of Ischemic Heart Disease by two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging. J CardiothoracSurg 15(1):325
Wang H, Tong M, Mu J, Wu T, Ruan L (2021) Assessment of myocardial function by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with Kawasaki Disease: a mid-term follow-up study. Coron Artery Dis 32(6):500–508
Zhu H, Yang C, Li Y, Guo Y, Meng X, Ren Y, Tan L, Zhang R, Wang F (2021) Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography identifies coronary artery Disease in 690 patients: a retrospective study from a single Center. Med SciMonit 27:e929476
d’Entremont MA, Fortin G, Huynh T, Croteau É, Farand P, Lemaire-Paquette S, Brochu MC, Do DH, Lepage S, Mampuya WM, Couture ÉL, Nguyen M, Essadiqi B (2021) The feasibility, reliability, and incremental value of two-dimensional speckle-tracking for the detection of significant coronary stenosis after treadmill stress echocardiography. 19(1):27
Moustafa S, Elrabat K, Swailem F, Galal A The correlation between speckle tracking echocardiography and coronary artery Disease in patients with suspected stable Angina Pectoris. Indian Heart J2018 May-Jun ;70(3):379–386
Giridharan S, Karthikeyan S, Aashish A, Ganesh BA, Prasath PA, Usha P (2021) Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography derived post systolic shortening in patients with unstable angina and normal left ventricular systolic function. Anatol J Cardiol 25(12):880–886
Yu T, Cui H, Chang W, Li Y, Cui X, Li G (2022) Real-time three-dimensional echocardiography and two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging in the evaluation of left atrial function in patients with triple-vessel coronary artery Disease without Myocardial Infarction. J ClinUltrasound 50(4):445–454
Hagemann RA, Hoffmann S, Brainin P, Hagemann CA, Fritz-Hansen T, Olsen FJ, Møgelvang R, Biering-Sørensen T (2020) Early diastolic strain rate by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography is a predictor of coronary artery Disease and cardiovascular events in stable Angina Pectoris. Int J CardiovascImaging 36(7):1249–1260
Mahjoob MP, AlipourParsa S, Mazarei A, Safi M, Khaheshi I, Esmaeeli S (2018) Rest 2D speckle tracking echocardiography may be a sensitive but nonspecific test for detection of significant coronary artery Disease. Acta Biomed 88(4):457–461
Villelabeitia-Jaureguizar K, Vicente-Campos D, BerenguelSenen A, Hernández Jiménez V, Ruiz Bautista L, Barrios Garrido-Lestache ME, LópezChicharro J (2019) Mechanical efficiency of high versus moderate intensity aerobic exercise in coronary Heart Disease patients: a randomized clinical trial. 26(2):130–137CardiolJ
Kowalczyk E, Kasprzak JD, Wejner-Mik P, Wdowiak-Okrojek K, Lipiec P (2019) Diagnostic utility of two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography to identify ischemic etiology of left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Echocardiography 36(4):702–706
Marques-Alves P, Espírito-Santo N, Baptista R, Teixeira R, Martins R, Gonçalves F, Pego M (2018) Two-dimensional speckle-tracking global longitudinal strain in high-sensitivity troponin-negative low-risk patients with unstable angina: a resting ischemia test? Int J CardiovascImaging 34(4):561–568
CalvilhoJúnior AA, Assef JE, Le Bihan D, Barretto RBM, PaladinoFilho AT, Abizaid AAC, Braga SLN, Vilela AA, Pedra SRFF, de Jesus CA (2019) E/e` ratio is superior to speckle tracking for detecting elevated left ventricular end-diastolic pressure in patients with coronary artery Disease and preserved ejection fraction. Echocardiography 36(7):1263–1272
Wang H, Shang J, Tong M, Song Y, Ruan L (2019) Evaluation of left ventricular function in immunoglobulin-resistant children with Kawasaki Disease: a two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography study. 42(8):753–759
Wang P, Liu Y, Ren L (2019) Evaluation of left ventricular function after percutaneous recanalization of chronic coronary occlusions: the role of two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Herz 44(2):170–174
Nishi T, Funabashi N, Ozawa K, Nishi T, Kamata T, Fujimoto Y, Kobayashi Y (2019) Regional layer-specific longitudinal peak systolic strain using exercise stress two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography for the detection of functionally significant coronary artery Disease. Heart Vessels 34(8):1394–1403
Hu J, Zheng Q, Ren W (2022) Evaluation of left ventricular myocardial stratified strain in patients with Kawasaki Disease using two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging. Front CardiovascMed 9:899945
Scharrenbroich J, Hamada S, Keszei A, Schröder J, Napp A, Almalla M, Becker M, Altiok E (2018) Use of two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography to predict cardiac events: comparison of patients with acute Myocardial Infarction and chronic coronary artery Disease. 41(1):111–118
Sharma JB, Deora S, Choudhary R, Kaushik A (2021) Comparison of mitral annular displacement and global longitudinal strain imaging for predicting significant coronary atherosclerotic Disease in patients of chronic stable Angina Pectoris. Int J CardiovascImaging 37(3):861–870
Hadadi M, Mohseni-Badalabadi R, Hosseinsabet A (2022) Effects of obesity on left atrial phasic functions in patients with chronic Ischemic Heart Disease and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction without recent Myocardial Infarction: a two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography study. J Ultrasound 25(3):521–527
Meng S, Qiu L, Wu J, Huang R, Wang H (2021) Two-year left ventricular systolic function of percutaneous coronary intervention vs optimal medical therapy for patients with single coronary chronic total occlusion. Echocardiography 38(2):368–373
Kozuma A, Asanuma T, Masuda K, Adachi H, Minami S, Nakatani S (2019) Assessment of myocardial ischemic memory using three-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography: a Novel Integrated Analysis of Early Systolic Lengthening and Postsystolic Shortening. J Am SocEchocardiogr 32(11):1477–1486
Raslan M, Elkhashab KA, Mousa MG, Alghamdi YA, Ghareb HS (2022) A comparison between two-dimensional and three-Dimensional Regional and Global Longitudinal strain Echocardiography to Evaluate Complex Coronary lesions in patients with Non-ST-Segment elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome. Cureus 14(4):e24025
Atici A, Barman HA, Durmaz E, Demir K, Cakmak R, Tugrul S, Elitok A, Onur İ, Sahin İ, Oncul A (2019) Predictive value of global and territorial longitudinal strain imaging in detecting significant coronary artery Disease in patients with Myocardial Infarction without persistent ST-segment elevation. Echocardiography 36(3):512–520
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Feiou Zhou: Research plan and write manuscript Hong Yuan: data collectionJindong Sun: analysisHongmei Ran: literature studyHong Pan: resultsPeian Wu: conclusionQian Yang: review paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, F., Yuan, H., Sun, J. et al. Two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging cardiac motion-based quantitative evaluation of global longitudinal strain among patients with coronary Heart Disease and functions of left ventricular ischemic myocardial segment. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 40, 351–359 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-023-02993-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-023-02993-w