Abstract
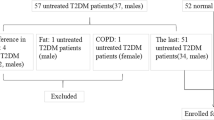
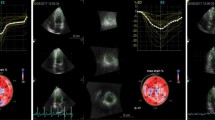
Three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (3D-STE) was used to evaluate the improvement of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on the left ventricular (LV) systolic function of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitu (T2DM). We recruited T2DM patients (38 cases, diabetic group) and healthy volunteers (35 cases, control group) to collect LV full volume imaging. TomTec software was used for calculating LV global longitudinal strain (LVGLS), global circumferential strain (LVGCS), peak twist (LVTW), peak apical rotation (LVPAR), ejection fraction (LVEF), and torsion (LVT). All indices were re-tested 2 weeks later after intensive treatment of insulin pump. LVGLS, LVGCS, LVTW and LVPAR in diabetic group were significantly decreased than control group. LVGLS and LVGCS in pre-treatment diabetic group were significantly increased than post-treatment. LVGLS, LVGCS, LVTW and LVPAR had correlations among control, pre-treatment and post-treatment diabetic groups. There were no significant differences in LVEDV, LVESV, LVEF, LVT and R-R. LV systolic function of patients with T2DM complicated with microangiopathy was improved after treatment of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. In addition, therapeutic effect could be accurately evaluated by 3D-STE which had vital clinical application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamed SA (2017) Brain injury with diabetes mellitus: evidence, mechanisms and treatment implications. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 10(4):409–428
Yokomichi H et al (2017) Survival of macrovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic respiratory disease, cancer and smoking in patients with type 2 diabetes: BioBank Japan cohort. J Epidemiol 27(3 s):S98-s106
Careyva B, Stello B (2016) Diabetes mellitus: management of gastrointestinal complications. Am Fam Phys 94(12):980–986
Al Rawahi AH et al (2017) Cardiovascular disease Incidence and risk factor patterns among Omanis with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Oman Med J 32(2):106–114
Kocyigit D et al (2017) Anti-hyperglycemic agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: role in cardioprotection during the last decade. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 17:19–31
Dickson-Humphries T, Bottenberg B, Kuntz S (2013) Lipoprotein abnormalities in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. JAAPA 26(7):13–18
Ernande L et al (2011) Diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: is it really the first marker of diabetic cardiomyopathy? J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24(11):1268–1275
Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Abreu-Gonzalez P, Avanzas P (2014) Usefulness of growth differentiation factor-15 levels to predict diabetic cardiomyopathy in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 114(6):890–894
Leung M et al (2015) Left ventricular diastolic reserve in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Open Heart 2(1):e000214
Lamy A et al (2014) Cost implications of the use of basal insulin glargine in people with early dysglycemia: the ORIGIN trial. J Diabetes Complicat 28(4):553–558
Fredersdorf S et al (2012) Increased myocardial SERCA expression in early type 2 diabetes mellitus is insulin dependent: in vivo and in vitro data. Cardiovasc Diabetol 11:57
Urbano-Moral JA et al (2012) Three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography: methodological aspects and clinical potential. Echocardiography 29(8):997–1010
Nesser HJ et al (2009) Quantification of left ventricular volumes using three-dimensional echocardiographic speckle tracking: comparison with MRI. Eur Heart J 30(13):1565–1573
Tadic M et al (2015) Left Ventricular mechanics in untreated normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a two- and three-dimensional speckle tracking study. Echocardiography 32(6):947–955
Boudina S, Abel ED (2010) Diabetic cardiomyopathy, causes and effects. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 11(1):31–39
Zoungas S et al (2017) Effects of intensive glucose control on microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 5:431–437
Klein LJ, Visser FC (2010) The effect of insulin on the heart. Part 1: effects on metabolism and function. Neth Heart J 18(4):197–201
Schulten RJ et al (2016) Lower dose basal insulin infusion has positive effect on glycaemic control for children with type I diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy. Pediatr Diabetes 18(1):45–50
Weng J et al (2008) Effect of intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet 371(9626):1753–1760
Meneghini L, Sparrow-Bodenmiller J (2010) Practical aspects and considerations when switching between continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion and multiple daily injections. Diabetes Technol Ther 12(Suppl 1):S109-14
Tang X et al (2017) Left ventricular myocardial strain in ventricular arrhythmia without structural heart disease using cardiac magnetic resonance. Am J Transl Res 9(6):3006–3016
Cheng N et al (2017) The improvement of torsion assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking after coronary artery bypass grafting: a sensitive index of cardiac function. Heart Surg Forum 20(1):E026-e031
Shang Q et al (2017) Assessment of ventriculo-vascular properties in repaired coarctation using cardiac magnetic resonance-derived aortic, left atrial and left ventricular strain. Eur Radiol 27(1):167–177
Gayat E et al (2011) Reproducibility and inter-vendor variability of left ventricular deformation measurements by three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24(8):878–885
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Hx., Zhou, Xl., Kou, Hj. et al. Improvement of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion on patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by 3-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 34, 379–384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1245-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-017-1245-5