Abstract
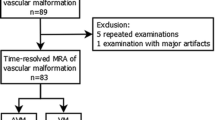
To evaluate the feasibility and diagnostic impact of time-resolved MR angiography (TR-MRA) combined with parallel imaging and low contrast dose for the assessment of peripheral high-flow vascular malformations (VM) at 1.5 Tesla (T). Twelve consecutive patients (7 female, 5 male, mean age 24.7 ± 11.1 years) with known or suspected high-flow VM underwent time-resolved MRA. Two readers individually assessed image quality, diagnostic confidence as well as hemodynamic features. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) correlation was available in 9 patients. TR-MRA provided a comprehensive assessment of all VMs with good quality images, allowing reliable differentiation of the early and main arterial phases and of at least the early venous phase. Based on hemodynamic features VM were classified as predominantly arterial malformations in 5 cases (42%), or arteriovenous malformations in the remaining 7 cases (58%). The high-flow component of a VM was confirmed by DSA in 9/9 (100%) cases during the interventional treatment procedure. TR-MRA of peripheral VMs with temporal interpolation and stochastic spiral trajectories is feasible, allowing the assessment of dynamic inflow and vessel-specific information similar to conventional DSA. Therefore, TR-MRA represents a reasonable alternative imaging technique for the pre-treatment evaluation of high-flow VMs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubois J, Alison M (2010) Vascular anomalies: what a radiologist needs to know. Pediatr Radiol 40:895–905
Finn MC, Glowacki J, Mulliken JB (1983) Congenital vascular lesions: clinical application of a new classification. J Pediatr Surg 18:894–900
Garzon MC, Huang JT, Enjolras O et al (2007) Vascular malformations: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 56:353–370
Legiehn GM, Heran MK (2008) Venous malformations: classification, development, diagnosis, and interventional radiologic management. Radiol Clin North Am 46:545–597
Meyer JS, Hoffer FA, Barnes PD et al (1991) Biological classification of soft-tissue vascular anomalies: MR correlation. AJR 157:559–564
Kim YH, Choi JY, Kim YW et al (2009) Characterization of congenital vascular malformation in the extremities using whole body blood pool scintigraphy and lymphscintigraphy. Lymphology 42:77–84
Lee BB, Laredo J, Lee SJ et al (2007) Congenital vascular malformations: general diagnostic principles. Phlebology 22:253–257
Elsharawy MA, Moghazy KM (2007) Surgical and endovascular management of arteriovenous malformation: case series from a single center. Vascular 15:134–140
van Rijswijk CS, van der Linden E, van der Woude HJ et al (2002) Value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging in diagnosing and classifying peripheral vascular malformations. AJR 178:1181–1187
Fayad LM, Hazirolan T, Bluemke D et al (2006) Vascular malformations in the extremities: emphasis on MR imaging features that guide treatment options. Skeletal Radiol 35:127–137
Rinker B, Karp NS, Margiotta M et al (2003) The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the management of vascular malformations of the trunk and extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:504–510
Moukaddam H, Pollak J, Haims AH (2009) MRI characteristics and classification of peripheral vascular malformations and tumors. Skeletal Radiol 38:535–547
Cornfeld D, Mojibian H (2009) Clinical uses of time-resolved imaging in the body and peripheral vascular system. AJR 193:W546–W557
Mulliken JB, Glowacki J (1982) Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: a classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast Reconstr Surg 69:412–422
Korosec FR, Frayne R, Grist TM et al (1996) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography. Magn Reson Med 36:345–351
Pinto C, Hickey R, Carroll TJ et al (2006) Time-resolved MR angiography with generalized auto calibrating partially parallel acquisition and time-resolved echo-sharing angiographic technique for hemodialysis arteriovenous fistulas and grafts. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:1003–1009
Swan JS, Carroll TJ, Kennell TW et al (2002) Time-resolved three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the peripheral vessels. Radiology 225:43–52
Mende KA, Froehlich JM, von Weymarn C et al (2007) Time-resolved, high-resolution contrast-enhanced MR angiography of dialysis shunts using the CENTRA keyhole technique with parallel imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:832–840
Gauvrit JY, Law M, Xu J et al (2007) Time-resolved MR angiography: optimal parallel imaging method. AJNR 28:835–838
Kohout MP, Hansen M, Pribaz JJ, Mulliken JB (1998) Arteriovenous malformations of the head and neck: natural history and management. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:643–654
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM et al (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kramer, U., Ernemann, U., Mangold, S. et al. Diagnostic value of high spatial and temporal resolution time-resolved MR angiography in the workup of peripheral high-flow vascular malformations at 1.5 Tesla. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28, 823–834 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-9887-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-011-9887-1