Abstract
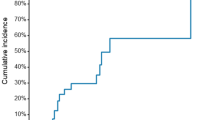
Despite the undeniable contribution of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) to assess drug-eluting stent (DES) effectiveness, the way these image modalities correlate to each other and to target-lesion revascularization (TLR) after PCI, is yet to be established. Thus we sought to evaluate whether there is an acceptable correlation between QCA and IVUS after DES implantation. We analyzed 204 pts treated with DES: Zotarolimus- (126), Sirolimus- (57), and Biolimus (31) with baseline and follow-up QCA and IVUS. The correlation between QCA lumen loss (LL) and intimal hyperplasia (IH) volume obstruction by IVUS was assessed by multiple regression analysis. Two QCA parameters (in-segment diameter stenosis and in-segment LL) and one IVUS variable (in-stent volume of IH) were evaluated as quantitative surrogates of 6 month TLR. The receiver operating characteristic method with c-statistics was used to assess the ability of each surrogate endpoint to predict TLR. QCA LL correlated positively with IVUS IH volume of obstruction (r = 0.69; CI95% 0.61–0.75: P < 0.0001), independent of DES type. The 2 QCA parameters were superior to the IVUS parameter as surrogates for TLR. Of note, QCA LL (c = 0.99) correlated best with TLR, even better than percent DS. In the DES era there is a good correlation between QCA measured LL and IVUS IH volume and therefore can be used as a surrogate of DES efficacy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffmann R, Mintz GS, Dussaillant GR, Popma JJ, Pichard AD, Satler LF, Kent KM, Griffin J, Leon MB (1996) Patterns and mechanisms of in-stent restenosis. A serial intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation 94(6):1247–1254
Dussaillant GR, Mintz GS, Pichard AD, Kent KM, Satler LF, Popma JJ, Wong SC, Leon MB (1995) Small stent size and intimal hyperplasia contribute to restenosis: a volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 26(3):720–724. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(95)00249-4
Mintz GS, Hong MK, Raizner AE, Lee CW, Kim JJ, Escolar E, Fearnot NE, Park SW, Park SJ, Weissman NJ (2005) Comparison of quantitative angiographic parameters with the magnitude of neointimal hyperplasia measured by volumetric intravascular ultrasound in patients treated with bare metal and nonpolymeric paclitaxel-coated stents. Am J Cardiol 95(1):105–107. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.08.071
Carlier S, Tanaka K (2006) Studying coronary plaque regression with IVUS: a critical review of recent studies. J Interv Cardiol 19:11–15. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8183.2006.00098.x
Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, Fajadet J, Ban Hayashi E, Perin M, Colombo A, Schuler G, Barragan P, Guagliumi G, Molnàr F, Falotico R, RAVEL Study Group (2002) Randomized study with the sirolimus-coated Bx velocity balloon-expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions. N Engl J Med 346(23):1773–1780. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012843
Grube E, Hauptmann KE, Buellesfeld L, Lim V, Abizaid A (2005) Six-month results of a randomized study to evaluate safety and efficacy of a Biolimus A9 eluting stent with a biodegradable polymer coating. EuroInterv 1:53–57
e LI, de Costa JR, Abizaid AA, Feres F, Tanajura LF, Staico R, Abizaid AA, Beraldo P, Sousa AM, Sousa JE (2007) A three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound comparison between the new zotarolimus-eluting stent (ZoMaxx™) and the non-drug-eluting TriMaxx™ stent. J Invasive Cardiol 19:303–308
Mintz GS, Nissen SE, Anderson WD, Bailey SR, Erbel R, Fitzgerald PJ, Pinto FJ, Rosenfield K, Siegel RJ, Tuzcu EM, Yock PG (2001) American college of cardiology clinical expert consensus document on standards for acquisition, measurement and reporting of intravascular ultrasound studies (IVUS). A report of the American college of cardiology task force on clinical expert consensus documents. J Am Coll Cardiol 37:1478–1492. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01175-5
Mauri L, Orav EJ, Kuntz R (2005) Late loss in lumen diameter and binary restenosis for drug-eluting stent comparison. Circulation 111:3435–3442. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.513952
Mauri L, Orav EJ, Candia S, Cutlip D, Kuntz R (2005) Robustness of late lumen loss in discriminating drug-eluting stents across variable observational and randomized trials. Circulation 112:2833–2839. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA105.570093
Mauri L, Orav EJ, O’Malley AJ, Moses JW, Leon MB, Holmes DR Jr, Teirstein PS, Schofer J, Breithardt G, Cutlip DE, Kereiakes DJ, Shi C, Firth BG, Donohoe DJ, Kuntz RE (2005) Relationship of late loss in lumen diameter to coronary restenosis in sirolimus-eluting stents. Circulation 111:321–327. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000153356.72810.97
Mehran R, Mintz GS, Hong MK, Tio FO, Bramwell O, Brahimi A, Kent KM, Pichard AD, Satler LF, Popma JJ, Leon MB (1998) Validation of the in vivo intravascular ultrasound measurement of in-stent neointimal hyperplasia volumes. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:794–799. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(98)00316-7
Colombo A, Drzewiecki J, Banning A, Grube E, Hauptmann K, Silber S, Dudek D, Fort S, Schiele F, Zmudka K, Guagliumi G, Russell ME (2003) TAXUS II Study Group. Randomized study to assess the effectiveness of slow- and moderate-release polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stents for coronary artery lesions. Circulation 108:788–794. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000086926.62288.A6
Park SJ, Shim WH, Ho DS, Raizner AE, Park SW, Hong MK, Lee CW, Choi D, Jang Y, Lam R, Weissman NJ, Mintz GS (2003) A paclitaxel-eluting stent for the prevention of coronary restenosis. N Engl J Med 348:1537–1545. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021007
Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, Song JM, Han KH, Kang DH, Song JK, Kim JJ, Weissman NJ, Fearnot NE, Park SW, Park SJ (2003) Asian paclitaxel-eluting stent clinical trial. Paclitaxel coating reduces in-stent intimal hyperplasia in human coronary arteries: a serial volumetric intravascular ultrasound analysis from ASPECT. Circulation 107:517–520. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000054163.42072.D4
Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, Hermiller J, O’Shaughnessy C, Mann JT, Turco M, Caputo R, Bergin P, Greenberg J, Popma JJ, Russell ME (2004) TAXUS-IV investigators. A polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 350:221–231. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasave, L.I., Costa, J.R., Costa, R. et al. Correlation between quantitative angiographic and intravascular ultrasound parameters in patients treated with sirolimus analogous-eluting stents. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 25, 345–351 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-009-9431-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-009-9431-8