Abstract
Background
This study was conducted to collect clinical safety, tolerability, and efficacy data with the use of everolimus (EVE) combined with exemestane (EXE) in patients with advanced breast cancer (ABC).
Methods
The EVEREXES trial initiated in 2012, provided early access to the first dual blockade treatment with EVE + EXE in patients with HR+, HER2 − ABC in Asia and other emerging growth countries. Postmenopausal women with HR+, HER2 − ABC who had documented recurrence or progression, following a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor therapy, were treated with EVE (10 mg/day) + EXE (25 mg/day) orally.
Results
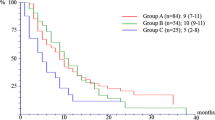
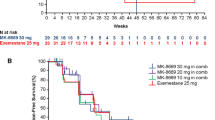
A total of 235 patients received ≥ 1 dose of study medication. At the end of the study, all patients ceased the treatment. Disease progression (66.0%) was the primary reason of discontinuation. The most common AEs (≥ 20%) were stomatitis, decreased appetite, hyperglycemia, rash, aspartate aminotransferase increased, anemia, alanine aminotransferase increased, cough, and fatigue. No new safety concerns were identified in the current study. Median progression-free survival (PFS) in the Asian subset was similar to that of the overall population (9.3 months in both groups). Confirmed overall response rate (ORR) was achieved for 19.6% of the patients. Efficacy of EVE + EXE across subgroups (prior CT, line of treatment, and presence of visceral metastases) was maintained.
Conclusion
The safety and efficacy results from EVEREXES trial are consistent to data previously reported in BOLERO-2. These results support that EVE + EXE could be a viable treatment option for the postmenopausal women with HR+, HER2 − ABC in Asian region.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Breast cancer, early diagnosis and screening (2020) https://www.who.int/cancer/prevention/diagnosis-screening/breast-cancer/en/. Accessed 6 Nov 2020
Yeo W, Ueno T, Lin CH, Liu Q, Lee KH, Leung R, Naito Y, Park YH, Im SA, Li H, Yap YS, Lu YS (2019) Treating HR+/HER2- breast cancer in premenopausal Asian women: Asian breast cancer cooperative group 2019 consensus and position on ovarian suppression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 177:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05318-5
El Saghir NS, Khalil MK, Eid T, El Kinge AR, Charafeddine M, Geara F, Seoud M, Shamseddine AI (2007) Trends in epidemiology and management of breast cancer in developing Arab countries: a literature and registry analysis. Int J Surg 5:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2006.06.015
Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Yip CH, Baade PD (2014) Incidence and mortality of female breast cancer in the Asia-Pacific region. Cancer Biol Med 11:101–115. https://doi.org/10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.005
Sammons S, Kornblum NS, Blackwell KL (2019) Fulvestrant-based combination therapy for second-line treatment of hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Target Oncol 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0587-9
Xie Y, Zhao Y, Gong C, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Yuan P, Hu S, Li Y, Hu X, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang B (2019) Treatment after progression on fulvestrant among metastatic breast cancer patients in clinical practice: a multicenter. Retrospective study. Sci Rep 9:1710. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37472-z
Beaver JA, Park BH (2012) The BOLERO-2 trial: the addition of everolimus to exemestane in the treatment of postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Future Oncol 8:651–657. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.12.49
Smith IE, Dowsett M (2003) Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 348:2431–2442. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra023246
Mouridsen H, Sun Y, Gershanovich M, Perez-Carrion R, Becquart D, Chaudri-Ross HA, Lang R (2004) Superiority of letrozole to tamoxifen in the first-line treatment of advanced breast cancer: evidence from metastatic subgroups and a test of functional ability. Oncologist 9:489–496. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.9-5-489
Nabholtz JM, Buzdar A, Pollak M, Harwin W, Burton G, Mangalik A, Steinberg M, Webster A, von Euler M (2000) Anastrozole is superior to tamoxifen as first-line therapy for advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women: results of a North American multicenter randomized trial. Arimidex study group. J Clin Oncol 18:3758–3767. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2000.18.22.3758
Bonneterre J, Thürlimann B, Robertson JF, Krzakowski M, Mauriac L, Koralewski P, Vergote I, Webster A, Steinberg M, von Euler M (2000) Anastrozole versus tamoxifen as first-line therapy for advanced breast cancer in 668 postmenopausal women: results of the tamoxifen or arimidex randomized group efficacy and tolerability study. J Clin Oncol 18:3748–3757. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2000.18.22.3748
Mauri D, Pavlidis N, Polyzos NP, Ioannidis JP (2006) Survival with aromatase inhibitors and inactivators versus standard hormonal therapy in advanced breast cancer: meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1285–1291. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djj357
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA 3rd, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F, Beck JT, Ito Y, Yardley D, Deleu I, Perez A, Bachelot T, Vittori L, Xu Z, Mukhopadhyay P, Lebwohl D, Hortobagyi GN (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1109653
Johnston SR (2010) New strategies in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:1979–1987. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-09-1823
NCCN guidelined for patients (2020) Breast cancer Metastatic. https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/content/PDF/stage_iv_breast-patient.pdf. Accessed Dec 2020
ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines (2020) Advanced Breast Cancer. 4th ESO–ESMO International Consensus Guidelines for Advanced Breast Cancer. https://www.esmo.org/content/download/181639/3308758/1/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines-Slideset-Advanced-Breast-Cancer.pdf. Accessed Dec 2020
Rossi V, Berchialla P, Giannarelli D, Nisticò C, Ferretti G, Gasparro S, Russillo M, Catania G, Vigna L, Mancusi RL, Bria E, Montemurro F, Cognetti F, Fabi A (2019) Should all patients with HR-positive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer receive CDK 4/6 inhibitor as first-line based therapy? A network meta-analysis of data from the PALOMA 2, MONALEESA 2, MONALEESA 7, MONARCH 3, FALCON SWOG and FACT trials. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111661
Shah AN, Metzger O, Bartlett CH, Liu Y, Huang X, Cristofanilli M (2020) Hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer in young women: emerging data in the era of molecularly targeted agents. Oncologist 25:e900–e908. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0729
Chia S, Gradishar W, Mauriac L, Bines J, Amant F, Federico M, Fein L, Romieu G, Buzdar A, Robertson JF, Brufsky A, Possinger K, Rennie P, Sapunar F, Lowe E, Piccart M (2008) Double-blind, randomized placebo controlled trial of fulvestrant compared with exemestane after prior nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor therapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer: results from EFECT. J Clin Oncol 26:1664–1670. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.13.5822
Di Leo A, Jerusalem G, Petruzelka L, Torres R, Bondarenko IN, Khasanov R, Verhoeven D, Pedrini JL, Smirnova I, Lichinitser MR, Pendergrass K, Garnett S, Lindemann JP, Sapunar F, Martin M (2010) Results of the CONFIRM phase III trial comparing fulvestrant 250 mg with fulvestrant 500 mg in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:4594–4600. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.28.8415
du Rusquec P, Blonz C, Frenel JS, Campone M (2020) Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in estrogen-receptor positive HER2 negative advanced breast cancer. Therapeutic Adv Med Oncol 12:1758835920940939. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920940939
Hortobagyi GN, Chen D, Piccart M, Rugo HS, Burris HA 3rd, Pritchard KI, Campone M, Noguchi S, Perez AT, Deleu I, Shtivelband M, Masuda N, Dakhil S, Anderson I, Robinson DM, He W, Garg A, McDonald ER 3rd, Bitter H, Huang A, Taran T, Bachelot T, Lebrun F, Lebwohl D, Baselga J (2016) Correlative analysis of genetic alterations and everolimus benefit in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: results from BOLERO-2. J Clin Oncol 34:419–426. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2014.60.1971
Yamnik RL, Holz MK (2010) mTOR/S6K1 and MAPK/RSK signaling pathways coordinately regulate estrogen receptor alpha serine 167 phosphorylation. FEBS Lett 584:124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.11.041
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10:331s–336s. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-031212
Rugo HS, Lerebours F, Ciruelos E, Drullinsky P, Borrego MR, Neven P, Park YH, Prat A, Bachelot T, Juric D, Turner NC, Sophos N, Zarate JP, Arce C, Shen Y-M, Chia SKL (2020) Alpelisib (ALP) + fulvestrant (FUL) in patients (pts) with PIK3CA-mutated (mut) hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2–) advanced breast cancer (ABC) previously treated with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor (CDKi) + aromatase inhibitor (AI): BYLieve study results. J Clin Oncol 38:1006–1006. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.1006
Lousberg L, Jerusalem G (2016) Safety, efficacy, and patient acceptability of everolimus in the treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer 10:239–252. https://doi.org/10.4137/bcbcr.s12443
Tancredi R, Furlanetto J, Loibl S (2018) Endocrine therapy in premenopausal hormone receptor positive/human epidermal growth receptor 2 negative metastatic breast cancer: between guidelines and literature. Oncologist 23:974–981. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0077
Jeong J, Kim JE, Ahn JH, Jung KH, Koh SJ, Cheon J, Sohn J, Kim GM, Lee KS, Park IH, Sim SH, Kim SB (2019) 311PD - Leuprorelin (LEUP) combined with Letrozole (LET) with/without everolimus (EVE) in ovarian suppressed premenopausal women with hormone receptor (HR) positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC): primary analysis of LEO trial (NCT02344550). Ann Oncol 30:v107. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz242.006
Rugo HS, Pritchard KI, Gnant M, Noguchi S, Piccart M, Hortobagyi G, Baselga J, Perez A, Geberth M, Csoszi T, Chouinard E, Srimuninnimit V, Puttawibul P, Eakle J, Feng W, Bauly H, El-Hashimy M, Taran T, Burris HA 3rd (2014) Incidence and time course of everolimus-related adverse events in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: insights from BOLERO-2. Annal Oncol 25:808–815. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu009
Rugo HS, Seneviratne L, Beck JT, Glaspy JA, Peguero JA, Pluard TJ, Dhillon N, Hwang LC, Nangia C, Mayer IA, Meiller TF, Chambers MS, Sweetman RW, Sabo JR, Litton JK (2017) Prevention of everolimus-related stomatitis in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer using dexamethasone mouthwash (SWISH): a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30109-2
Gomez HL, Castañeda C, Valencia F, Muñoz-Bermeo R, Torrico MDC, Neciosup S (2020) ABC4 consensus: first Latin American meeting-assessment, comments, and application of its recommendations. JCO Global Oncol 6:819–827. https://doi.org/10.1200/go.20.00081
Hortobagyi GN (2015) Everolimus plus exemestane for the treatment of advanced breast cancer: a review of subanalyses from BOLERO-2. Neoplasia 17:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2015.01.005
Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, Petrakova K, Bianchi GV, Esteva FJ, Martín M, Nusch A, Sonke GS, De la Cruz-Merino L, Beck JT, Pivot X, Sondhi M, Wang Y, Chakravartty A, Rodriguez-Lorenc K, Taran T, Jerusalem G (2020) Overall survival with ribociclib plus fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 382:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911149
Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, Petrakova K, Bianchi GV, Esteva FJ, Martin M, Nusch A, Sonke GS, De la Cruz-Merino L, Beck JT, Pivot X, Vidam G, Wang Y, Rodriguez Lorenc K, Miller M, Taran T, Jerusalem G (2018) Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin Oncol 36:2465–2472. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2018.78.9909
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, Koh H, Grischke EM, Frenzel M, Lin Y, Barriga S, Smith IC, Bourayou N, Llombart-Cussac A (2017) MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women With HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 35:2875–2884. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.73.7585
Sammons S, Shastry M, Dent S, Anders C, Hamilton E (2020) Practical treatment strategies and future directions after progression while receiving cdk4/6 inhibition and endocrine therapy in advanced HR(+)/HER2(-) breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 20:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2019.06.017
Cardoso F, Paluch-Shimon S, Senkus E, Curigliano G, Aapro MS, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya GS, Biganzoli L, Boyle F, Cardoso MJ, Carey LA, Cortés J, El Saghir NS, Elzayat M, Eniu A, Fallowfield L, Francis PA, Gelmon K, Gligorov J, Haidinger R, Harbeck N, Hu X, Kaufman B, Kaur R, Kiely BE, Kim SB, Lin NU, Mertz SA, Neciosup S, Offersen BV, Ohno S, Pagani O, Prat A, Penault-Llorca F, Rugo HS, Sledge GW, Thomssen C, Vorobiof DA, Wiseman T, Xu B, Norton L, Costa A, Winer EP (2020) 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5)(†). Annal Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.010
André F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, Iwata H, Conte P, Mayer IA, Kaufman B, Yamashita T, Lu YS, Inoue K, Takahashi M, Pápai Z, Longin AS, Mills D, Wilke C, Hirawat S, Juric D (2019) Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 380:1929–1940. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1813904
Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N, Colleoni M, DeMichele A, Loi S, Verma S, Iwata H, Harbeck N, Loibl S, André F, Puyana Theall K, Huang X, Giorgetti C, Huang Bartlett C, Cristofanilli M (2018) Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 379:1926–1936. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1810527
Acknowledgements
The EVEREXES trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03176238). Financial support for medical editorial assistance was provided by Novartis Pharmaceuticals. The authors thank the patients who have enrolled in this study and their families as well as all the participating investigators and their site teams. The authors also thank Arundhati Halder, PhD, and Susmita Bhattacharjee, MSc. Biotechnology, of Novartis Healthcare Pvt Ltd (Hyderabad, India) for providing medical editorial assistance in accordance with the Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines for the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
The EVEREXES trial was funded by Novartis Pharma AG, Base, Switzerland. Funding for medical editorial support was also provided by Novartis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YHI and SBK contributed to the concept, design, and conduct of the study and analysis and interpretation of the data. BK, KSL, BWP, AA, HYC, HAR, YCC, SA, SAI, JJ, YC, JB, KS, HX contributed to the study conduct. YHI, SBK, JB, KS and HX contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. All authors contributed to the development of the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
SA has received personal fees from Roche, Merck, Eli Lilly, Abdi Ibrahim AS, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, Mustafa Nevzat İlaç Sanayii. SBK has received grant from Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, Kyowa-Kirin Inc, Dongkook Pharm Co, others from Novartis, Personal fees from Astra-Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Enzychem, Dae Hwa Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, ISU Abix, and Daiichi-Sankyo. KSL has received personal fees from Roche, Novartis, Lilly and nonfinancial support from Dong-A Pharm. SAI has received grant from AstraZeneca, Roche, Pfizer, personal fees from Novartis, and others from Amgen, Eisai, Hanmi, and Novartis. JB, KS, and HX are Novartis employees. FR owns Novartis stocks. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval was obtained at each participating center for the collection of the data described in this report.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from each participant for inclusion in this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, YH., Karabulut, B., Lee, K.S. et al. Safety and efficacy of everolimus (EVE) plus exemestane (EXE) in postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: final results from EVEREXES. Breast Cancer Res Treat 188, 77–89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06173-z