Abstract
Purpose
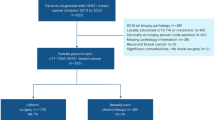
To analyze the prognostic role of pathologic confirmation of internal mammary lymph nodes (IMNs) for breast cancer patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods
Of the patients who were treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy between 2009 and 2013, 114 women had suspicious IMNs and FNAB was attempted. Clinical IMN metastasis was diagnosed by 18F-FDG PET/CT positivity or pathologic confirmation (N = 70). Patients were divided into the FNAB(+) or FNAB(−) IMN group.
Results
The pathologic confirmation rate was 57% (40 of 70 patients). Rates were 74% in US-positive, 70% in MRI-positive, and 55% in PET-positive patients. Nodal stage was cN2b (6%) or cN3b (94%). Five-year progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly worse in patients with FNAB(+) IMN metastasis than FNAB(−) IMN metastasis (61% vs. 87%, P = 0.03). FNAB(+) IMN patients showed worse distant metastasis and regional recurrence-free survival without statistical significance (69% vs. 86%, P = 0.06, and 81% vs. 96%, P = 0.06). With median follow-up of 50.5 months (13.0–97.0 months), overall survival at 5 years was 77%, and PFS was 72%.
Conclusions
Patients with FNAB-proven IMN metastasis had worse treatment outcomes compared to patients with clinically diagnosed IMN metastasis in cN2b/N3b breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sugg SL, Ferguson DJ, Posner MC, Heimann R (2000) Should internal mammary nodes be sampled in the sentinel lymph node era? Ann Surg Oncol 7(3):188–192
Cody HS 3rd, Urban JA (1995) Internal mammary node status: a major prognosticator in axillary node-negative breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2(1):32–37
Heuts EM, van der Ent FW, Hulsewe KW, von Meyenfeldt MF, Voogd AC (2009) Results of tailored treatment for breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph node metastases. Breast 18(4):254–258. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2009.05.003
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, Godwin J, Gray R, Hicks C, James S, MacKinnon E, McGale P, McHugh T, Peto R, Taylor C, Wang Y (2005) Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet (London, England) 366(9503):2087–2106. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67887-7
Vassallo P, Wernecke K, Roos N, Peters PE (1992) Differentiation of benign from malignant superficial lymphadenopathy: the role of high-resolution US. Radiology 183(1):215–220. doi:10.1148/radiology.183.1.1549675
Dihge L, Grabau DA, Rasmussen RW, Bendahl PO, Ryden L (2016) The accuracy of preoperative axillary nodal staging in primary breast cancer by ultrasound is modified by nodal metastatic load and tumor biology. Acta Oncol 55(8):976–982. doi:10.3109/0284186X.2016.1146826
Gradishar WJ, Anderson BO, Balassanian R, Blair SL, Burstein HJ, Cyr A, Elias AD, Farrar WB, Forero A, Giordano SH, Goetz M, Goldstein LJ, Hudis CA, Isakoff SJ, Marcom PK, Mayer IA, McCormick B, Moran M, Patel SA, Pierce LJ, Reed EC, Salerno KE, Schwartzberg LS, Smith KL, Smith ML, Soliman H, Somlo G, Telli M, Ward JH, Shead DA, Kumar R (2016) Invasive breast cancer version 1.2016, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw: JNCCN 14(3):324–354
van Wely BJ, de Wilt JH, Francissen C, Teerenstra S, Strobbe LJ (2015) Meta-analysis of ultrasound-guided biopsy of suspicious axillary lymph nodes in the selection of patients with extensive axillary tumour burden in breast cancer. Br J Surg 102(3):159–168. doi:10.1002/bjs.9663
Dings PJ, Elferink MA, Strobbe LJ, de Wilt JH (2013) The prognostic value of lymph node ratio in node-positive breast cancer: a Dutch nationwide population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol 20(8):2607–2614. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-2932-7
Woodward WA, Vinh-Hung V, Ueno NT, Cheng YC, Royce M, Tai P, Vlastos G, Wallace AM, Hortobagyi GN, Nieto Y (2006) Prognostic value of nodal ratios in node-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(18):2910–2916. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.1526
Eubank WB, Mankoff DA, Takasugi J, Vesselle H, Eary JF, Shanley TJ, Gralow JR, Charlop A, Ellis GK, Lindsley KL, Austin-Seymour MM, Funkhouser CP, Livingston RB (2001) 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to detect mediastinal or internal mammary metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 19(15):3516–3523. doi:10.1200/jco.2001.19.15.3516
Aukema TS, Straver ME, Peeters MJ, Russell NS, Gilhuijs KG, Vogel WV, Rutgers EJ, Olmos RA (2010) Detection of extra-axillary lymph node involvement with FDG PET/CT in patients with stage II-III breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 46(18):3205–3210. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.07.034
Seo MJ, Lee JJ, Kim HO, Chae SY, Park SH, Ryu JS, Ahn SH, Lee JW, Son BH, Gong GY, Moon DH (2014) Detection of internal mammary lymph node metastasis with (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with stage III breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 41(3):438–445. doi:10.1007/s00259-013-2600-y
Wang CL, Eissa MJ, Rogers JV, Aravkin AY, Porter BA, Beatty JD (2013) (18)F-FDG PET/CT-positive internal mammary lymph nodes: pathologic correlation by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and assessment of associated risk factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200(5):1138–1144. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.8754
Huang O, Wang L, Shen K, Lin H, Hu Z, Liu G, Wu J, Lu J, Shao Z, Han Q, Shen Z (2008) Breast cancer subpopulation with high risk of internal mammary lymph nodes metastasis: analysis of 2,269 Chinese breast cancer patients treated with extended radical mastectomy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 107(3):379–387. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9561-4
Veronesi U, Marubini E, Mariani L, Valagussa P, Zucali R (1999) The dissection of internal mammary nodes does not improve the survival of breast cancer patients. 30-year results of a randomised trial. Eur J Cancer 35(9):1320–1325
Coombs NJ, Boyages J, French JR, Ung OA (2009) Internal mammary sentinel nodes: ignore, irradiate or operate? Eur J Cancer 45(5):789–794. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.11.002
Tanis PJ, Nieweg OE, Valdes Olmos RA, Peterse JL, Rutgers EJ, Hoefnagel CA, Kroon BB (2002) Impact of non-axillary sentinel node biopsy on staging and treatment of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 87(7):705–710. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600359
Caudle AS, Yi M, Hoffman KE, Mittendorf EA, Babiera GV, Hwang RF, Meric-Bernstam F, Sahin AA, Hunt KK (2014) Impact of identification of internal mammary sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol 21(1):60–65. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3276-z
Zhang YJ, Oh JL, Whitman GJ, Iyengar P, Yu TK, Tereffe W, Woodward WA, Perkins G, Buchholz TA, Strom EA (2010) Clinically apparent internal mammary nodal metastasis in patients with advanced breast cancer: incidence and local control. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77(4):1113–1119. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.081
Park HJ, Shin KH, Cho KH, Park IH, Lee KS, Ro J, Jung SY, Lee S, Kim SW, Kang HS, Chie EK, Ha SW (2011) Outcomes of positron emission tomography-staged clinical N3 breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery, and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(5):e689–695. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.061
Author contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data for the work presented in this paper. All authors were involved in drafting the manuscript for scientific and intellectual content.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joo, J.H., Kim, S.S., Ahn, SD. et al. Impact of pathologic diagnosis of internal mammary lymph node metastasis in clinical N2b and N3b breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 166, 511–518 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4422-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4422-2