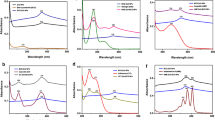
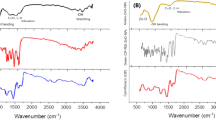
Abstract
The development of antibiotic alternatives that entail distinctive chemistry and modes of action is necessary due to the threat posed by drug resistance. Nanotechnology has gained increasing attention in recent years, as a vehicle to enhance the efficacy of existing antimicrobials. In this study, Chitosan copper oxide nanoparticles (CHI-CuO) were synthesized and were further loaded with Quercetagetin (QTG) to achieve the desired (CHI-CuO-QTG). Size distribution, zeta potential and morphological analysis were accomplished. Next, the developed CHI-CuO-QTG was assessed for synergistic antibacterial properties, as well as cytotoxic attributes. Bactericidal assays revealed that CHI-CuO conjugation showed remarkable effects and enhanced QTG effects against a range of Gram + ve and Gram − ve bacteria. The MIC50 of QTG against S. pyogenes was 107 µg/mL while CHI-CuO-QTG reduced it to 9 µg/mL. Similar results were observed when tested against S. pneumoniae. Likewise, the MIC50 of QTG against S. enterica was 38 µg/mL while CHI-CuO-QTG reduced it to 7 µg/mL. For E. coli K1, the MIC50 of QTG was 42 µg/mL while with CHI-CuO-QTG it was 23 µg/mL. Finally, the MIC50 of QTG against S. marcescens was 98 µg/mL while CHI-CuO-QTG reduced it to 10 µg/mL. Notably, the CHI-CuO-QTG nano-formulation showed limited damage when tested against human cells using lactate dehydrogenase release assays. Importantly, bacterial-mediated human cell damage was reduced by prior treatment of bacteria using drug nano-formulations. These findings are remarkable and clearly demonstrate that drug-nanoparticle formulations using nanotechnology is an important avenue in developing potential therapeutic interventions against microbial infections.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed M, Alhadlaq HA, Khan MM, Karuppiah P, Al-Dhabi NA (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2014:17–17
Akbar N, Khan NA, Sagathevan K, Iqbal M, Tawab A, Siddiqui R (2019) Gut bacteria of Cuora amboinensis (turtle) produce broad-spectrum antibacterial molecules. Sci Rep 9:1–19
Akbar N, Aslam Z, Siddiqui R, Shah MR, Khan NA (2021a) Zinc oxide nanoparticles conjugated with clinically-approved medicines as potential antibacterial molecules. AMB Exp 11(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-021-01261-1
Akbar N, Kawish M, Jabri T, Khan NA, Shah MR, Siddiqui R (2021b) Enhancing efficacy of existing antibacterials against selected multiple drug resistant bacteria using cinnamic acid-coated magnetic iron oxide and mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Pathogens and Global Health 116(7):438–454
Amiri M, Etemadifar Z, Daneshkazemi A, Nateghic M (2017) Antimicrobial effect of copper oxide nanoparticles on some oral bacteria and candida species. J Dent Biomater 4:347–352
Angelé-Martínez C, Nguyen KVT, Ameer FS, Anker JN, Brumaghim JL (2017) Reactive oxygen species generation by copper (II) oxide nanoparticles determined by DNA damage assays and EPR spectroscopy. Nanotoxicology 11(2):278–288
Anitha R, Ramesh KV, Ravishankar TN, Kumar KS, Ramakrishnappa T (2018) Cytotoxicity, antibacterial and antifungal activities of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the Artocarpus gomezianus fruit mediated facile green com- bustion method. J Sci Adv Mat Dev 3(4):440–451
Anwar A, Khalid S, Perveen S, Ahmed S, Siddiqui R, Khan NA, Shah MR (2018) Synthesis of 4-(dimethylamino) pyridine propylthioacetate coated gold nanoparticles and their antibacterial and photophysical activity. J Nano- Biotechnol 16(1):1–8
Baptista PV, Mccusker MP, Carvalho A, Ferreira DA, Mohan NM, Martins M et al (2018) Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria—” a battle of the titans”. Front Microbiol 9:1441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01441
Barabadi H, Webster TJ, Vahidi H, Sabori H, Kamali KD, Shoushtari FJ, Mahjoub MA, Rashedi M, Mostafavi E, Cruz DM, Hosseini O (2020) Green nanotechnology-based gold nanomaterials for hepatic cancer therapeutics: a systematic review. Iran J Pharm Res: IJPR 19(3):3
Baranwal A, Srivastava A, Kumar P, Bajpai VK, Maurya PK, Chandra P (2018) Prospects of nanostructure materials and their composites as antimicrobial agents. Front Microbiol 9:422. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00422
Barros CHN, Fulaz S, Stanisic D, Tasic L (2018) Biogenic nanosilver against multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDRB). Antibiotics (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics7030069
Blair JM, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO, Piddock LJ (2015) Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:42–51
Catalano A, Iacopetta D, Ceramella J, Scumaci D, Giuzio F, Saturnino C, Aquaro SR, Sinicropi C (2022) MS Multidrug Resistance (MDR): a widespread phenomenon in pharmacological therapies. Molecules 27:61
Chen J, Mao S, Xua Z, Ding W (2019) Various antibacterial mechanisms of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles against soilborne Ralstonia solanacearum. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09186B
Couvreur P, Fattal E, Andremont A (1991) Liposomes and nanoparticles in the treatment of intracellular bacterial infections. Pharm Res 8:1079–1086. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015885814417
Dubal D, Dhawale D, Salunkhe R, Jamdade V, Lokhande C (2010) Fabrication of copper oxide multilayer nanosheets for supercapacitor application. J Alloy Compd 492(1–2):26–30
Faizi S, Siddiqi H, Bano S, Naz A, Lubna Mazhar K, Nasim S, Riaz T, Kamal S, Ahmad A, Khan SA (2008) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of different parts of tagetes patula: preparation of patuletin derivatives. Pharmaceut Biol 46(5):309–320
Gopal A, Kant V, Gopalakrishnan A, TandanKumar SK (2014) D. Chitosan-based copper nanocomposite accelerates healing in excision wound model in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 731:8–19
Gupta A, Saleh NM, Das R, Landis RF, Bigdeli A, Motamedchaboki K et al (2017) Synergistic antimicrobial therapy using nanoparticles and antibiotics for the treatment of multidrug-resistant bacterial infection. Nano Futures 1:015004. https://doi.org/10.1088/2399-1984/aa69fb
Hajipour MJ, Saei AA, Walker ED, Conley B, Omidi Y, Lee K-B, Mahmoudi M (2021) Nanotechnology for targeted detection and removal of bacteria: opportunities and challenges. Adv Sci 8:2100556
Imran M, Shah MR, Ullah F, Ullah S, Elhissi AM, Nawaz W, Ahmad F, Sadiq A, Ali I (2016) Glycoside-based niosomal nanocarrier for enhanced in-vivo performance of Cefixime. Int J Pharm 505(1–2):122–132
Jadhav S, Gaikwad S, Nimse M, Rajbhoj A (2011) Copper oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and their antibacterial activity. J Cluster Sci 22:121–129
Kawish M, Elhissi A, Jabri T, Muhammad I, H, Zahid, M.R and Shah. (2020) Enhancement in oral absorption of ceftriaxone by highly functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 12(6):492
Khameneh B, Diab R, Ghazvini K, Bazzaz BSF (2016) Breakthroughs in bacterial resistance mechanisms and the potential ways to combat them. Microb Pathog 95:32–42
Kong Z-L, Kuo H-P, Johnson A, Li-Cyuan W, KeChang LB (2019) Curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles markedly enhanced cytotoxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(12):2918
Lee N-Y, Ko WC, Hsueh P-O (2019) Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Front Pharmaco 10:1153
Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM et al (2021) Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:101–124
Mukheem A, Muthoosamy K, Manickam S, Sudesh K, Shahabuddin S, Saidur R, Akbar N, Sridewi N (2018) Fabrication and characterization of an electrospun PHA/graphene silver nanocomposite scaffold for antibacterial applications. Materials 11(9):1673
Naser SS, Ghosh B, Simnani FZ, Singh D, Choudhury A, Nandi A, Sinha A, Jha E, Panda PK, Suar M, Verma SK (2023) Emerging trends in the application of green synthesized biocompatible ZnO nanoparticles for translational paradigm in cancer therapy. J Nanother 4(3):248–279
Nikaido H (2009) Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 78:119–146
Panda PK, Verma SK, Suar M (2021) Nanoparticle–biological interactions: the renaissance of bionomics in the myriad nanomedical technologies. Nanomedicine 16(25):2249–2254
Pelgrift RY, Friedman AJ (2013) Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1803–1815
Pereira do Amaral F, Napolitano A, Masullo M, Campaner dos Santos L, Festa M, Vilegas W, Pizza C, Piacente S (2012) HPLC-ESIMS n profiling, isolation, structural elucidation, and evaluation of the antioxidant potential of phenolics from Paepalanthus geniculatus. J Nat Prod 75(4):547–556
Phiwdang K, Suphankij S, Mekprasart S, Pecharapa W (2013) Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by precipitation method using different precursors. Energy Procedia 34:740–745
Ren G, Hu D, Cheng EW, Vargas-Reus MA, Reip P, Allaker RP (2009) Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int J Antimicrobial Agent 33:587–590
Saha B, Bhattacharya J, Mukherjee A, Ghosh A, Santra C, Dasgupta AK et al (2007) In vitro structural and functional evaluation of gold nanoparticles conjugated antibiotics. Nanoscale Res Lett 2:614–622
Seleem MN, Munusamy P, Ranjan A, Alqublan A, Pickrell G, Sriranganathan N (2009) Silica-Antibiotic Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeting Intracellular Pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00815-09
Somu P, Paul S (2018) Bio-conjugation of curcumin with self-assembled casein nanostructure via surface loading enhances its bioactivity: an efficient therapeutic system. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.094
Stewart M, Bartholomew B, Currie F, Abbiw D, Latif Z, Sarker S, Nash R (2000) Pyranoisoflavones from Rinorea welwitschii. Fitoterapia 71(5):595–597
Talank N, Morad H, Barabadi H, Mojab F, Amidi S, Kobarfard F, Mahjoub MA, Jounaki K, Mohammadi N, Salehi G, Ashrafizadeh M (2022) Bioengineering of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles: In vitro physicochemical, antibacterial, biofilm inhibitory, anticoagulant, and antioxidant performance. Talanta 243:123374
Ul Ain N, Anis I, Ahmed F, Shah MR, Parveen S, Faizi S, Ahmed S (2018) Colorimetric detection of amoxicillin based on querecetagetin coated silver nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B: Chem 265:617–624
Verma SK, Jha E, Panda PK, Thirumurugan A, Suar M (2019) Biological effects of green-synthesized metal nanoparticles: a mechanistic view of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity. In: Naushad Mu, Rajendran S, Gracia F (eds) Advanced nanostructured materials for environmental remediation. Springer
Wang W, Xu H, Chen H, Tai K, Liu F, Gao Y (2016) In vitro antioxidant, anti-diabetic and antilipemic potentials of quercetagetin extracted from marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) inflorescence residues. J Food Sci Technol 53:2614–2624
Wang L, Hu C, Shao L (2017) The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: pre- sent situation and prospects for the future. Int J Nanomed 12:1227
Yanat M, Schroën K (2021) Preparation methods and applications of chitosan nanoparticles; with an outlook toward reinforcement of biodegradable packaging. React Funct Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2021.104849
Yusof NAA, Zain NM, Pauzi N (2019) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles with chi- tosan as stabilizing agent and their antibacterial properties against Gram- positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Biol Macromol 124:1132–1136
Zazo H, Colino CI, Lanao JM (2016) Current applications of nanoparticles in infectious diseases. J Control Release 224:86–102
Funding
Ruqaiyyah Siddiqui and Naveed Ahmed Khan are supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS and NAK: conceptualized the study amid discussions with MRS and SA. AA, and NA: carried out all microbiology related work under the supervision of RS, NAK, and SA. BK, MK, AMA, HF and SF: carried out chemistry related work under the supervision of MRS. AA, RS, and MK analysed the data. AA and RS: prepared the first draft of the manuscript together with NAK and SA. BK, MK, SF, and MRS: corrected the manuscript. All authors agreed with the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alvi, A., Alqassim, S., Khan, N.A. et al. Antibacterial effects of quercetagetin are significantly enhanced upon conjugation with chitosan engineered copper oxide nanoparticles. Biometals 37, 171–184 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00539-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00539-0