Abstract
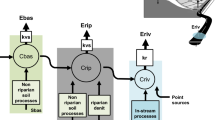
The relative contributions of different anthropogenic and natural sources of in-stream nitrogen (N) cannot be directly measured at whole-watershed scales. Hence, source attribution estimates beyond the scale of small catchments must rely on models. Although such estimates have been accomplished using individual models, there has not yet been a comparison of N source attribution predictions at large spatial scales. We compared results from two models applied to the continental US: Nutrient Export from WaterSheds (NEWS) and SPAtially Referenced Regressions On Watersheds (SPARROW). NEWS and SPARROW predictions for total N delivery to the US coastal zone were 373 and 429 kg N km−2 year−1, respectively, for the contemporary period. Despite differences in how inputs were represented and defined by the models, NEWS and SPARROW both identified the same single-largest N sources for 67 % of the surface area that drains to the US coastal zone. When only anthropogenic sources were considered, agreement increased to 78 % of surface area. Fertilizer and crop N-fixation were dominant in the Mississippi River Basin, where the bulk of agricultural lands are located. Sewage and population-related sources were most important in urban areas and natural N (primarily N-fixation on non-agricultural land) was most important in the Pacific Northwest. Attribution to fertilizer plus crop N-fixation, atmospheric deposition, and sewage and population-related sources was generally greater by SPARROW than NEWS, and the reverse was true for manure and natural sources. Nonetheless, both models agreed in attributing 62–81 % of N delivered to the coastal zone in the continental US to human activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcamo J, Van vuuren DP, Cramer W (2006) Changes in ecosystem services and their drivers across the scenarios. In: Carpenter SR (ed) Ecosystems and human well-being: scenarios. Island Press, Washington, DC, pp 279–354
Alexander RB, Johnes PJ, Boyer EW, Smith RA (2002) A comparison of models for estimating the riverine export of nitrogen from large watersheds. Biogeochemistry 57:295–339
Alexander RB, Smith RA, Schwarz GE, Boyer EW, Nolan JV, Brakebill JW (2008) Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River basin. Environ Sci Technol 42:822–830
Barnes RT, Raymond PA, Casciotti KL (2008) Dual isotope analyses indicate efficient processing of atmospheric nitrate by forested watersheds in the northeastern US. Biogeochemistry 90:15–27
Battaglin WA, Kendall C, Chang CCY, Silva SR, Campbell DH (2001) Isotopic and chemical composition of inorganic and organic water quality samples from the Mississippi River Basin, 1997–98. U.S. Geological Survey: Water-Resources Investigations Report 01-4095, Denver
Bouwman AF, Beusen AHW, Billen G (2009). Human alteration of the global nitrogen and phosphorus soil balances for the period 1970–2050. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23:GB0A04. doi:10.1029/2009GB003576
Boyer EW, Goodale CL, Jaworsk NA, Howarth RW (2002) Anthropogenic nitrogen sources and relationships to riverine nitrogen export in the northeastern USA. Biogeochemistry 57:137–169
Boyer EW, Alexander RB, Parton WJ, Li CS, Butterbach-Bahl K, Donner SD, Skaggs RW, Del Gross SJ (2006) Modeling denitrification in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems at regional scales. Ecol Appl 16:2123–2142
Bricker S, Longstaff B, Dennison W, Jones A, Boicourt K, Wicks C, Woerner J (2007) Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: a decade of change. NOAA Coastal Ocean Program, Decision Analysis Series No. 26. National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD
Carmichael RH, Hattenrath T, Valiela I, Michener RH (2008) Nitrogen stable isotopes in the shell of Mercenaria mercenaria trace wastewater inputs from watersheds to estuarine ecosystems. Aquat Biol 4:99–111
Castro MS, Driscoll CT, Jordan TE, Reay WG, Boynton WR, Seitzinger SP, Styles RV, Cable JM (2001) Contribution of atmospheric deposition to the total nitrogen loads to thirty-four estuaries on the Atlantic and Gulf Coasts of the United States. In: Valigura RA, Alexander RB, Castro MS, Meyers TP, Paerl HW, Stacey PE, Turner RE (eds) Nitrogen loading in coastal water bodies: an atmospheric perspective. American Geophysical Union
Castro MS, Driscoll CT, Jordan TE, Reay WG, Boynton WR (2003) Sources of nitrogen to estuaries in the United States. Estuaries 26:803–814
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Schimel DS, Fisher H, Howarth RW, Hedin LO, Perakis SS, Latty EF, Von Fischer JC, Elseroad A, Wasson MF (1999) Global patterns of terrestrial biological nitrogen (N2) fixation in natural ecosystems. Global Biogeochem Cycles 13:623–645
Compton JE, Church MR, Larned ST, Hogsett WE (2003) Nitrogen export from forested watersheds in the Oregon Coast Range: the role of N-2-fixing red alder. Ecosystems 6:773–785
Compton JE, Harrison JA, Dennis RL, Greaver TL, Hill BH, Jordan SJ, Walker H, Campbell HV (2011) Ecosystem services altered by human changes in the nitrogen cycle: a new perspective for US decision making. Ecol Lett 14:804–815
David MB, Drinkwater LE, McIsaac GF (2010) Sources of nitrate yield in the Mississippi River Basin. J Environ Qual 39:1657–1667
Davidson EA, David MB, Galloway JN, Goodale CL, Haeuber R, Harrison JA, Howarth RW, Jaynes DB, Lowrance RR, Nolan BT, Peel JL, Pinder RW, Porter E, Snyder CS, Townsend AR, Ward MH (2012) Excess nitrogen in the US environment: trends, risks, and solutions. Issues in Ecology
Dentener F, Stevenson D, Ellingsen K, van Noije T, Schultz M, Amann M, Atherton C, Bell N, Bergmann D, Bey I, Bouwman L, Butler T, Cofala J, Collins B, Drevet J, Doherty R, Eickhout B, Eskes H, Fiore A, Gauss M, Hauglustaine D, Horowitz L, Isaksen ISA, Josse B, Lawrence M, Krol M, Lamarque JF, Montanaro V, Muller JF, Peuch VH, Pitari G, Pyle J, Rast S, Rodriguez J, Sanderson M, Savage NH, Shindell D, Strahan S, Szopa S, Sudo K, Van Dingenen R, Wild O, Zeng G (2006) The global atmospheric environment for the next generation. Environ Sci Technol 40:3586–3594
Dodds WK, Bouska WW, Eitzmann JL, Pilger TJ, Pitts KL, Riley AJ, Schloesser JT, Thornbrugh DJ (2009) Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environ Sci Technol 43:12–19
Dumont E, Harrison J, Kroeze C, Bakker EJ, Seitzinger S (2005) Global distribution and sources of dissolved inorganic nitrogen export to the coastal zone: results from a spatially explicit, global model. Global Biogeochem Cycles 19:GB4S02. doi:10.1029/2005GB002488
Exbrayat J-F, Viney NR, Frede H-G, Breuer L (2011) Probabilistic multi-model ensemble predictions of nitrogen concentrations in river systems. Geophys Res Lett 38:L12401. doi:12410.11029/12011GL047522
Galloway JN, Aber JD, Erisman JW, Seitzinger SP, Howarth RW, Cowling EB, Cosby BJ (2003) The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 53:341–356
GeoLytics I (2000) Census 2000: demographic data and estimates
Goolsby DA, Battaglin WA, Aulenbach BT, Hooper RP (2000) Nitrogen flux and sources in the Mississippi River Basin. Sci Total Environ 248:75–86
Green PA, Vorosmarty CJ, Meybeck M, Galloway JN, Peterson BJ, Boyer EW (2004) Pre-industrial and contemporary fluxes of nitrogen through rivers: a global assessment based on typology. Biogeochemistry 68:71–105
Hejzlar J, Anthony S, Arheimer B, Behrendt H, Bouraoui F, Grizzetti B, Groenendijk P, Jeuken M, Johnsson H, Lo Porto A, Kronvang B, Panagopoulos Y, Siderius C, Silgram M, Venohr M, Zaloudik J (2009) Nitrogen and phosphorus retention in surface waters: an inter-comparison of predictions by catchment models of different complexity. J Environ Monit 11:584–593
Hoos AB, McMahon G (2009) Spatial analysis of instream nitrogen loads and factors controlling nitrogen delivery to streams in the southeastern United States using spatially referenced regression on watershed attributes (SPARROW) and regional classification frameworks. Hydrol Process 23:2275–2294
Houlton BZ, Wang YP, Vitousek PM, Field CB (2008) A unifying framework for dinitrogen fixation in the terrestrial biosphere. Nature 454:327–334
Howarth RW (2008) Coastal nitrogen pollution: a review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae 8:14–20
Howarth RW, Billen G, Swaney D, Townsend A, Jaworski N, Lajtha K, Downing JA, Elmgren R, Caraco N, Jordan T, Berendse F, Freney J, Kudeyarov V, Murdoch P, Zhu ZL (1996) Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N and P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 35:75–139
Howarth R, Swaney D, Billen G, Garnier J, Hong B, Humborg C, Johnes P, Mörth C-M, Marino R (2012) Nitrogen fluxes from the landscape are controlled by net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs and by climate. Front Ecol Environ 10:37–43
IFA/IFDC/FAO (2003) Fertilizer use by crop, 5th edn. International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC), and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome
Kellogg RL, Lander CH, Moffitt DC, Gollehon N (2000) Manure nutrients relative to the capacity of cropland and pastureland to assimilate nutrients: spatial and temporal trends for the U.S. USDA-NRCS Economic Research Service, Pub. No. nps00-0579. http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/land/pubs/manntr.html.
Latimer JS, Charpentier MA (2010) Nitrogen inputs to seventy-four southern New England estuaries: application of a watershed nitrogen loading model. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 89:125–136
Mayer B, Boyer EW, Goodale C, Jaworski NA, Van Breemen N, Howarth RW, Seitzinger S, Billen G, Lajtha LJ, Nosal M, Paustian K (2002) Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern US: isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 57:171–197
Mayorga E, Seitzinger S, Harrison AF, Dumont E, Beusen AHW, Bouwman AF, Fekete BM, Kroeze C, Van Drecht G (2010) Global nutrient export from watersheds 2 (NEWS 2): model development and implementation. Environ Model Softw. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2010.1001.1007
McIsaac GF, David MB, Gertner GZ, Goolsby DA (2002) Relation of net nitrogen input in the Mississippi River Basin to nitrate flux in the lower Mississippi River: a comparison of approaches. J Environ Qual 31:1610–1622
Moore RB, Johnston CM, Smith RA, Milstead B (2011) Source and delivery of nutrients to receiving waters in the Northeastern and mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. J Am Water Resour Assoc 47:965–990
NADP (1993) Annual data summary: precipitation chemistry in the United States 1983 to 1993. National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP), National Resources Ecology Laboratory, Colorado State University, Fort Collins
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models: a discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10:282–290
NASS (2002) Census of agriculture: census quick stats: Ag statistics for U.S., state, and county. National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS), U.S. Department of Agriculture
Pruell RJ, Taplin BK, Lake JL, Jayaraman S (2006) Nitrogen isotope ratios in estuarine biota collected along a nutrient gradient in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, USA. Mar Pollut Bull 52:612–620
Rebich RA, Houston NA, Mize SV, Pearson DK, Ging PB, Hornig CE (2011) Sources and delivery of nutrients to the northwestern Gulf of Mexico from streams in the south-central United States. J Am Water Resour Assoc 47:1061–1086
Ruddy BC, Lorenz DL, Muellwe DK (2006) County-level estimates of nutrient inputs to the land surface of the conterminous United States, 1982–2001. U.S. Geological Survey, Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5012
SAB (2011) Reactive nitrogen in the United States: an analysis of inputs, flows, consequences, and management options. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA-SAB-11-013
Schaefer SC, Hollibaugh JT, Alber M (2009) Watershed nitrogen input and riverine export on the west coast of the US. Biogeochemistry 93:219–233
Schlesinger WH (2009) On the fate of anthropogenic nitrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:203–208
Silva SR, Kendall C, Wilkison DH, Ziegler AC, Chang CCY, Avanzino RJ (2000) A new method for collection of nitrate from fresh water and the analysis of nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios. J Hydrol 228:22–36
Sobota DJ, Compton JE, Harrison JA, Neale AC (2013) Reactive nitrogen inputs to land and waterways in the United States: how certain are we about sources and fluxes? Front Ecol Environ. doi:10.1890/110216
Suddick EC, Davidson EA (2012) The role of nitrogen in climate change and the impacts of nitrogen-climate interactions on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, agriculture, and human health in the United States: a technical report submitted to the US National Climate Assessment. North American Nitrogen Center of the International Nitrogen Initiative (NANC-INI), Woods Hole Research Center, 149 Woods Hole Road, Falmouth, MA, 02540-1644 USA
Tebaldi C, Knutti R (2007) The use of the multi-model ensemble on probabilistic climate projections. Philos Trans R Soc A 365:2053–2075
Valiela I, Collins G, Kremer J, Lajtha K, Geist M, Seely B, Brawley J, Sham CH (1997) Nitrogen loading from coastal watersheds to receiving estuaries: new method and application. Ecol Appl 7:358–380
Valiela I, Geist M, McClelland J, Tomasky G (2000) Nitrogen loading from watersheds to estuaries: verification of the Waquoit Bay nitrogen loading model. Biogeochemistry 49:277–293
Valiela I, Bowen JL, Kroeger KD (2002) Assessment of models for estimation of land-derived nitrogen loads to shallow estuaries. Appl Geochem 17:935–953
Van Drecht G, Bouwman AF, Harrison J, Knoop JM (2009) Global nitrogen and phosphate in urban wastewater for the period 1970 to 2050. Global Biogeochem Cycles 23:GB0A03. 10.1029/2009GB003458
Vogelmann JE, Howard SM, Yang L, Larson CR, Wylie BK, Van Driel N (2001) Completion of the 1990’s National Land Cover Data Set for the conterminous United States from Landsat Thematic Mapper data and ancillary data sources. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 67:650–652
Vörösmarty C, Fekete B (2011) ISCSCP II River routing data (STN-30p). In: Hall FG, Collatz G, Meeson B, Los S, Brown de Colstoun E, Landis E (eds) ISLSCP initiative II collection. Available via http://daac.ornl.gov from Oak Ridge National Laboratory Distributed Active Archive Center, Oak Ridge
Whitall D, Hendrickson B, Paerl H (2003) Importance of atmospherically deposited nitrogen to the annual nitrogen budget of the Neuse River estuary, North Carolina. Environ Int 29:393–399
Whitall D, Castro M, Driscoll C (2004) Evaluation of management strategies for reducing nitrogen loadings to four US estuaries. Sci Total Environ 333:25–36
Wigand C, McKinney RA, Cole ML, Thursby GB, Cummings J (2007) Varying stable nitrogen isotope ratios of different coastal marsh plants and their relationships with wastewater nitrogen and land use in New England, USA. Environ Monit Assess 131:71–81
Wise DR, Johnson HM (2011) Surface-water nutrient concentrations and sources in the United States Pacific Northwest. J Am Water Resour Assoc 47:1110–1135
Acknowledgments
We thank Richard Smith for a helpful review of this manuscript and, along with Richard Alexander, for providing SPARROW data. Three anonymous reviewers provided comments that greatly improved this paper. The information in this document was funded by the National Academies of Science Research Associateship Program and the US Environmental Protection Agency. It has been subjected to review by the National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory’s Western Ecology Division and approved for publication. Approval does not signify that the contents reflect the views of the Agency, nor does mention of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement or recommendation for use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCrackin, M.L., Harrison, J.A. & Compton, J.E. A comparison of NEWS and SPARROW models to understand sources of nitrogen delivered to US coastal areas. Biogeochemistry 114, 281–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9809-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9809-x