Abstract
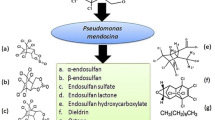
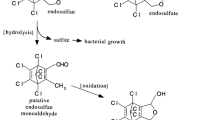
Endosulfan is one of the most widely used wide spectrum cyclodiene organochlorine insecticide. In environment, endosulfan can undergo either oxidation or hydrolysis reaction to form endosulfan sulfate and endosulfan diol respectively. Endosulfan sulfate is as toxic and as persistent as its parent isomers. In the present study, endosulfan degrading bacteria were isolated from soil through selective enrichment technique using sulfur free medium with endosulfan as sole sulfur source. Out of the 8 isolated bacterial strains, strain C8B was found to be the most efficient endosulfan degrader, degrading 94.12% α-endosulfan and 84.52% β-endosulfan. The bacterial strain was identified as Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B on the basis of 16S rDNA sequence similarity. Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B was also found to degrade 80.10% endosulfan sulfate using it as sulfur source. No known metabolites were found to be formed in the culture media during the entire course of degradation. Besides, the bacterial strain was found to degrade all the known endosulfan metabolites. There was marked increase in the quantity of released CO2 from the culture media with endosulfan as sulfur source as compared to MgSO4 suggesting that the bacterial strain, Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B probably degraded endosulfan completely through the formation of endosulfan ether.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awasthi N, Manickam N, Kumar A (1997) Biodegradation of endosulfan by a bacterial coculture. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:928–934. doi:10.1007/S001289900571
Dorough HW, Huhtanen K, Marshall TC, Bryant HE (1978) Fate of endosulfan in rats and toxicological considerations of apolar metabolites. Pestic Biochem Physiol 8:241–252
Goebel H, Gorbanch S, Khauf W (1982) Properties, effects, residues, and analytics of the insecticide endosulfan. Residue Rev 83:1–100
Goswami S, Singh DK (2009) Biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan in broth medium and soil microcosm by bacterial strain Bordetella sp. B9. Biodegradation 20:199–207. doi:10.1007/s10532-008-9213-3
Haney RL, Brinton WH, Evans E (2008) Estimating soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus mineralization from short-term carbon dioxide respiration. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:2706–2720. doi:10.1080/00103620802358862
Kate MS, Stephen ST, Martin A (1986) Kinetics of mineralization of organic compounds at low concentrations in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1028–1035
Kaur I, Mathur RP, Tandon SN, Dureja P (1998) Persistence of endosulfan (technical) in water and soil. Environ Technol 19:115–119. doi:10.1080/09593331908616663
Kumar M, Philip L (2006) Enrichment and isolation of a mixed bacterial culture for complete mineralization of endosulfan. J Environ Sci Health 41:81–96. doi:10.1080/10889860601021415
Kwon GS, Kim JE, Kim TK, Sohn HY, Koh SC, Shin KS, Kim DG (2002) Klebsiella pneumoniae KE-1 degrades endosulfan without formation of the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:255–259
Kwon GS, Sohn HY, Shin KS, Kim E, Seo BI (2005) Biodegradation of the organochlorine insecticide, endosulfan, and the toxic metabolite, endosulfan sulfate, by Klebsiella oxytoca KE-8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:845–850. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1879-9
Lee JB, Sohn HY, Shin KS, Jo MS, Kim JE, Lee SW, Shin JW, Kum EJ, Kwon GS (2006) Isolation of a soil bacterium capable of biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan and endosulfan sulphate. J Agric Food Chem 54:8824–8828. doi:10.1021/JF061276E
Martens R (1976) Degradation of [8, 9,-14C]endosulfan by soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:853–858
Rajendra M, Harishchandra K, Balasaheb D, Madhukar M, Rukmani K (2008) Thin layer chromatographic technique for detection and identification of endosulfan insecticide with m-dinitrobenzene reagent. J Planar Chromatogr 21:197–198. doi:10.1556/JPC.21.2008.3.8
Siddique T, Okeke BC, Arshad M, Frankenberger WT Jr (2003) Enrichment and isolation of endosulfan-degrading microorganisms. J Environ Qual 32:47–54
Sunlu FS, Kutlu B, Buyukisik HB (2010) Comparison of growth kinetics of Chaetoceros gracilis isolated from two different areas in the Aegean Sea (The Bay of Izmir and the Homa Lagoon). J Anim Vet Adv 9:1796–1803
Sutherland TD, Horne I, Lacey MJ, Harcourt RL, Russel RJ, Oakeshott JG (2000) Enrichment of an endosulfan degrading mixed bacterial culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2822–2828. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.7.2822-2828.2000
Sutherland TD, Weir KM, Lacey MJ, Horne I, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2002) Enrichment of a microbial culture capable of degrading endosulphate, the toxic metabolite of endosulfan. J Appl Microbiol 92:541–548
Van Woerden HF (1963) Organic sulfites. Chem Rev 63:557–571
Weir KM, Sutherland TD, Horne I, Russel RJ, Oakeshott JG (2006) A single monooxygenase, Ese, is involved in the metabolism of the organochlorides endosulfan and endosulfate in an Arthrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3524–3530. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.5.3524-3530.2006
Wen L, Yun D, Beibei X, Yingying L, Xiang P, Zhangg J, Yanchun Y (2009) Biodegradation and detoxification of endosulfan in aqueous medium and soil by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain CS5. J Hazard Mater 167:209–216. doi:10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2008.12.111
Acknowledgement
This work was partially supported by DBT research grant, sanction no. BT/PR5755/BCE/08/385/2005, which is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N.S., Singh, D.K. Biodegradation of endosulfan and endosulfan sulfate by Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain C8B in broth medium. Biodegradation 22, 845–857 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9442-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9442-0