Abstract
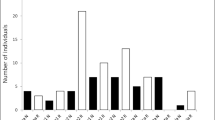
In aquatic ecosystems, impacts by invasive introduced fish can be likened to press disturbances that persistently influence communities. This study examined invasion disturbances by determining the relationship between non-native sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus and aquatic macroinvertebrates in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. A Multiple Before–After Control–Impact (MBACI) experimental design was used to examine macroinvertebrate communities within two rivers: one with catfish and another one without catfish. Within the invaded river, macroinvertebrates showed little response to catfish presence, whereas predator exclusion appeared to benefit community structure. This suggests that the macroinvertebrate community within the invaded river was adapted to predation impact because of the dominance of resilient taxa, such as Hirudinea, Oligochaeta and Chironomidae that were abundant in the Impact treatment relative to the Control treatment. High macroinvertebrate diversity and richness that was observed in the Control treatment, which excluded the predator, relative to the Impact treatment suggests predator avoidance behaviour within the invaded river. By comparison, within the uninvaded river, catfish introduction into the Impact treatment plots indicated negative effects on macroinvertebrate community that was reflected by decrease in diversity, richness and biomass. A community-level impact was also reflected in the multivariate analysis that indicated more variation in macroinvertebrate composition within the Impact treatment relative to the Control in the uninvaded river. Catfish impact within the uninvaded river suggests the dominance of vulnerable taxa, such as odonates that were less abundant in the Impact treatment plots after catfish introduction. From a disturbance perspective, this study revealed different macroinvertebrate responses to catfish impact, and suggests that within invaded habitats, macroinvertebrates were less responsive to catfish presence, whereas catfish introduction within uninvaded habitats demonstrated invasion impact that was shown by a decrease in the abundance of vulnerable taxa. The occurrence of non-native sharptooth catfish within many Eastern Cape rivers is a concern because of its predation impact and potential to influence trophic interrelationships, and efforts should be taken to protect uninvaded rivers, and, where possible, eradicate the invader.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abjornsson K, Hansson L, Bronmark C (2004) Responses of prey from habitats with different predator regimes: local adaptation and heritability. Ecology 85:1859–1866
Angeler DG, Moreno JM (2007) Zooplankton community resilience after press-type anthropogenic stress in temporary ponds. Ecol Appl 17:1105–1115
Beugly J, Pyron M (2010) Temporal and spatial variation in the long-term functional organization of fish assemblages in a large river. Hydrobiologia 654:215–226
Bruton MN (1979) The food and feeding behaviour of Clarias gariepinus (Pisces: Clariidae) in Lake Sibaya, South Africa, with emphasis on its role as a predator of cichlids. Trans Zool Soc Lon 35:47–114
Bruton MN (1988) Systematics and biology of clariid catfish. In: Hecht T, Uys W, Britz PJ (eds) The culture of sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus in southern Africa. South African National Scientific Program Report No 153, pp 1–10
Cambray JA, Jubb R (1977) Dispersal of fishes via the Orange-Fish Tunnel, South Africa. J Limnol Socof S Afr 3:33–35
Carlisle DM, Hawkins CP (1998) Relationships between invertebrate assemblage structure, 2 trout species, and habitat structure in Utah mountain lakes. J N Am Benthol Soc 17:286–300
Collier KJ, Quinn JM (2003) Land-use influences macroinvertebrate community response following a pulse disturbance. Freshw Biol 48:1462–1481
De Graaf G, Janssen H (1996) Artificial reproduction and pond rearing of the African catfish Clarias gariepinus in Sub-Saharan Africa—a handbook, vol 362. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, Rome
de Moor I, Bruton MN (1988) Atlas of alien and translocated indigenous aquatic animals in southern Africa. South African National Scientific Program Report No 144, CSIR, Pretoria, South Africa, pp 414–423
Donald DB, Anderson SR (2003) Resistance of the prey-to-predator ratio to environmental gradients and to biomanipulations. Ecology 84:2387–2394
Douglas PL, Forrester GE, Cooper SD (1994) Effects of trout on the diel periodicity of drifting in baetid mayflies. Oecologia 98:48–56
Downes BJ, Barmuta LA, Fairweather PG, Faith DP, Keough MJ, Lake PS, Mapstone BD, Quinn GP (2002) Monitoring ecological impacts: concepts and practice in flowing waters. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Duxbury C, Holland J, Pluchino M (2010) Experimental evaluation of the impacts of the invasive catfish Hoplosternum littorale (Hancock, 1828) on aquatic macroinvertebrates. Aquat Invas 5:97–102
Effenberger M, Engel J, Diehl S, Matthaei CD (2008) Disturbance history influences the distribution of stream invertebrates by altering microhabitat parameters: a field experiment. Freshw Biol 53:996–1011
Englund RA, Polhemus DA (2001) Evaluating the effects of introduced rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) on native stream insects on Kauai Island, Hawaii. J Insect Conserv 5:265–281
Englund G, Cooper SD, Sarnelle O (2001) Application of a model of scale dependence to quantify scale domains in open predation experiments. Oikos 92:501–514
Flecker AS, Townsend CR (1994) Community-wide consequences of trout introduction in New Zealand streams. Ecol Appl 4:798–807
Gibbs HL, Gibbs KE, Siebenmann M, Collins L (1998) Genetic differentiation among populations of the rare mayfly Siphlonisca aerodromia Needham. J N Am Benthol Soc 17:464–474
Graf J, Kikuchi Y, Rio RVM (2006) Leeches and their microbiota: naturally simple symbiosis models. Trends Microbiol 14:365–371
Green RH (1979) Sampling design and statistical methods for environmental biologists. Wiley Interscience, Chichester, England, UK
Grossman GD, Dowd JF, Crawford M (1990) Assemblage stability in stream fishes: a review. Environ Manage 14:661–671
Harper MP, Peckarsky BL (2005) Effects of pulsed and pressed disturbances on the benthic invertebrate community following a coal spill in a small stream in northeastern USA. Hydrobiologia 544:241–247
Hurlbert SH (1984) Pseudoreplication and design of ecological field experiments. Ecol Monogr 54:187–211
Huryn AD (1998) Ecosystem level evidence for topdown and bottom-up control of production in a grassland stream system. Oecologia 115:173–183
Johnson PTJ, Olden JD, Solomon CT, Vander Zanden MJ (2009) Interactions among invaders: community and ecosystem effects of multiple invasive species in an experimental aquatic system. Oecologia 159:161–170
Jongman RHG, ter Braak CJF, van Tongeren OFR (1995) Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Kadye WT, Booth AJ (2012) Integrating stomach content and stable isotope analyses to elucidate the feeding habits of non-native sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus. Biol Invas 14:779–795
Kadye WT, Magadza CHD (2008) Trout induces a shift from preferred habitat types for indigenous species: the example of the indigenous catfish, Amphilius uranoscopus (Pfeffer, 1889), on an African montane plateau. Hydrobiologia 614:329–337
Keough MJ, Mapstone BD (1997) Designing environmental monitoring for pulp mills in Australia. Water Sci Technol 35:397–404
Khan MF, Panikkar P (2009) Assessment of impacts of invasive fishes on the food web structure and ecosystem properties of a tropical reservoir in India. Ecol Model 220:2281–2290
Kitano J, Bolnick DI, Beauchamp DA, Mazur MM, Mori S, Nakano T, Peichel CL (2009) Reverse evolution of armor plates in the threespine stickleback. Curr Biol 18:769–774
Knapp RA, Matthews KR, Sarnelle O (2001) Resistance and resilience of alpine lake fauna to fish introductions. Ecol Monogr 71:401–421
Lake PS (2000) Disturbance, patchiness, and diversity in streams. J N Am Benthol Soc 19:573–592
Lal KK, Singh RK, Mohindra V, Singh B, Ponniah AG (2003) Genetic make up of exotic catfish Clarias gariepinus in India. Asian Fish Sci 16:229–234
Laurenson LB, Hocutt CH (1986) Colonisation theory and invasive biota: the Great Fish River, a case history. Environ Monit Assess 6:71–90
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology, 2nd English edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Maezono Y, Miyashita T (2003) Community-level impacts induced by introduced largemouth bass and bluegill in farm ponds in Japan. Biol Conserv 109:111–121
Maezono Y, Kobayashi R, Kusahara M, Miyashita T (2005) Direct and indirect effects of exotic bass and bluegill on exotic and native organisms in farm ponds. Ecol Appl 15:638–650
Meissner K, Moutka T (2006) The role of trout in stream food webs: integrating evidence from field surveys and experiments. J Anim Ecol 75:421–433
Merron GS (1993) Pack-hunting in two species of catfish, Clarias gariepinus and C. ngamensis, in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. J Fish Biol 43:575–584
Miller SA, Crowl TA (2006) Effects of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) on macrophytes and invertebrate communities in a shallow lake. Freshw Biol 51:85–94
Muehlbauer JD, Doyle WM, Bernhardt ES (2011) Macroinvertebrate community response to a dewatering disturbance gradient in a restored stream. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:1771–1783
Niemi GJ, DeVore P, Detenbeck N, Taylor D, Lima A, Pastor J, Yount JD, Naiman RJ (1990) Overview of case studies on recovery of aquatic systems to disturbance. Environ Manage 14:571–587
Nyström P, McIntosh AR (2003) Are impacts of an exotic predator on a stream food web influenced by disturbance history? Oecologia 136:279–288
Nyström P, Svensson O, Lardner B, Brönmark C, Granéli W (2001) The influence of multiple introduced predators on a littoral pond community. Ecology 82:1023–1039
O’Keeffe JH, de Moor FC (1988) Changes in the physico-chemistry and benthic invertebrates of the Great Fish River, South Africa, following an interbasin transfer of water. Regul Rivers: Res Manage 2:39–55
Parkyn SM, Collier KJ (2004) Interaction of press and pulse disturbance on crayfish populations: flood impacts in pasture and forest streams. Hydrobiologia 527:113–124
Phillips ID, Vinebrooke RD, Turner MA (2009) Experimental reintroduction of crayfish species Orconectes virilis into formerly acidified Lake 302S (Experimental Lakes Area, Canada). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 66:1892–1902
Quinn G, Keough M (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
R Development Core Team (2011) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York, USA
Ruetz CR, Newman RM, Vondracek B (2002) Top-down control in a detritus-based food web: fish, shredders, and leaf breakdown. Oecologia 132:307–315
Schilling EG, Loftin CS, Huryin AD (2009) Effects of introduced fish on macroinvertebrate communities in historically fishless headwater and kettle lakes. Biol Conserv 142:3030–3038
Shurin JB (2001) Interactive effects of predation and dispersal on zooplankton communities. Ecology 82:3404–3416
Simberloff D, Von Holle B (1999) Positive interaction of nonindigenous species: invasional meltdown. Biol Invas 1:21–32
Simon KS, Townsend CR (2003) Impacts of freshwater invaders at different levels of ecological organization, with emphasis on salmonids and ecosystems consequences. Freshw Biol 48:982–994
Sket B, Trontelj P (2008) Global diversity of leeches (Hirudinea) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:129–137
Stewart-Oaten A, Bence JR (2001) Temporal and spatial variation in environmental impact assessment. Ecol Monogr 71:305–339
Stewart-Oaten A, Murdoch WW, Parker KR (1986) Environmental impact assessment: ‘‘pseudoreplication’’ in time? Ecology 67:929–940
Stoks R, McPeek MA, Mitchell JL (2003) Evolution of prey behavior in response to changes in predation regime: damselflies in fish and dragonfly lakes. Evolution 57:574–585
Suding KN, Gross KL, Houseman GR (2004) Alternative states and positive feedbacks in restoration ecology. Trends Ecol Evolut 19:46–53
Teugels G.G. (1986) A systematic revision of the African species of the genus Clarias (Pisces; Clariidae). Annales Musée Royal de l’Afrique Centrale 247
Underwood AJ (1991) Beyond BACI: experimental designs for detecting human impacts on temporal variations in natural populations. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 42:569–587
Underwood AJ (1992) Beyond BACI: the detection of environmental impacts on populations in the real, but variable, world. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 161:145–178
Underwood AJ (1994) On Beyond BACI: sampling designs that might reliably detect environmental disturbances. Ecol Appl 4:3–15
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology: their logical design and interpretation using analysis of variance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Weyl PSR, de Moor FC, Hill MP, Weyl OLF (2010) The effect of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides on aquatic macroinvertebrate communities in the Wit River, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 35:273–281
Williams LR, Taylor CM (2003) Influence of fish predation on assemblage structure of macroinvertebrates in an intermittent stream. Trans Am Fish Soc 132:120–130
Winemiller KO, Kelso-Winemiller LC (1996) Comparative ecology of catfishes of the Upper Zambezi River floodplain. J Fish Biol 49:1043–1061
Yalçin S, Akyurt I, Solak K (2001) Stomach contents of the catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) in the River Asi (Turkey). Turk J Zool 25:461–468
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Research Foundation of South Africa (FA2007043000021) and the Rufford Small Grants Foundation for funding this study. The Eastern Cape’s Department of Economic Development and Environmental Affairs, through permit number CRO16/10CR, and the Rhodes University Ethics committee, through research proposal 2010Q2-1, granted permission for this study. Albert Chakona, Alison Gocke, Alexander Zuniga and Stanley Tsarwe assisted with field sampling and their help is greatly appreciated. Carl Schwarz, Olaf Weyl and Kirk Winemiller provided valuable comments on previous drafts of this paper. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for the valuable comments that improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadye, W.T., Booth, A.J. Detecting impacts of invasive non-native sharptooth catfish, Clarias gariepinus, within invaded and non-invaded rivers. Biodivers Conserv 21, 1997–2015 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-012-0291-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-012-0291-5