Abstract.
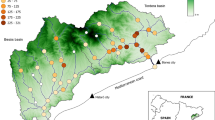
We used general linear modelling to assess the influence of environmental variables on the spatial distribution patterns of the bullhead (Cottus gobio) at stream system, site, and microhabitat scales in southwestern France. Bullheads occurred at 67 sites (out of 554 sampling sites), chiefly close to the source, in small and shallow streams. Population density at a site was primarily influenced by thermal conditions. Stream width was negatively related to the probability of presence of bullheads within the stream system, but positively related to local density, showing that bullhead density could increase within a range of stream width, but that wider rivers were unsuitable. Slope was negatively correlated to bullhead’s occurrence and local density, and depth was negatively correlated to local density and microhabitat use, suggesting that bullhead’s shimming performance was weak under greater erosive forces. Therefore, the most significant results suggested that the distribution of populations and individuals was first governed by the suitability of physical and hydraulic habitat, then population dynamics at a site was mainly governed by the thermal regime. Multi-scale studies of factors influencing a species’ distribution thus allow to integrate patterns observed at different scales, and enhance our understanding of interactions between animals and their environment. Such models are essential in the exploratory phase of fundamental and applied investigations, because they help to target further research, and they should influence the measures to be taken in field surveys or conservation plans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Andreasson (1971) ArticleTitleFeeding habits of a bullhead (Cottus gobio L. Pisces) population Report Institute of Freshwater Research Drottningholm 51 5–30
M.B. Bain J.T. Finn H.E. Booke (1988) ArticleTitleSteamflow regulation and fish community structure Ecology 69 382–392
M. Begon J.L. Harper C.R. Townsend (1996) Ecology: Individuals, Populations and Communities, 3rd edn Blackwell Science OxfordUK
P. Bomassi C. Brugel (2000) L’état des connaissances sur les populations en Auvergne des espèces de l‘ichtyofaune inscrites à l’annexe 2 de la directive ‘habitats’. Rapport du Conseil Supérieur de la Pêche Délégation Régionale Auvergne Lempdes, France 5–11
D.G. Cobb J.F. Flannagan (1990) ArticleTitleTrichoptera and substrate stability in the Ochre RiverManitoba Hydrobiologia 206 29–38
D.G. Cobb T.D. Galloway J.F. Flannagan (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of discharge and substrate stability on density and species composition of stream insects Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 49 1788–1795
M.J. Crawley (1993) Glim for Ecologists Blackwell Science OxfordUK
H. Décamps M. Fortuné F. Gazelle G. Pautou (1988) ArticleTitleHistorical influence of man in the riparian dynamics of a fluvial landscape Landscape Ecology 1 163–173 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00162742
E. Degerman B. Sers (1993) ArticleTitleA study of interactions between fish species in streams using survey data and the PCA-hyperspace technique Nordic Journal of Freshwater Research 68 5–13
E. Degerman B. Sers (1994) ArticleTitleThe effect of lakes on the stream fish fauna Ecology of Freshwater Fish 3 116–122
D.B. De Lury (1947) ArticleTitleOn the estimation of biological populations Biometrics 3 145–167
J.F. Downhower P. Lejeune P. Gaudin L. Brown (1990) ArticleTitleMovements of the chabot (Cottus gobio) in a small stream Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 37 119–126
C.C. Englbrecht J. Freyhof A. Nolte K. Rassmann U. Schliewen D. Tautz (2000) ArticleTitlePhylogeography of the bullhead Cottus gobio (Pisces: Teleostei: Cottidae) suggests a pre-Pleistocene origin of the major central European populations Molecular Ecology 9 709–722 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXksFSisr4%3D Occurrence Handle10849287
H.-M. Gabler P.-A. Amundsen T. Herfindal (2001) ArticleTitleDiet segregation between introduced bullhead (Cottus gobio L.) and Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar L.) in a sub-Arctic river Archiv für Hydrobiologie 151 609–625
P. Gaudin (1981) Eco-éthologie d’un poisson benthiquele chabotCottus gobio L. (Cottidae): distribution, alimentation et rapports avec la truiteSalmo trutta L Université Claude-Bernard Lyon, France
P. Gaudin L. Caillère (1990) ArticleTitleMicrodistribution of Cottus gobio L. and fry of Salmo trutta L. in a first order stream Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 37 81–93
P. Gaudin L. Caillère (2000) ArticleTitleExperimental study of the influence of presence and predation by sculpin, Cottus gobio L., on the drift of emergent brown troutSalmo trutta L Archiv für Hydrobiologie 147 257–271
T. Gittings D. O’Keefe F. Gallagher J. Finn T. O’Mahony (1998) ArticleTitleLongitudinal variation in abundance of a freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera population in relation to riverine habitats Biol. Environ. Proc. R. Irish Acad. 98B 171–178
O.T. Gorman J.R. Kar (1978) ArticleTitleHabitat structure and stream fish communities Ecology 59 507–515
G.D. Grossman J.F. Dowd M. Crawford (1990) ArticleTitleAssemblage stability in stream fishes: a review Environmental Management 14 661–671
R.Z. Guan P.R. Wiles (1997) ArticleTitleEcological impact of introduced crayfish on benthic fishes in a British lowland river Conservation Biology 11 641–647 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1523-1739.1997.96073.x
B. Hänfling B. Helleman F.A.M. Volckaert G.R. Carvalho (2002) ArticleTitleLate glacial history of the cold-adapted freshwater fish Cottus gobiorevealed by microsatellites Molecular Ecology 11 1717–1729 Occurrence Handle12207722
J.H. Harris R. Silveira (1999) ArticleTitleLarge-scale assessments of river health using an index of biotic integrity with low-diversity fish communities Freshwater Biology 41 235–252
L.C. Hastie P.J. Boon M.R. Young (2000) ArticleTitlePhysical microhabitat requirements of freshwater pearl mussels, Margaritifera margaritifera (L) Hydrobiologia 429 59–71
L.C. Hastie S.L. Cooksley F. Scougall M.R. Young P.J. Boon M.J. Gaywood (2003) ArticleTitleCharacterization of freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) riverine habitat using River Habitat Survey data Aquatic Conservation Marine Freshwater Ecosystems 13 213–224
J.M. Hellawell (1978) Biological Surveillance of Rivers Water Research Center Stevenage Laboratory, UK 332
J. Holcík (2003) ArticleTitleChanges in the fish fauna and fisheries in the Slovak section of the Danube River: a review Annals of Limnology 39 177–195
M. Inoue M. Nunokawa (2002) ArticleTitleEffects of longitudinal variations in stream habitat structure on fish abundance: an analysis based on subunit-scale classification Freshwater Biology 47 1594–1607 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00898.x
L. Jørgensen P.A. Amundsen H.M. Gabler M. Halvorsen J. Erkinaro E. Niemelä (1999) ArticleTitleSpatial distribution of Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar L.) and bullhead (Cottus gobio L.) in lotic and lentic habitats of a diversified watercourse in northern Fennoscandia Fish. Res. 41 201–211 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0165-7836(99)00014-4
E. Kainz H.P. Gollmann (1989) ArticleTitleBeiträge zur Verbreitung einiger Kleinfischarten in ö sterreichischen Fließgewässern Oesterreichs Fischerei 42 204–207
P. Keith J. Allardi (2001) Atlas des poissons d’eau douce de FranceVol. 47 Patrimoines Naturels Paris 387
L. Koli (1969) ArticleTitleGeographical variation of Cottus gobio L. (Pisces, Cottidae) in Northern Europe Annales Zoologici Fennici 6 353–390
T. Kontula R. Väinölä (2001) ArticleTitlePostglacial colonization of Northern Europe by distinct phylogeographic lineages of the bullheadCottus gobio Molecular Ecology 10 1983–2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmslyht74%3D Occurrence Handle11555242
A. Kruk T. Penczak (2003) ArticleTitleImpoundment impact on populations of facultative riverine fish Annals of Limnology 39 197–210
D.P. Larsen J.M. Omernik R.M. Hugues C.M. Rohm T.R. Whittier A.J. Kinney A.L. Gallant D.R. Dudley (1986) ArticleTitleCorrespondence between spatial patterns in fish assemblages in Ohio streams and aquatic ecoregions Environmental Management 10 815–828
P. Lavandier H. Décamps (1984) Estaragne B.A. Whitton (Eds) Ecology of European Rivers Blackwell Scientific Publications OxfordUK 237–264
M.D. Lobb D.J. Orth (1991) ArticleTitleHabitat use by an assemblage of fish in a large warmwater stream Transactions of the American Fishery Society 120 65–78
J. Lobon-Cervia Y. Dgebuadze C.G. Utrilla P.A. Rincon C. Granado-Lorencio (1996) ArticleTitleThe reproductive tactic of dace in central Siberia: evidence for temperature regulation of the spatio-temporal variability of its life history Journal of Fish Biology 48 1074–1087
S. Mastrorillo S. Lek F. Dauba A. Belaud (1997) ArticleTitleThe use of artificial neural networks to predict the presence of small-bodied fish in a river Freshwater Biology 38 237–246
C.A. Mills R.H.K. Mann (1983) ArticleTitleThe bullhead Cottus gobio a versatile and successful fish Annual Report of the Freshwater Biology Association 51 76–88
D.W. Morris (1987) ArticleTitleEcological scale and habitat use Ecology 68 362–369
P.R. Newall J.J. Magnuson (1999) ArticleTitleThe importance of ecoregion versus drainage area on fish distributions in the St. Croix River and its Wisconsin tributaries Environ. Biol. Fish. 55 245–254
J.D. Newbold B.W. Sweeney R.L. Vannote (1994) ArticleTitleA model for seasonal synchrony in stream mayflies Journal of the North American Benthological Society 13 3–18
J.-C. Pedroli B. Zaugg A. Kirchhofer (1991) Atlas de distribution des poissons et cyclostomes de Suisse Centre Suisse de cartographie de la faune Neuchâtel, Switzerland 155
E.R. Pianka (1978) Evolutionary Ecology, 2nd ed Harper and Row New York
N. Poulet (2000) Impact de la fragmentation des cours d’eau sur la morphologie des poissons. Cas de la vandoise rostrée (Leuciscus leuciscus burdigalensis) du Viaur. D.E.A report Université Toulouse III France
B.J. Pusey A.H. Arthington M.G. Read (1993) ArticleTitleSpatial and temporal variation in fish assemblage structure in the Mary Riversouth-eastern Queensland: the influence of habitat structure Environ. Biol. Fish. 37 355–380
D. Rathert D. White J.C. Sifneos R.M. Hughes (1999) ArticleTitleEnvironmental correlates of species richness for native freshwater fish in Oregon, USA Journal of Biogeography 26 257–273 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2699.1999.00274.x
J.M. Roussel A. Bardonnet (1997) ArticleTitleDiel and seasonal patterns of habitat use by fish in a natural salmonid brook: an approach to the functional role of the riffle-pool sequence Bulletin Français de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture 346 573–588
J.M. Roussel A. Bardonnet (2002) ArticleTitleThe habitat of juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) in small streams: preferences, movements, diel and seasonal variations Bulletin Français de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture 365–366 435–454
J.M. Roussel A. Bardonnet A. Claude (1999) ArticleTitleMicrohabitat of brown trout when feeding on drift and when resting in a lowland salmonid brook: effects on Weighted Usable Area Archiv für Hydrobiologic 146 413–429
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS Institute Inc. (1996) SAS System for Mixed Models SAS Institute Inc. Cary, North Carolina
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS Institute Inc. (2000) SAS/STAT® Software: User’s Guide SAS Institute Inc. Cary, North Carolina
F. Schiemer T. Spindler (1989) ArticleTitleEndangered fish species of the Danube river in Austria Regul. River. Res. Manage. 4 397–407
G.A.F. Seber E.D. Le Cren (1967) ArticleTitleEstimating populations parameters from catches large to relative populations Journal of Animal Ecology 36 631–643
D.L. Strayer J. Ralley (1993) ArticleTitleMicrohabitat use by an assemblage of stream-dwelling unionaceans (Bivalvia), including two rare species of Alismodonta Journal of the North American Benthological Society 12 247–258
R.L. Vannote B.W. Sweeney (1980) ArticleTitleGeographic analysis of thermal equilibria: a conceptual model for evaluating the effect of natural and modified thermal regimes on aquatic insect communities American Naturalist 115 667–695
F.A.M. Volckaert B. Hänfling B. Hellemans G.R. Carvalho (2002) ArticleTitleTiming of the population dynamics of bullhead Cottus gobio (Teleostei: Cottidae) during the pleistocene Journal of Evolutionary Biology 15 930–944
J.V. Ward J.A. Stanford (1979) Ecological factors controlling stream zoobenthos with emphasis on thermal modification of regulated streams J.V. Ward J.A. Stanford (Eds) The Ecology of Regulated Streams Plenum Press New York 35–55
J.S. Welton C.A. Mills J.R. Pygott (1991) ArticleTitleThe effect of interaction between the stone loach Noemacheilus barbatulus (L.) and the bullhead Cottus gobio (L.) on prey and habitat selection Hydrobiologia 220 1–7
J.S. Welton C.A. Mills E.L. Rendle (1983) ArticleTitleFood and habitat partitioning in two small benthic fishes, Noemacheilus barbatulus (L.) and Cottus gobio L Archiv für Hydrobiologie 97 434–454
J.F. Wright D.W. Sutcliffe M.T. Furse (Eds) (2000) Assessing the Biological Quality of Fresh Waters: RIVPACS and Other Techniques Freshwater Biological Association AmblesideUK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Legalle, M., Santoul, F., Figuerola, J. et al. Factors influencing the spatial distribution patterns of the bullhead (Cottus gobio L., Teleostei Cottidae): a multi-scale study. Biodivers Conserv 14, 1319–1334 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-004-9673-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-004-9673-7