Abstract
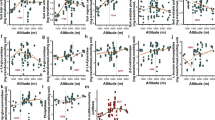
Conservation and restoration of ecosystems impacted by nonnative ungulates increasingly involves their removal and exclusion. While the influence of nonnative ungulate removal on plant communities is commonly monitored, impacts on underlying ecological processes are seldom quantified. Here we examined how nonnative feral pig (Sus scrofa) removal from Hawaiian tropical montane wet forests affects soil physical and chemical properties. Unique to this study, measurements were taken in paired sites inside and outside of five feral pig removal units representing a ~20 year, highly constrained chronosequence where other potentially confounding variables are held constant. Additional targeted measurements were taken inside and outside of a single exclosure in areas characterized by ‘low’ versus ‘high’ feral pig activity. Overall, nonnative feral pig removal increased stable soil aggregates and porosity, and decreased bulk density, water-filled pore space, and soil moisture content. Further, feral pig removal increased soil nutrient regeneration as evidenced by increased extractable cations, increased resin available NO3 − and total inorganic N, and enriched foliar δ15N. Increasing time since feral pig removal was positively related to net nitrification and total net inorganic N mineralization, and negatively related to pH and net ammonification. Results from both the chronosequence and targeted sampling were consistent in direction and support a central role of feral pig removal in modifying soil physical and chemical properties. Changes in soil properties following ungulate removal coincided with large increases in understory vegetation cover, highlighting the need to better understand aboveground-belowground linkages following nonnative ungulate removal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezketa E (1999) Soil aggregate stability: a review. J Sustain Agric 14:83–151
Anderson SJ, Stone CP (1994) Indexing sizes of feral pig populations in a variety of Hawaiian natural areas. Trans West Sect Wildl Soc 30:26–39
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kauffman R, Schmidt SK (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 20(11):634–641
Barrios-Garcia MN, Ballari SA (2012) Impact of wild boar (Sus scrofa) in its introduced and native range: a review. Biol Invasions 14:2283–2300
Barrios-García MN, Classen AT, Simberloff D (2014) Disparate responses of above- and belowground properties to soil disturbance by an invasive mammal. Ecosphere 5:1–13
Beever EA, Huso M, Pyke DA (2006) Multiscale responses of soil stability and invasive plants to removal of non-native grazers from an arid conservation reserve. Divers Distrib 12:258–268
Brady NC, Weil RR (2010) Elements of the nature and properties of soils. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Bronick CJ, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22
Bruinderink G, Hazebroek E (1996) Wild boar (Sus scrofa scrofa L.) rooting and forest regeneration on podzolic soils in the Netherlands. For Ecol Manage 88:71–80
Bueno CG, Azorín J, Gómez-García D, Alados CL, Badía D (2013) Occurrence and intensity of wild boar disturbances, effects on the physical and chemical soil properties of alpine grasslands. Plant Soil 373:243–256
Cabin RJ, Weller SG, Lorence DH, Flynn TW, Sakai AK, Sandquist D, Hadway LJ (2000) Effects of long-term ungulate exclusion and recent alien species control on the preservation and restoration of a Hawaiian tropical dry forest. Conserv Biol 14:439–453
Caley P (1993) Population dynamics of feral pigs (Sus scrofa) in a tropical riverine habitat complex. Wildl Res 20:625–636
Campbell T, Long DB (2009) Feral swine damage and damage management in forested ecosystems. For Ecol Manage 257:2319–2326
Cole RJ, Litton CM (2014) Vegetation response to removal of non-native feral pigs from Hawaiian tropical montane wet forest. Biol Invasions 16:125–140
Cole RJ, Litton CM, Koontz MJ, Loh RK (2012) Vegetation recovery 16 Years after feral pig removal from a wet Hawaiian forest. Biotropica 44:463–471
Courchamp F, Chapuis J-L, Pascal M (2003) Mammal invaders on islands: impact, control and control impact. Biol Rev 78:347–383
Craine JM, Elmore AJ, Aidar MPM, Bustamante M, Dawson TE, Hobbie EA, Kahmen A, Mack MC, McLauchlan KK, Michelsen A, Nardoto GB, Pardo LH, Peñuelas J, Reich PB, Schuur EAG, Stock WD, Templer PH, Virginia RA, Welker JM, Wright IJ (2009) Global patterns of foliar nitrogen isotopes and their relationships with climate, mycorrhizal fungi, foliar nutrient concentrations, and nitrogen availability. New Phytol 183:980–992
Cushman J, Tierney T, Hinds J (2004) Variable effects of feral pig disturbances on native and exotic plants in a California grassland. Ecol Appl 14:1746–1756
Davidson AD, Hewitt CL (2014) How often are invasion-induced ecological impacts missed? Biol Invasions 16:1165–1173
Davis MA, Grime JP, Thompson K (2000) Fluctuating resources in plant communities: a general theory of invasibility. J Ecol 88:528–534
Didham RK, Tylianakis JM, Hutchison MA, Ewers RM, Gemmell NJ (2005) Are invasive species drivers of ecological change. Trends Ecol Evol 20:470–474
Diong CH (1982) Population biology and management of the feral pig (Sus scrofa L.) in Kipahulu Valley, Maui. Dissertation, University of Hawaii at Manoa
Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems 6:503–523
Elledge AE, McAlpine CA, Murray PJ, Gordon IJ (2012) Modelling habitat preferences of feral pigs for rooting in lowland rainforest. Biol Invasions 15:1523–1535
Evans RD (2001) Physiological mechanisms influencing plant nitrogen isotope composition. Trends Plant Sci 6(3):121–126
Frank DA, Groffman PM, Evans RD, Tracy BF (2000) Ungulate stimulation of nitrogen cycling and retention in Yellowstone Park grasslands. Oecologia 123:116–121
Ghani A, Dexter M, Perrott K (2003) Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: a sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilisation, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1231–1243
Giambelluca TW, Chen Q, Frazier AG, Price JP, Chen Y-L, Chu P-S, Eischeid JK, Delparte DM (2013) Online rainfall atlas of Hawaii. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 94:313–316
Giambelluca TW, Shuai X, Barnes ML, Alliss RJ, Longman RJ, Miura T, Chen Q, Frazier AG, Mudd RG, Cuo L, Businger AD (2014) Evapotranspiration of Hawai‘i. Final report submitted to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers—Honolulu District, and the Commission on Water Resource Management, State of Hawai‘i
Hess S, Jacobi J (2011) The history of mammal eradications in Hawaii and the United States associated islands of the Central Pacific. Island Invasives: eradication and management. IUCN, Gland, pp 67–73
Hobbs N (1996) Modification of ecosystems by ungulates. J Wildl Manage 60:695–713
Hue NV, Uchida R, Ho MC (2000) Sampling and analysis of soils and plant tissues. In: Silva JA, Uchida RS (eds) Plant nutrient management in Hawaii soils. College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, pp 23–30
Kardol P, Dickie IA, St. John MG, Husheer SW, Bonner KI, Bellingham PJ, Wardle DA (2014) Soil-mediated effects of invasive ungulates on native tree seedlings. J Ecol 102:622–631
Kellner JR, Asner GP, Kinney KM, Loarie SR, Knapp DE, Kennedy-Bowdoin T, Questad EJ, Cordell S, Thaxton JM (2011) Remote analysis of biological invasion and the impact of enemy release. Ecol Appl 21:2094–2104
Krull CR, Waipara NW, Choquenot D, Burns BR, Gormley AM, Stanley MC (2013) Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence: feral pigs as vectors of soil-borne pathogens. Austral Ecol 38:534–542
Lacki M, Lancia R (1983) Changes in soil properties of forests rooted by wild boar. In: Proceedings of the annual conference of the Southeastern association of fish and wildlife agencies, pp 228–236
Li AY, Williams N, Fenwick SG, Hardy GESJ, Adams PJ (2013) Potential for dissemination of Phytophthora cinnamomi by feral pigs via ingestion of infected plant material. Biol Invasions 16:765–774
Lincoln NK (2014) Effect of various monotypic forest canopies on earthworm biomass and feral pig rooting in Hawaiian wet forests. For Ecol Manage 331:79–84
Linderholm A, Spencer D, Battista V, Frantz L, Barnett R, Fleischer RC, James HF, Duffy D, Sparks JP, Clements DR, Andersson L, Dobney K, Leonard JA, Larson G (2016) A novel MC1R allele for black coat colour reveals the Polynesian ancestry and hybridization patterns of Hawaiian feral pigs. R Soc Open Sci 3(9):160304
Litton CM, Raich JW, Ryan MG (2007) Review: carbon allocation in forest ecosystems. Glob Change Biol 13:2089–2109
Lohse KA, Matson P (2005) Consequences of nitrogen additions for soil losses from wet tropical forests. Ecol Appl 15:1629–1648
Macci C, Doni S, Bondi G, Davini D, Masciandaro G, Pistoia A (2012) Effects of wild boar (Sus scrofa) grazing on soil properties in Mediterranean environment. Catena 98:79–86
Mack M, D’Antonio C (1998) Impacts of biological invasions on disturbance regimes. Trends Ecol Evol 13:195–198
Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol Appl 10:689–710
Mohr D, Cohnstaedt LW, Topp W (2005) Wild boar and red deer affect soil nutrients and soil biota in steep oak stands of the Eifel. Soil Biol Biochem 37:693–700
Moody A, Jones JA (2000) Soil response to canopy position and feral pig disturbance beneath Quercus agrifolia on Santa Cruz Island, California. Appl Soil Ecol 14:269–281
Murphy MJ, Inman-Narahari F, Ostertag R, Litton CM (2014) Invasive feral pigs impact native tree ferns and woody seedlings in Hawaiian forest. Biol Invasions 16(1):63–71
Nanzyo M (2002) Unique properties of volcanic ash soils. Glob Environ Res Ed 6:99–112
Nogueira-Filho SLG, Nogueira SSC, Fragoso JMV (2009) Ecological impacts of feral pigs in the Hawaiian Islands. Biodivers Conserv 18:3677–3683
NRCS (2010) Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Web Soil Survey. http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/. Accessed 23 Aug 2010
Nuñez MA, Bailey JK, Schweitzer JA (2009) Population, community and ecosystem effects of exotic herbivores: a growing global concern. Biol Invasions 12:297–301
Nuttle T, Ristau TE, Royo AA (2014) Long-term biological legacies of herbivore density in a landscape-scale experiment: forest understoreys reflect past deer density treatments for at least 20 years. J Ecol 102:221–228
Oduor A, Gómez J, Strauss S (2010) Exotic vertebrate and invertebrate herbivores differ in their impacts on native and exotic plants: a meta-analysis. Biol Invasions 12:407–419
Palacio S, Bueno CG, Azorín J, Maestro M, Gómez-García D (2013) Wild-boar disturbance increases nutrient and C stores of geophytes in subalpine grasslands. Am J Bot 100:1790–1799
Pejchar L, Mooney HA (2009) Invasive species, ecosystem services and human well-being. Trends Ecol Evol 24:497–504
Peltzer DA, Allen RB, Lovett GM, Whitehead D, Wardle DA (2010) Effects of biological invasions on forest carbon sequestration. Glob Chang Biol 16:732–746
Perret S, Dorel M (2006) Relationships between land use, fertility and Andisol behaviour: examples from volcanic islands. Soil Use Manag 15:144–149
Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. Bioscience 50:53–65
Scheffler PY, Pratt LW, Foote D, Magnacca KN (2012) A preliminary study of effects of feral pig density on native Hawaiian montane rainforest vegetation. Technical Report No. 182. Pactific Cooperative Studies Unit, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii. p 43
Schrama M, Heijning P, Bakker JP, van Wijnen HJ, Berg MP, Olff H (2012) Herbivore trampling as an alternative pathway for explaining differences in nitrogen mineralization in moist grasslands. Oecologia 172:231–243
Schuur E, Matson P (2001) Net primary productivity and nutrient cycling across a mesic to wet precipitation gradient in Hawaiian montane forest. Oecologia 128:431–442
Schuur E, Chadwick OA, Matson P (2001) Carbon cycling and soil carbon storage in mesic to wet Hawaiian montane forests. Ecology 82:3182–3196
Scowcroft PG, Hobdy R (1987) Recovery of goat-damaged vegetation in an insular tropical montane forest. Biotropica 19:208–215
Seybold C, Herrick J (2001) Aggregate stability kit for soil quality assessments. Catena 44:37–45
Siemann E, Carrillo JA, Gabler CA, Zipp R, Rogers WE (2009) Experimental test of the impacts of feral hogs on forest dynamics and processes in the southeastern US. For Ecol Manage 258:546–553
Silva JHS, Deenik JL, Yost RS, Bruland GL, Crow SE (2015) Improving clay content measurement in oxidic and volcanic ash soils of Hawaii by increasing dispersant concentration and ultrasonic energy levels. Geoderma 237–238:211–223
Singer FJ, Swank WT, Clebsch EEC (1984) Effects of wild pig rooting in a deciduous forest. J Wildl Manage 48:464–473
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Soil Survey Field and Laboratory Methods Manual. Soil Survey Investigations Report No. 51, Version 2.0. R. Burt and Soil Survey Staff (ed). U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service
Spear D, Chown SL (2009) Non-indigenous ungulates as a threat to biodiversity. J Zool 279:1–17
Stone C, Cuddihy L, Tunison JT (1992) Responses of Hawaiian ecosystems to removal of feral pigs and goats. In: Stone C, Scott J (eds) Alien plant invasions on native ecosystems in Hawai‘i: management and research. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu, pp 666–704
Stritar M, Schweitzer J, Hart S, Bailey J (2010) Introduced ungulate herbivore alters soil processes after fire. Biol Invasions 12:313–324
Tanentzap AJ, Burrows LE, Lee WG, Nugent G, Maxwell JM, Coomes DA (2009) Landscape-level vegetation recovery from herbivory: progress after four decades of invasive red deer control. J Appl Ecol 46:1064–1072
Thaxton JM, Cole TC, Cordell S, Cabin RJ, Sandquist DR, Litton CM (2010) Native species regeneration following ungulate exclusion and nonnative grass removal in a remnant Hawaiian dry forest. Pac Sci 64:533–544
Tisdale JM, Oades JM (1982) Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J Soil Sci 33:141–163
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Westbrooks R (1996) Biological invasions as global environmental change. Am Sci 84:468–478
Vtorov I (1993) Feral pig removal: effects on soil microarthropods in a Hawaiian rain forest. J Wildl Manage 57:875–880
Wagner W, Herbst D, Sohmer S (1990) Manual of the flowering plants of Hawaii. Bishop Museum, Honolulu
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, Van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633
Weller SG, Cabin RJ, Lorence DH, Perlman S, Wood K, Flynn T, Sakai AK (2011) Alien plant invasions, introduced ungulates, and alternative states in a mesic forest in Hawaii. Restor Ecol 19:671–680
Wirthner S, Schütz M, Page-dumroese DS, Busse MD, Kirchner JW, Risch AC (2012) Do changes in soil properties after rooting by wild boars (Sus scrofa) affect understory vegetation in Swiss hardwood forests? Can J For Res 42:585–592
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources, University of Hawaii at Manoa via the USDA-NIFA Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture Research (TSTAR) (2009-34135-20101 to CML), Hatch (HAW00132H and HAW01127H to CML), and McIntire Stennis (HAW00188M and HAW01123M to CML) programs; the Department of Defense Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (RC-2433 to CML, JPS, RJC and CPG); and the USDA Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Research Station (to CPG). We thank Hawaii Volcanoes National Park and the State of Hawaii Department of Land and Natural Resources, Division of Forestry and Wildlife, Natural Areas Reserve System for access to field sites. We thank J.B. Friday for access to laboratory space and logistical support; N. Friday, M. Johansen, and I. Ito from the University of Hawaii Pacific Internship Programs for Exploring Sciences for tireless field and laboratory work; and A. Taylor, K. Gerow, P. Selmants, and R. Camp for advice on statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, M.S., Litton, C.M., Giardina, C.P. et al. Impact of nonnative feral pig removal on soil structure and nutrient availability in Hawaiian tropical montane wet forests. Biol Invasions 19, 749–763 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1368-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-017-1368-6