Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of lowering culture temperature on monoclonal antibody charge variation distribution in Chinese hamster ovary cell cultures.
Results
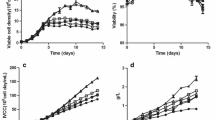
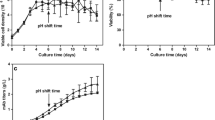
In both batch and fed-batch cultures, lowering the culture temperature decreased the antibody acidic variant levels. The acidic variant levels (defined as variants eluting earlier than the main peak of an antibody during HPLC) at 32 °C were about 10 % lower than those at 37 °C at the end of both batch and fed-batch cultures. Additionally, lowering the culture temperature increased the lysine variant level, which further increased basic variant level. The lysine variant levels at 32 °C were about 8 % (batch culture) and 3 % (fed-batch culture) higher than those at 37 °C at the end of cultures. Real-time PCR results suggests that the decrease in carboxypeptidase B transcription level might be partially responsible for the increased lysine variant level at sub-physiological temperatures.
Conclusion
Culture temperature exhibits noticeable impact on antibody charge variation distribution, especially the acidic variants and lysine variants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal SR (2014) What’s fueling the biotech engine: 2012–2013. Nat Biotechnol 32:32–39
Aghamohseni H, Ohadi K, Spearman M, Krahn N, Moo-Young M, Scharer JM, Butler M, Budman HM (2014) Effects of nutrient levels and average culture pH on the glycosylation pattern of camelid-humanized monoclonal antibody. J Biotechnol 186:98–109
Ahn WS, Jeon JJ, Jeong YR, Lee SJ, Yoon SK (2008) Effect of culture temperature on erythropoietin production and glycosylation in a perfusion culture of recombinant CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 101:1234–1244
Borys MC, Dalal NG, Abu-Absi NR, Khattak SF, Jing Y, Xing Z, Li ZJ (2010) Effects of culture conditions on N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) content of a recombinant fusion protein produced in CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 105:1048–1057
Bradley G, Naudé RJ, Muramoto K, Yamauchi F, Oelofsen W (1996) Ostrich (Struthio camelus) carboxypeptidase B: purification, kinetic properties and characterization of the pancreatic enzyme. Int J Biochem Cell B 28:521–529
Du Y, Walsh A, Ehrick R, Xu W, May K, Liu H (2012) Chromatographic analysis of the acidic and basic species of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. MAbs 4:578–585
Fan L, Zhao L, Ye Z, Sun Y, Kou T, Zhou Y, Tan WS (2010) Effect of culture temperature on TNFR-Fc productivity in recombinant glutamine synthetase-chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Lett 32:1239–1244
Gomez N, Ouyang J, Nguyen MD, Vinson AR, Lin AA, Yuk IH (2010) Effect of temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and hydrolysate on the formation of triple light chain antibodies in cell culture. Biotechnol Prog 26:1438–1445
Gomez N, Subramanian J, Ouyang J, Nguyen MD, Hutchinson M, Sharma VK, Lin AA, Yuk IH (2012) Culture temperature modulates aggregation of recombinant antibody in cho cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:125–136
Harris RJ, Kabakoff B, Macchi FD, Shen FJ, Kwong M, Andya JD, Shire SJ, Bjork N, Totpal K, Chen AB (2001) Identification of multiple sources of charge heterogeneity in a recombinant antibody. J Chromatogr B 752:233–245
Khawli LA, Goswami S, Hutchinson R, Kwong ZW, Yang J, Wang X, Yao Z, Sreedhara A, Cano T, Tesar D, Nijem I, Allison DE, Wong PY, Kao YH, Quan C, Joshi A, Harris RJ, Motchnik P (2010) Charge variants in IgG1: isolation, characterization, in vitro binding properties and pharmacokinetics in rats. MAbs 2:613–624
Marchant RJ, Al-Fageeh MB, Underhill MF, Racher AJ, Smales CM (2008) Metabolic rates, growth phase, and mRNA levels influence cell-specific antibody production levels from in vitro-cultured mammalian cells at sub-physiological temperatures. Mol Biotechnol 39:69–77
Mason M, Sweeney B, Cain K, Stephens P, Sharfstein S (2014) Reduced culture temperature differentially affects expression and biophysical properties of monoclonal antibody variants. Antibodies 3:253–271
Pace AL, Wong RL, Zhang YT, Kao YH, Wang YJ (2013) Asparagine deamidation dependence on buffer type, pH, and temperature. J Pharm Sci 102:1712–1723
Yoon SK, Kim SH, Lee GM (2003a) Effect of low culture temperature on specific productivity and transcription level of Anti-4-1BB antibody in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Prog 19:1383–1386
Yoon SK, Song JY, Lee GM (2003b) Effect of low culture temperature on specific productivity, transcription level, and heterogeneity of erythropoietin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:289–298
Sun Y-T, Zhao L, Ye Z, Fan L, Liu X-P, Tan W-S (2013) Development of a fed-batch cultivation for antibody-producing cells based on combined feeding strategy of glucose and galactose. Biochem Eng J 81:126–135
Zhang X, Tang H, Sun YT, Liu X, Tan WS, Fan L (2015) Elucidating the effects of arginine and lysine on a monoclonal antibody C-terminal lysine variation in CHO cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6617-y
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21406066, 21206040), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA02A303), the National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2013ZX10004003-003-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Sun, YT., Tang, H. et al. Culture temperature modulates monoclonal antibody charge variation distribution in Chinese hamster ovary cell cultures. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2151–2157 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1904-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1904-3