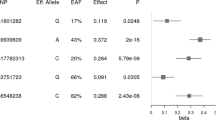
Abstract
Obesity is a multifactorial disorder and requires favorable environment for its expression. However, some individuals are more prone to weight gain than others in an obesogenic environment. Thus, at individual level, who becomes overweight or obese is mostly determined by genetic factors. The current study was undertaken to explore for the first time the association of the TMEM18 rs7561317 variant with overweight/obesity and related anthropometric, metabolic, physical, and behavioral traits in a sample of Pakistani population with association between the rs7561317 and many traits was not investigated before in any population. The current study involved a total of 612 subjects including 306 overweight/obese and equal number of age- and sex-matched normal weight individuals. Obesity-related parameters were determined and the variant was genotyped by allelic discrimination assay. All the aforementioned associations were assessed by regression analyses adjusted for covariates and corrected for multiple comparisons. The results revealed a significant association of the TMEM18 rs7561317 with overweight/obese phenotype in more than one genetic model. Therefore, h-index (degree of dominance) was calculated, which indicated the recessive mode of inheritance for the above-said association. Similarly, a significant association of the rs7561317 with obesity-related anthropometric traits and clinical surrogate markers of visceral adiposity was observed. Thus, GG genotype of the rs7561317 was found to increase 1.74 times the risk of overweight/obesity in Pakistani population (OR = 1.74, 95% CI 1.210–2.496, p = 0.003) while low physical activity seemed to accentuate the TMEM18 rs7561317-associated risk of overweight/obesity (OR = 2.696, 95% CI 1.485–4.896, p = 0.004).
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Abadi A, Peralta-Romero J, Suarez F, Gomez-Zamudio J, Burguete-Garcia AI, Cruz M, Meyre D (2016) Assessing the effects of 35 European-derived BMI-associated SNPs in Mexican children. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md) 24(9):1989–1995. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.21590
Albuquerque D, Nobrega C, Rodriguez-Lopez R, Manco L (2014) Association study of common polymorphisms in MSRA, TFAP2B, MC4R, NRXN3, PPARGC1A, TMEM18, SEC16B, HOXB5 and OLFM4 genes with obesity-related traits among Portuguese children. J Hum Genet 59(6):307–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2014.23
Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, Padez C (2017) The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull 123(1):159–173. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldx022
Almen MS, Jacobsson JA, Shaik JH, Olszewski PK, Cedernaes J, Alsio J, Sreedharan S, Levine AS, Fredriksson R, Marcus C et al (2010) The obesity gene, TMEM18, is of ancient origin, found in majority of neuronal cells in all major brain regions and associated with obesity in severely obese children. BMC Med Genet 11:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-11-58
Amato MC, Giordano C, Galia M, Criscimanna A, Vitabile S, Midiri M, Galluzzo A (2010) Visceral Adiposity Index: a reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care 33(4):920–922. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1825
Bassali R, Waller JL, Gower B, Allison J, Davis CL (2010) Utility of waist circumference percentile for risk evaluation in obese children. Int J Pediatr Obes 5(1):97–101. https://doi.org/10.3109/17477160903111722
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B (Methodological) 57(1):289–300
Bush WS, Moore JH (2012) Chapter11: Genome-wide association studies. PLOS Comput Biol 8(12):e1002822. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822
Dusatkova L, Zamrazilova H, Sedlackova B, Vcelak J, Hlavaty P, Aldhoon Hainerova I, Korenkova V, Bradnova O, Bendlova B, Kunesova M et al (2013) Association of obesity susceptibility gene variants with metabolic syndrome and related traits in 1,443 Czech adolescents. Folia Biol 59(3):123–133
Elks CE, den Hoed M, Zhao JH, Sharp SJ, Wareham NJ, Loos RJ, Ong KK (2012) Variability in the heritability of body mass index: a systematic review and meta-regression. Front Endocrinol 3:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2012.00029
Entringer S, Buss C, Swanson J, Cooper D, Wing D, Waffarn F, Wadhwa DP (2012) Fetal programming of body composition, obesity, and metabolic function: the role of intrauterine stress and stress biology. J Nutr Metab 2012:632548. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/632548
Gong J, Schumacher F, Lim U, Hindorff LA, Haessler J, Buyske S, Carlson CS, Rosse S, Buzkova P, Fornage M et al (2013) Fine mapping and identification of BMI loci in African Americans. Am J Hum Genet 93(4):661–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.08.012
Guerrero-Romero F, Simental-Mendia LE, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, Martinez-Abundis E, Ramos-Zavala MG, Hernandez-Gonzalez SO, Jacques-Camarena O, Rodriguez-Moran M (2010) The product of triglycerides and glucose, a simple measure of insulin sensitivity. Comparison with the euglycemic–hyperinsulinemic clamp. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(7):3347–3351. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-0288
Hauk L (2012) NHLBI expert panel releases guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children. Am Fam Phys 86(8):776–781
Hofer T, Ray N, Wegmann D, Excoffier L (2009) Large allele frequency differences between human continental groups are more likely to have occurred by drift during range expansions than by selection. Ann Hum Genet 73(1):95–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00489.x
Hotta K, Nakamura M, Nakamura T, Matsuo T, Nakata Y, Kamohara S, Miyatake N, Kotani K, Komatsu R, Itoh N et al (2009) Association between obesity and polymorphisms in SEC16B, TMEM18, GNPDA2, BDNF, FAIM2 and MC4R in a Japanese population. J Hum Genet 54(12):727–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2009.106
Jackson AS, Pollock ML (1985) Practical assessment of body composition. Phys Sportsmed 13(5):76–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/00913847.1985.11708790
Jastreboff AM, Kotz CM, Kahan S, Kelly AS, Heymsfield SB (2019) Obesity as a disease: the obesity society 2018 position statement. Obesity 27(1):7–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22378
Kahn HS (2005) The "lipid accumulation product" performs better than the body mass index for recognizing cardiovascular risk: a population-based comparison. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 5:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2261-5-26
Larder R, Sim MFM, Gulati P, Antrobus R, Tung YCL, Rimmington D, Ayuso E, Polex-Wolf J, Lam BYH, Dias C et al (2017) Loss and gain of function experiments implicate TMEM18 as a mediator of the strong association between genetic variants at human chromosome 2p25.3 and obesity. bioRxiv. 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1101/122853
Levin BE (2005) Factors promoting and ameliorating the development of obesity. Physiol Behav 86(5):633–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.08.054
NCEP (2002) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation 106(25):3143–3421
Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF et al (2014) Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet (London, England) 384(9945):766–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60460-8
O’Hara L, Taylor J (2018) What’s wrong with the ‘war on obesity?’ a narrative review of the weight-centered health paradigm and development of the 3C framework to build critical competency for a paradigm shift. SAGE Open 8(2):2158244018772888. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244018772888
Ogden CL, Kuczmarski RJ, Flegal KM, Mei Z, Guo S, Wei R, Grummer-Strawn LM, Curtin LR, Roche AF, Johnson CL (2002) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2000 growth charts for the United States: improvements to the 1977 National Center for Health Statistics version. Pediatrics 109(1):45–60
Oussaada SM, van Galen KA, Cooiman MI, Kleinendorst L, Hazebroek EJ, van Haelst MM, Ter Horst KW, Serlie MJ (2019) The pathogenesis of obesity. Metabolism 92:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.12.012
Park S, Yang JS, Kim J, Shin YE, Hwang J, Park J, Jang SK, Kim S (2012) Evolutionary history of human disease genes reveals phenotypic connections and comorbidity among genetic diseases. Sci Rep 2:757. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00757
Perez-Escamilla R, Bermudez O, Buccini GS, Kumanyika S, Lutter CK, Monsivais P, Victora C (2018) Nutrition disparities and the global burden of malnutrition. BMJ (Clinical Research ed) 361:k2252. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k2252
Pigeyre M, Saqlain M, Turcotte M, Raja GK, Meyre D (2018) Obesity genetics: insights from the Pakistani population. Obes Rev 19(3):364–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12644
Popkin BM, Adair LS, Ng SW (2012) Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr Rev 70(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00456.x
Rask-Andersen M, Jacobsson JA, Moschonis G, Chavan RA, Sikder MA, Allzen E, Alsio J, Chrousos GP, Manios Y, Fredriksson R et al (2012) Association of TMEM18 variants with BMI and waist circumference in children and correlation of mRNA expression in the PFC with body weight in rats. Eur J Hum Genet 20(2):192–197. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.176
Report of a WHO Expert Committee (1995) Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. WHO Technical Report Series No. 854. https://www.who.int/childgrowth/publications/physical_status/en/. Accessed Sept 2019.
Rodriguez S, Gaunt TR, Day INM (2009) Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium testing of biological ascertainment for Mendelian randomization studies. Am J Epidemiol 169(4):505–514. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwn359
Rosenberg NA, Huang L, Jewett EM, Szpiech ZA, Jankovic I, Boehnke M (2010) Genome-wide association studies in diverse populations. Nat Rev Genet 11(5):356–366. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2760
Sandholt CH, Vestmar MA, Bille DS, Borglykke A, Almind K, Hansen L, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Witte D, Jorgensen T et al (2011) Studies of metabolic phenotypic correlates of 15 obesity associated gene variants. PLoS ONE 6(9):e23531. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023531
Speakman JR (2013) Functional analysis of seven genes linked to body mass index and adiposity by genome-wide association studies: a review. Hum Heredity 75(2–4):57–79. https://doi.org/10.1159/000353585
Templeton GF, Burney LL (2016) Using a two-step transformation to address non-normality from a business value of information technology perspective. J Inform Syst 31(2):149–164. https://doi.org/10.2308/isys-51510
Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, Steinthorsdottir V, Sulem P, Helgadottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Gretarsdottir S, Thorlacius S, Jonsdottir I et al (2009) Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat Genet 41(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.274
Västermark Å, Jacobsson J, Johansson A, Fredriksson R, Gyllensten U, Schiöth BH (2012) Polymorphisms in sh2b1 and spns1 loci are associated with triglyceride levels in a healthy population in northern Sweden. J Genet 91:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-012-0167-1
Wang YC, McPherson K, Marsh T, Gortmaker SL, Brown M (2011) Health and economic burden of the projected obesity trends in the USA and the UK. Lancet (London, England) 378(9793):815–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60814-3
Wiemerslage L, Gohel PA, Maestri G, Hilmarsson TG, Mickael M, Fredriksson R, Williams MJ, Schioth HB (2016) The Drosophila ortholog of TMEM18 regulates insulin and glucagon-like signaling. J Endocrinol 229(3):233–243. https://doi.org/10.1530/joe-16-0040
Zhao J, Bradfield JP, Li M, Wang K, Zhang H, Kim CE, Annaiah K, Glessner JT, Thomas K, Garris M et al (2009) The role of obesity-associated loci identified in genome-wide association studies in the determination of pediatric BMI. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md) 17(12):2254–2257. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.159
Zintzaras E, Santos M (2011) Estimating the mode of inheritance in genetic association studies of qualitative traits based on the degree of dominance index. BMC Med Res Methodol 11(1):171. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-171
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Mr. Adil Anwar Bhatti, Mr. Saad Mirza, and Ms. Soma Rahmani for their contribution in sample collection.
Funding
This work was supported by a recurring grant provided by the International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences (ICCBS), University of Karachi, Pakistan. However, biochemical assays regarding lipid profile were supported by a research grant given by the Higher Education Commission (HEC) (Ref. No. 5740/Sindh/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2016) under National Research Program for Universities (NRPU). The funding bodies did not play any role in the design of the study, sample collection, data collection, data analysis and interpretation or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR conceived the project and arranged funding. AS performed the experiments. AS and SR performed the statistical analysis with major contribution of AS. SR and AS wrote the manuscript with major contribution of SR. SR also has major role in collecting the samples. All authors carefully checked and approved this version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the current study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional ethics committee (International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, Pakistan) and Advanced Studies and Research Board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All individual participants or parents/guardians of the participants signed the informed consent prior to their participation in the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, S., Sultana, A. Association of the Variant rs7561317 Downstream of the TMEM18 Gene with Overweight/Obesity and Related Anthropometric Traits in a Sample of Pakistani Population. Biochem Genet 58, 257–278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-019-09940-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-019-09940-2