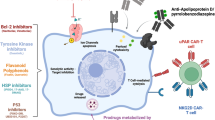
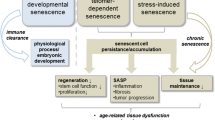
Abstract
Of the factors studied in individual ageing, the accumulation of senescent cells has been considered as an essential cause of organ degeneration to eventually initiate age-related diseases. Cellular senescence is attributed to the accumulation of damage for an inducement in the activation of cell cycle inhibitory pathways, resulting the cell permanently withdraw from the cell proliferation cycle. Further, senescent cells will activate the inflammatory factor secretion pathway to promote the development of various age-related diseases. Senolytics, a small molecule compound, can delay disease development and extend mammalian lifespan. The evidence from multiple trials shows that the targeted killing of senescent cells has a significant clinical application for the treatment of age-related diseases. In addition, senolytics are also significant for the development of ageing research in solid organ transplantation, which can fully develop the potential of elderly organs and reduce the age gap between demand and supply. We conclude that the main characteristics of cellular senescence, the anti-ageing drug senolytics in the treatment of chronic diseases and organ transplantation, and the latest clinical progress of related researches in order to provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of ageing and related diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Andle J, Lee TJ, Midha A, Talemal L, Chipashvili V, Hollister-Lock J, van Deursen J, Weir G, Bonner-Weir S (2019) Acceleration of beta cell aging determines diabetes and senolysis improves disease outcomes. Cell Metab 30:129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.006
Ahlenstiel T, Burkhardt G, Kohler H, Kuhlmann MK (2006) Improved cold preservation of kidney tubular cells by means of adding bioflavonoids to organ preservation solutions. Transplantation 81:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000191945.09524.a1
Anon. (2015) Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc15-S005
Armitage J, Bowman L, Wallendszus K, Bulbulia R, Rahimi K, Haynes R, Parish S, Peto R, Collins R (2010) Intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol with 80 mg versus 20 mg simvastatin daily in 12,064 survivors of Myocardial Infarction: a double-blind randomised trial. Lancet 376:1658–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60310-8
Bai P, Canto C, Oudart H, Brunyanszki A, Cen Y, Thomas C, Yamamoto H, Huber A, Kiss B, Houtkooper RH, Schoonjans K, Schreiber V, Sauve AA, Menissier-de MJ, Auwerx J (2011) PARP-1 inhibition increases mitochondrial metabolism through SIRT1 activation. Cell Metab 13:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.004
Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Childs BG, van de Sluis B, Kirkland JL, van Deursen JM (2011) Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing-associated disorders. Nature 479:232–236. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10600
Basisty N, Kale A, Jeon OH, Kuehnemann C, Payne T, Rao C, Holtz A, Shah S, Sharma V, Ferrucci L, Campisi J, Schilling B (2020) A proteomic atlas of senescence-associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. Plos Biol 18:e3000599. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000599
Beausejour CM, Krtolica A, Galimi F, Narita M, Lowe SW, Yaswen P, Campisi J (2003) Reversal of human cellular senescence: roles of the p53 and p16 pathways. Embo J 22:4212–4222. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg417
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P (2002) Diabetes and Atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 287:2570–2581. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.287.19.2570
Birch J, Gil J (2020) Senescence and the SASP: many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev 34:1565–1576. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.343129.120
Borodkina AV, Deryabin PI, Giukova AA, Nikolsky NN (2018) Social life of senescent cells: what is SASP and why study. It? Acta Naturae 10:4–14
Breccia M, Molica M, Alimena G (2014) How tyrosine kinase inhibitors impair metabolism and endocrine system function: a systematic updated review. Leuk Res 38:1392–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2014.09.016
Brem H, Tomic-Canic M (2007) Cellular and molecular basis of wound healing in diabetes. J Clin Invest 117:1219–1222. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI32169
Bruning A (2013) Inhibition of mTOR signaling by quercetin in cancer treatment and prevention. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 13:1025–1031. https://doi.org/10.2174/18715206113139990114
Burova E, Borodkina A, Shatrova A, Nikolsky N (2013) Sublethal oxidative stress induces the premature senescence of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from endometrium. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:474931. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/474931
Burton DG, Krizhanovsky V (2014) Physiological and pathological consequences of cellular senescence. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:4373–4386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1691-3
Bussian TJ, Aziz A, Meyer CF, Swenson BL, van Deursen JM, Baker DJ (2018) Clearance of senescent glial cells prevents tau-dependent pathology and cognitive decline. Nature 562:578–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0543-y
Campisi J (2013) Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer. Annu Rev Physiol 75:685–705. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183653
Castner SA, Gupta S, Wang D, Moreno AJ, Park C, Chen C, Poon Y, Groen A, Greenberg K, David N, Boone T, Baxter MG, Williams GV, Dubal DB (2023) Longevity factor klotho enhances cognition in aged nonhuman primates. Nat Aging. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-023-00441-x
Chandak P, Phillips BL, Uwechue R, Thompson E, Bates L, Ibrahim I, Sewpaul A, Figueiredo R, Olsburgh J, Hosgood S, Nicholson ML, Wilson C, Callaghan CJ (2019) Dissemination of a novel organ perfusion technique: ex vivo normothermic perfusion of deceased donor kidneys. Artif Organs 43:E308–E319. https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.13499
Chang J, Wang Y, Shao L, Laberge RM, Demaria M, Campisi J, Janakiraman K, Sharpless NE, Ding S, Feng W, Luo Y, Wang X, Aykin-Burns N, Krager K, Ponnappan U, Hauer-Jensen M, Meng A, Zhou D (2016) Clearance of senescent cells by ABT263 rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Nat Med 22:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4010
Chen-Yoshikawa TF (2021) Ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation. Cells-Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061333
Chiang JL, Kirkman MS, Laffel LM, Peters AL (2014) Type 1 Diabetes through the life span: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 37:2034–2054. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1140
Childs BG, Baker DJ, Wijshake T, Conover CA, Campisi J, van Deursen JM (2016) Senescent intimal foam cells are deleterious at all stages of Atherosclerosis. Science 354:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf6659
Coppe JP, Patil CK, Rodier F, Sun Y, Munoz DP, Goldstein J, Nelson PS, Desprez PY, Campisi J (2008) Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 Tumor suppressor. Plos Biol 6:2853–2868. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060301
Cudejko C, Wouters K, Fuentes L, Hannou SA, Paquet C, Bantubungi K, Bouchaert E, Vanhoutte J, Fleury S, Remy P, Tailleux A, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Dombrowicz D, Staels B, Paumelle R (2011) p16INK4a deficiency promotes IL-4-induced polarization and inhibits proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. Blood 118:2556–2566. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-10-313106
Dar WA, Sullivan E, Bynon JS, Eltzschig H, Ju C (2019) Ischaemia reperfusion injury in liver transplantation: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Liver Int 39:788–801. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14091
Davids MS, Roberts AW, Seymour JF, Pagel JM, Kahl BS, Wierda WG, Puvvada S, Kipps TJ, Anderson MA, Salem AH, Dunbar M, Zhu M, Peale F, Ross JA, Gressick L, Desai M, Kim SY, Verdugo M, Humerickhouse RA, Gordon GB, Gerecitano JF (2017) Phase I first-in-human study of venetoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory non-hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 35:826–833. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.70.4320
de Haan G, Lazare SS (2018) Aging of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 131:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-06-746412
Demaria M, Ohtani N, Youssef SA, Rodier F, Toussaint W, Mitchell JR, Laberge RM, Vijg J, Van Steeg H, Dolle ME, Hoeijmakers JH, de Bruin A, Hara E, Campisi J (2014) An essential role for senescent cells in optimal wound healing through secretion of PDGF-AA. Dev Cell 31:722–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.11.012
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, Acosta M, Scott G, Roskelley C, Medrano EE, Linskens M, Rubelj I, Pereira-Smith O, Et A (1995) A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9363–9367. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.20.9363
Dookun E, Walaszczyk A, Redgrave R, Palmowski P, Tual-Chalot S, Suwana A, Chapman J, Jirkovsky E, Donastorg SL, Gill E, Yausep OE, Santin Y, Mialet-Perez J, Andrew OW, Grieve D, Spyridopoulos I, Taggart M, Arthur HM, Passos JF, Richardson GD (2020) Clearance of senescent cells during cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury improves recovery. Aging Cell 19:e13249. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13249
Dungan CM, Murach KA, Zdunek CJ, Tang ZJ, VonLehmden GL, Brightwell CR, Hettinger Z, Englund DA, Liu Z, Fry CS, Filareto A, Franti M, Peterson CA (2022) Deletion of SA beta-gal+cells using senolytics improves muscle regeneration in old mice. Aging Cell 21:e13528. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13528
Enge M, Arda HE, Mignardi M, Beausang J, Bottino R, Kim SK, Quake SR (2017) Single-cell analysis of human pancreas reveals transcriptional signatures of aging and somatic mutation patterns. Cell 171:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.004
Evangelou K, Gorgoulis VG (2017) Sudan black B, the specific histochemical stain for lipofuscin: a novel method to detect senescent cells. Methods Mol Biol 1534:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6670-7_10
Fang EF, Hou Y, Palikaras K, Adriaanse BA, Kerr JS, Yang B, Lautrup S, Hasan-Olive MM, Caponio D, Dan X, Rocktaschel P, Croteau DL, Akbari M, Greig NH, Fladby T, Nilsen H, Cader MZ, Mattson MP, Tavernarakis N, Bohr VA (2019) Mitophagy inhibits amyloid-beta and tau pathology and reverses cognitive deficits in models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat Neurosci 22:401–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0332-9
Faragher RG, Kipling D (1998) How might replicative senescence contribute to human ageing? Bioessays 20:985–991. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199812)20:12%3C985::AID-BIES4%3E3.0.CO;2-A
Farooqi AA, Attar R, Yaylim I, Qureshi MZ, Todorovska M, Karatoprak GS, Najafi S, Sabitaliyevich UY, Zhenisovna TG, De Sousa DP, Lin X (2018) Piperlongumine as anticancer agent: the story so far about killing many birds with one stone. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 64:102–107
Ferguson D, Finck BN (2021) Emerging therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 17:484–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00507-z
Franzke B, Halper B, Hofmann M, Oesen S, Jandrasits W, Baierl A, Tosevska A, Strasser EM, Wessner B, Wagner KH (2015) The impact of six months strength training, nutritional supplementation or cognitive training on DNA damage in institutionalised elderly. Mutagenesis 30:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geu074
Fumagalli M, Rossiello F, Clerici M, Barozzi S, Cittaro D, Kaplunov JM, Bucci G, Dobreva M, Matti V, Beausejour CM, Herbig U, Longhese MP, D’Adda DFF (2012) Telomeric DNA damage is irreparable and causes persistent DNA-damage-response activation. Nat Cell Biol 14:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2466
Gao C, Wang Q, Chung SK, Shen J (2017) Crosstalk of metabolic factors and neurogenic signaling in adult neurogenesis: implication of metabolic regulation for mental and neurological diseases. Neurochem Int 106:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.02.001
Garrido AM, Kaistha A, Uryga AK, Oc S, Foote K, Shah A, Finigan A, Figg N, Dobnikar L, Jørgensen H, Bennett M (2022) Efficacy and limitations of senolysis in Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 118:1713–1727. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvab208
Geovanini GR, Libby P (2018) Atherosclerosis and inflammation: overview and updates. Clin Sci (Lond) 132:1243–1252. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20180306
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer’s disease and down’s syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:1131–1135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9
Gochi M, Kato F, Toriumi A, Kawagoe T, Yotsuya S, Ishii D, Otani M, Nishikawa Y, Furukawa H, Matsuno N (2020) A novel preservation solution containing quercetin and sucrose for porcine kidney transplantation. Transplantation Direct 6:e624. https://doi.org/10.1097/TXD.0000000000001077
Gonzales MM, Garbarino VR, Marques ZE, Petersen RC, Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Musi N, Seshadri S, Craft S, Orr ME (2022) Senolytic therapy to modulate the progression of Alzheimer’s Disease (SToMP-AD): a Pilot Clinical Trial. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 9:22–29. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2021.62
Gonzalez-Gualda E, Baker AG, Fruk L, Munoz-Espin D (2021) A guide to assessing cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo. Febs J 288:56–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15570
Gorgoulis V, Adams PD, Alimonti A, Bennett DC, Bischof O, Bishop C, Campisi J, Collado M, Evangelou K, Ferbeyre G, Gil J, Hara E, Krizhanovsky V, Jurk D, Maier AB, Narita M, Niedernhofer L, Passos JF, Robbins PD, Schmitt CA, Sedivy J, Vougas K, von Zglinicki T, Zhou D, Serrano M, Demaria M (2019) Cellular Senescence: defining a path Forward. Cell 179:813–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.005
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:4913–4917. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913
Harada CN, Natelson LM, Triebel KL (2013) Normal cognitive aging. Clin Geriatr Med 29:737–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2013.07.002
Hassan S, Samanta S, Dash R, Karpinski TM, Habibi E, Sadiq A, Ahmadi A, Bunagu S (2022) The neuroprotective effects of fisetin, a natural flavonoid in neurodegenerative diseases: focus on the role of oxidative stress. Front Pharmacol 13:1015835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1015835
Hayflick L, Moorhead PS (1961) The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 25:585–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6
He S, Sharpless NE (2017) Senescence in health and disease. Cell 169:1000–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.015
Hewitt G, Jurk D, Marques FD, Correia-Melo C, Hardy T, Gackowska A, Anderson R, Taschuk M, Mann J, Passos JF (2012) Telomeres are favoured targets of a persistent DNA damage response in ageing and stress-induced senescence. Nat Commun 3:708. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1708
Hickson LJ, Langhi PL, Bobart SA, Evans TK, Giorgadze N, Hashmi SK, Herrmann SM, Jensen MD, Jia Q, Jordan KL, Kellogg TA, Khosla S, Koerber DM, Lagnado AB, Lawson DK, LeBrasseur NK, Lerman LO, McDonald KM, McKenzie TJ, Passos JF, Pignolo RJ, Pirtskhalava T, Saadiq IM, Schaefer KK, Textor SC, Victorelli SG, Volkman TL, Xue A, Wentworth MA, Wissler GE, Zhu Y, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL (2019) Senolytics decrease senescent cells in humans: preliminary report from a clinical trial of Dasatinib plus Quercetin in individuals with diabetic Kidney Disease. Ebiomedicine 47:446–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.069
Holdt LM, Sass K, Gabel G, Bergert H, Thiery J, Teupser D (2011) Expression of Chr9p21 genes CDKN2B (p15(INK4b)), CDKN2A (p16(INK4a), p14(ARF)) and MTAP in human atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis 214:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.06.029
Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, Ritchie C, Baldwin A, Barber R, Burns A, Dening T, Findlay D, Holmes C, Hughes A, Jacoby R, Jones R, Jones R, McKeith I, Macharouthu A, O’Brien J, Passmore P, Sheehan B, Juszczak E, Katona C, Hills R, Knapp M, Ballard C, Brown R, Banerjee S, Onions C, Griffin M, Adams J, Gray R, Johnson T, Bentham P, Phillips P (2012) Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s Disease. N Engl J Med 366:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1106668
Iske J, Seyda M, Heinbokel T, Maenosono R, Minami K, Nian Y, Quante M, Falk CS, Azuma H, Martin F, Passos JF, Niemann CU, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Elkhal A, Tullius SG (2020) Senolytics prevent mt-DNA-induced inflammation and promote the survival of aged organs following transplantation. Nat Commun 11:4289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18039-x
Itahana K, Campisi J, Dimri GP (2007) Methods to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: the senescence-associated beta-galactosidase assay. Methods Mol Biol 371:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-361-5_3
Jeon OH, Kim C, Laberge RM, Demaria M, Rathod S, Vasserot AP, Chung JW, Kim DH, Poon Y, David N, Baker DJ, van Deursen JM, Campisi J, Elisseeff JH (2017) Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med 23:775–781. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4324
Jimenez-Aliaga K, Bermejo-Bescos P, Benedi J, Martin-Aragon S (2011) Quercetin and rutin exhibit antiamyloidogenic and fibril-disaggregating effects in vitro and potent antioxidant activity in APPswe cells. Life Sci 89:939–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2011.09.023
Jun JI, Lau LF (2010) The matricellular protein CCN1 induces fibroblast senescence and restricts fibrosis in cutaneous wound healing. Nat Cell Biol 12:676–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2070
Justice JN, Nambiar AM, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Pascual R, Hashmi SK, Prata L, Masternak MM, Kritchevsky SB, Musi N, Kirkland JL (2019) Senolytics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: results from a first-in-human, open-label, pilot study. Ebiomedicine 40:554–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.052
Kadoglou NP, Sailer N, Moumtzouoglou A, Kapelouzou A, Gerasimidis T, Liapis CD (2010) Aggressive lipid-lowering is more effective than moderate lipid-lowering treatment in carotid plaque stabilization. J Vasc Surg 51:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2009.07.119
Kannel WB, McGee DL (1979) Diabetes and glucose tolerance as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: the Framingham study. Diabetes Care 2:120–126. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.2.2.120
Kim SR, Jiang K, Ogrodnik M, Chen X, Zhu XY, Lohmeier H, Ahmed L, Tang H, Tchkonia T, Hickson LJ, Kirkland JL, Lerman LO (2019) Increased renal cellular senescence in murine high-fat diet: effect of the senolytic drug quercetin. Transl Res 213:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2019.07.005
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T (2017) Cellular senescence: a translational perspective. Ebiomedicine 21:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.04.013
Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T, Zhu Y, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD (2017) The clinical potential of senolytic drugs. J Am Geriatr Soc 65:2297–2301. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14969
Klassen DK, Edwards LB, Stewart DE, Glazier AK, Orlowski JP, Berg CL (2016) The OPTN deceased donor potential study: implications for policy and practice. Am J Transplant 16:1707–1714. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13731
Kopp HG, Hooper AT, Shmelkov SV, Rafii S (2007) Beta-galactosidase staining on bone marrow. The osteoclast pitfall. Histol Histopathol 22:971–976. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-22.971
Kuilman T, Michaloglou C, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS (2010) The essence of senescence. Genes Dev 24:2463–2479. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1971610
Kumari R, Jat P (2021) Mechanisms of cellular senescence: cell cycle arrest and senescence associated secretory phenotype. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:645593. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.645593
Lagoumtzi SM, Chondrogianni N (2021) Senolytics and senomorphics: natural and synthetic therapeutics in the treatment of aging and chronic diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 171:169–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.003
LaPak KM, Burd CE (2014) The molecular balancing act of p16(INK4a) in cancer and aging. Mol Cancer Res 12:167–183. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0350
Lee HW, Heo CH, Sen D, Byun HO, Kwak IH, Yoon G, Kim HM (2014) Ratiometric two-photon fluorescent probe for quantitative detection of beta-galactosidase activity in senescent cells. Anal Chem 86:10001–10005. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5031013
Lehmann M, Korfei M, Mutze K, Klee S, Skronska-Wasek W, Alsafadi HN, Ota C, Costa R, Schiller HB, Lindner M, Wagner DE, Gunther A, Konigshoff M (2017) Senolytic drugs target alveolar epithelial cell function and attenuate experimental lung fibrosis ex vivo. Eur Respir J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02367-2016
Li Z, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, Gao B, Li Y, Li R, Wang J (2021) Protective effects of fisetin on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury through alleviation of apoptosis and oxidative stress. Arch Med Res 52:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.10.009
Libby P (2016) Assisted living in the Atheroma: Elderly macrophages promote plaques. Cell Metab 24:779–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.11.013
Liu C, Feng X, Li Q, Wang Y, Li Q, Hua M (2016) Adiponectin, TNF-alpha and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 86:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2016.06.028
Lopez-Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153:1194–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
Maher P, Dargusch R, Ehren JL, Okada S, Sharma K, Schubert D (2011) Fisetin lowers methylglyoxal dependent protein glycation and limits the complications of diabetes. PLoS ONE 6:e21226. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0021226
Matsunaga T, Roesel MJ, Schroeter A, Xiao Y, Zhou H, Tullius SG (2022) Preserving and rejuvenating old organs for transplantation: novel treatments including the potential of senolytics. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 27:481–487. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOT.0000000000001019
Mattson MP, Arumugam TV (2018) Hallmarks of brain aging: adaptive and pathological modification by Metabolic States. Cell Metab 27:1176–1199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.05.011
Maximova A, Werry EL, Kassiou M (2021) Senolytics: a novel strategy for neuroprotection in ALS? Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222112078
Mehta P, Pawar A, Mahadik K, Bothiraja C (2018) Emerging novel drug delivery strategies for bioactive flavonol fisetin in biomedicine. Biomed Pharmacother 106:1282–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.079
Messina M, Diena D, Dellepiane S, Guzzo G, Lo SL, Fop F, Segoloni GP, Amoroso A, Magistroni P, Biancone L (2017) Long-term outcomes and discard rate of kidneys by decade of extended criteria donor age. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 12:323–331. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.06550616
Minamino T, Orimo M, Shimizu I, Kunieda T, Yokoyama M, Ito T, Nojima A, Nabetani A, Oike Y, Matsubara H, Ishikawa F, Komuro I (2009) A crucial role for adipose tissue p53 in the regulation of insulin resistance. Nat Med 15:1082–1087. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2014
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF, Mason RP (2011) Inflammation and the development of Atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 18:351–358. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.7591
Mohamad AN, Nor HN, Liew SL, Ugusman A (2020) Clinical review: navitoclax as a pro-apoptotic and anti-fibrotic agent. Front Pharmacol 11:564108. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.564108
Montero JC, Seoane S, Ocana A, Pandiella A (2011) Inhibition of SRC family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases by dasatinib: possible combinations in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 17:5546–5552. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2616
Musi N, Valentine JM, Sickora KR, Baeuerle E, Thompson CS, Shen Q, Orr ME (2018) Tau protein aggregation is associated with cellular senescence in the brain. Aging Cell 17:e12840. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12840
Nabavi SF, Braidy N, Habtemariam S, Sureda A, Manayi A, Nabavi SM (2016) Neuroprotective effects of Fisetin in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: from chemistry to medicine. Curr Top Med Chem 16:1910–1915. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026616666160204121725
Nasralla D, Coussios CC, Mergental H, Akhtar MZ, Butler AJ, Ceresa C, Chiocchia V, Dutton SJ, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Heaton N, Imber C, Jassem W, Jochmans I, Karani J, Knight SR, Kocabayoglu P, Malago M, Mirza D, Morris PJ, Pallan A, Paul A, Pavel M, Perera M, Pirenne J, Ravikumar R, Russell L, Upponi S, Watson C, Weissenbacher A, Ploeg RJ, Friend PJ (2018) A randomized trial of normothermic preservation in liver transplantation. Nature 557:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0047-9
Ogrodnik M, Miwa S, Tchkonia T, Tiniakos D, Wilson CL, Lahat A, Day CP, Burt A, Palmer A, Anstee QM, Grellscheid SN, Hoeijmakers J, Barnhoorn S, Mann DA, Bird TG, Vermeij WP, Kirkland JL, Passos JF, von Zglinicki T, Jurk D (2017) Cellular senescence drives age-dependent hepatic steatosis. Nat Commun 8:15691. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15691
Ogrodnik M, Zhu Y, Langhi L, Tchkonia T, Kruger P, Fielder E, Victorelli S, Ruswhandi RA, Giorgadze N, Pirtskhalava T, Podgorni O, Enikolopov G, Johnson KO, Xu M, Inman C, Palmer AK, Schafer M, Weigl M, Ikeno Y, Burns TC, Passos JF, von Zglinicki T, Kirkland JL, Jurk D (2019) Obesity-induced cellular senescence drives anxiety and impairs neurogenesis. Cell Metab 29:1061–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.008
Ogrodnik M, Evans SA, Fielder E, Victorelli S, Kruger P, Salmonowicz H, Weigand BM, Patel AD, Pirtskhalava T, Inman CL, Johnson KO, Dickinson SL, Rocha A, Schafer MJ, Zhu Y, Allison DB, von Zglinicki T, LeBrasseur NK, Tchkonia T, Neretti N, Passos JF, Kirkland JL, Jurk D (2021) Whole-body senescent cell clearance alleviates age-related brain inflammation and cognitive impairment in mice. Aging Cell 20:e13296. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13296
Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N (2015) Coordination of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis during ageing in C. Elegans. Nature 521:525–528. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14300
Palmer AK, Tchkonia T, LeBrasseur NK, Chini EN, Xu M, Kirkland JL (2015) Cellular Senescence in Type 2 Diabetes: a therapeutic opportunity. Diabetes 64:2289–2298. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1820
Palmer AK, Gustafson B, Kirkland JL, Smith U (2019a) Cellular senescence: at the nexus between ageing and Diabetes. Diabetologia 62:1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4934-x
Palmer AK, Xu M, Zhu Y, Pirtskhalava T, Weivoda MM, Hachfeld CM, Prata LG, van Dijk TH, Verkade E, Casaclang-Verzosa G, Johnson KO, Cubro H, Doornebal EJ, Ogrodnik M, Jurk D, Jensen MD, Chini EN, Miller JD, Matveyenko A, Stout MB, Schafer MJ, White TA, Hickson LJ, Demaria M, Garovic V, Grande J, Arriaga EA, Kuipers F, von Zglinicki T, LeBrasseur NK, Campisi J, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL (2019b) Targeting senescent cells alleviates obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction. Aging Cell 18:e12950. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12950
Pan J, Li D, Xu Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Chen M, Lin S, Huang L, Chung EJ, Citrin DE, Wang Y, Hauer-Jensen M, Zhou D, Meng A (2017) Inhibition of Bcl-2/xl with ABT-263 selectively kills senescent type II pneumocytes and reverses persistent pulmonary fibrosis induced by ionizing radiation in mice. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.02.216
Petersmann A, Muller-Wieland D, Muller UA, Landgraf R, Nauck M, Freckmann G, Heinemann L, Schleicher E (2019) Definition, classification and diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 127:S1–S7. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1018-9078
Prata L, Ovsyannikova IG, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL (2018) Senescent cell clearance by the immune system: emerging therapeutic opportunities. Semin Immunol 40:101275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2019.04.003
Preiss D, Seshasai SR, Welsh P, Murphy SA, Ho JE, Waters DD, DeMicco DA, Barter P, Cannon CP, Sabatine MS, Braunwald E, Kastelein JJ, de Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Pedersen TR, Tikkanen MJ, Sattar N, Ray KK (2011) Risk of incident Diabetes with intensive-dose compared with moderate-dose statin therapy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 305:2556–2564. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2011.860
Pu JL, Huang ZT, Luo YH, Mou T, Li TT, Li ZT, Wei XF, Wu ZJ (2021) Fisetin mitigates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating GSK3beta/AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 20:352–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2021.04.013
Quillin RR, Guarrera JV (2018) Hypothermic machine perfusion in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 24:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.25004
Raina P, Santaguida P, Ismaila A, Patterson C, Cowan D, Levine M, Booker L, Oremus M (2008) Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating Dementia: evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med 148:379–397. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-148-5-200803040-00009
Roos CM, Zhang B, Palmer AK, Ogrodnik MB, Pirtskhalava T, Thalji NM, Hagler M, Jurk D, Smith LA, Casaclang-Verzosa G, Zhu Y, Schafer MJ, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Miller JD (2016) Chronic senolytic treatment alleviates established vasomotor dysfunction in aged or atherosclerotic mice. Aging Cell 15:973–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12458
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Garon EB, Ribeiro DOM, Bonomi PD, Camidge DR, Chu Q, Giaccone G, Khaira D, Ramalingam SS, Ranson MR, Dive C, McKeegan EM, Chyla BJ, Dowell BL, Chakravartty A, Nolan CE, Rudersdorf N, Busman TA, Mabry MH, Krivoshik AP, Humerickhouse RA, Shapiro GI, Gandhi L (2012) Phase II study of single-agent navitoclax (ABT-263) and biomarker correlates in patients with relapsed small cell Lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18:3163–3169. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3090
Saez-Atienzar S, Masliah E (2020) Cellular senescence and Alzheimer Disease: the egg and the chicken scenario. Nat Rev Neurosci 21:433–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-0325-z
Sanchez-Diaz L, Espinosa-Sanchez A, Blanco JR, Carnero A (2022) Senotherapeutics in cancer and HIV. Cells-Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071222
Schafer MJ, White TA, Iijima K, Haak AJ, Ligresti G, Atkinson EJ, Oberg AL, Birch J, Salmonowicz H, Zhu Y, Mazula DL, Brooks RW, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Pirtskhalava T, Prakash YS, Tchkonia T, Robbins PD, Aubry MC, Passos JF, Kirkland JL, Tschumperlin DJ, Kita H, LeBrasseur NK (2017) Cellular senescence mediates fibrotic pulmonary Disease. Nat Commun 8:14532. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14532
Schoenwaelder SM, Jarman KE, Gardiner EE, Hua M, Qiao J, White MJ, Josefsson EC, Alwis I, Ono A, Willcox A, Andrews RK, Mason KD, Salem HH, Huang DC, Kile BT, Roberts AW, Jackson SP (2011) Bcl-xL-inhibitory BH3 mimetics can induce a transient thrombocytopathy that undermines the hemostatic function of platelets. Blood 118:1663–1674. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-04-347849
Shafran D, Kodish E, Tzakis A (2014) Organ shortage: the greatest challenge facing transplant medicine. World J Surg 38:1650–1657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2639-3
Shao Z, Wang B, Shi Y, Xie C, Huang C, Chen B, Zhang H, Zeng G, Liang H, Wu Y, Zhou Y, Tian N, Wu A, Gao W, Wang X, Zhang X (2021) Senolytic agent Quercetin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the Nrf2/NF-kappaB axis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 29:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2020.11.006
Son DJ, Kim SY, Han SS, Kim CW, Kumar S, Park BS, Lee SE, Yun YP, Jo H, Park YH (2012) Piperlongumine inhibits atherosclerotic plaque formation and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by suppressing PDGF receptor signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.09.061
Sone H, Kagawa Y (2005) Pancreatic beta cell senescence contributes to the pathogenesis of type 2 Diabetes in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Diabetologia 48:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-004-1605-2
Song B, Guan S, Lu J, Chen Z, Huang G, Li G, Xiong Y, Zhang S, Yue Z, Deng X (2013) Suppressive effects of fisetin on mice T lymphocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Surg Res 185:399–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.05.093
Stein LR, Imai S (2014) Specific ablation of Nampt in adult neural stem cells recapitulates their functional defects during aging. Embo J 33:1321–1340. https://doi.org/10.1002/embj.201386917
Storer M, Mas A, Robert-Moreno A, Pecoraro M, Ortells MC, Di Giacomo V, Yosef R, Pilpel N, Krizhanovsky V, Sharpe J, Keyes WM (2013) Senescence is a developmental mechanism that contributes to embryonic growth and patterning. Cell 155:1119–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.041
Szaniawski MA, Spivak AM (2020) Senotherapeutics for HIV and aging. Curr Opin Hiv Aids 15:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/COH.0000000000000609
Tan SY, Mei WJ, Sim YJ, Wong SS, Mohamed ES, Tan SH, Ling LG, Rong TN, Annan NC, Bhattamisra SK, Candasamy M (2019) Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a review on current treatment approach and gene therapy as potential intervention. Diabetes Metab Syndr 13:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2018.10.008
Thompson PJ, Shah A, Ntranos V, Van Gool F, Atkinson M, Bhushan A (2019) Targeted elimination of senescent Beta cells prevents type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab 29:1045–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.01.021
Thongsom S, Suginta W, Lee KJ, Choe H, Talabnin C (2017) Piperlongumine induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma cells through the ROS-JNK-ERK signaling pathway. Apoptosis 22:1473–1484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1422-y
Tullius SG, Milford E (2011) Kidney allocation and the aging immune response. N Engl J Med 364:1369–1370. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1103007
Tullius SG, Rabb H (2018) Improving the supply and quality of deceased-donor organs for transplantation. N Engl J Med 379:693–694. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1808003
Tullius SG, Reutzel-Selke A, Egermann F, Nieminen-Kelha M, Jonas S, Bechstein WO, Volk HD, Neuhaus P (2000) Contribution of prolonged ischemia and donor age to chronic renal allograft dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.V1171317
Vergoni B, Cornejo PJ, Gilleron J, Djedaini M, Ceppo F, Jacquel A, Bouget G, Ginet C, Gonzalez T, Maillet J, Dhennin V, Verbanck M, Auberger P, Froguel P, Tanti JF, Cormont M (2016) DNA damage and the activation of the p53 pathway mediate alterations in metabolic and secretory functions of adipocytes. Diabetes 65:3062–3074. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-0014
Victorelli S, Passos JF (2019) Reactive oxygen species detection in senescent cells. Methods Mol Biol 1896:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8931-7_3
Wang DM, Li SQ, Wu WL, Zhu XY, Wang Y, Yuan HY (2014) Effects of long-term treatment with quercetin on cognition and mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 39:1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1343-x
Wang J, Uryga AK, Reinhold J, Figg N, Baker L, Finigan A, Gray K, Kumar S, Clarke M, Bennett M (2015) Vascular smooth muscle cell senescence promotes Atherosclerosis and features of Plaque vulnerability. Circulation 132:1909–1919. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016457
Wang L, Lankhorst L, Bernards R (2022) Exploiting senescence for the treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 22:340–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-022-00450-9
Wei W, Ji S (2018) Cellular senescence: molecular mechanisms and pathogenicity. J Cell Physiol 233:9121–9135. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26956
Wyss-Coray T (2006) Inflammation in Alzheimer Disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response? Nat Med 12:1005–1015. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1484
Xie N, Zhang L, Gao W, Huang C, Huber PE, Zhou X, Li C, Shen G, Zou B (2020) NAD(+) metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5:227. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00311-7
Xu M, Tchkonia T, Ding H, Ogrodnik M, Lubbers ER, Pirtskhalava T, White TA, Johnson KO, Stout MB, Mezera V, Giorgadze N, Jensen MD, LeBrasseur NK, Kirkland JL (2015) JAK inhibition alleviates the cellular senescence-associated secretory phenotype and frailty in old age. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E6301–E6310. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515386112
Xu M, Bradley EW, Weivoda MM, Hwang SM, Pirtskhalava T, Decklever T, Curran GL, Ogrodnik M, Jurk D, Johnson KO, Lowe V, Tchkonia T, Westendorf JJ, Kirkland JL (2017) Transplanted senescent cells induce an Osteoarthritis-like condition in mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 72:780–785. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glw154
Xu M, Pirtskhalava T, Farr JN, Weigand BM, Palmer AK, Weivoda MM, Inman CL, Ogrodnik MB, Hachfeld CM, Fraser DG, Onken JL, Johnson KO, Verzosa GC, Langhi L, Weigl M, Giorgadze N, LeBrasseur NK, Miller JD, Jurk D, Singh RJ, Allison DB, Ejima K, Hubbard GB, Ikeno Y, Cubro H, Garovic VD, Hou X, Weroha SJ, Robbins PD, Niedernhofer LJ, Khosla S, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL (2018) Senolytics improve physical function and increase lifespan in old age. Nat Med 24:1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0092-9
Xu P, Xiao J, Chi S (2021) Piperlongumine attenuates oxidative stress, inflammatory, and apoptosis through modulating the GLUT-2/4 and AKT signaling pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22763
Yan L, Jia Q, Cao H, Chen C, Xing S, Huang Y, Shen D (2021) Fisetin ameliorates Atherosclerosis by regulating PCSK9 and LOX-1 in apoE(-/-) mice. Exp Ther Med 21:25. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.9457
Yosef R, Pilpel N, Tokarsky-Amiel R, Biran A, Ovadya Y, Cohen S, Vadai E, Dassa L, Shahar E, Condiotti R, Ben-Porath I, Krizhanovsky V (2016) Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W and BCL-XL. Nat Commun 7:11190. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11190
Yoshino J, Baur JA, Imai SI (2018) NAD(+) intermediates: the Biology and therapeutic potential of NMN and NR. Cell Metab 27:513–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.11.002
Yousefzadeh MJ, Zhu Y, McGowan SJ, Angelini L, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Xu M, Ling YY, Melos KI, Pirtskhalava T, Inman CL, McGuckian C, Wade EA, Kato JI, Grassi D, Wentworth M, Burd CE, Arriaga EA, Ladiges WL, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Robbins PD, Niedernhofer LJ (2018) Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan. Ebiomedicine 36:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.015
Zaplatic E, Bule M, Shah S, Uddin MS, Niaz K (2019) Molecular mechanisms underlying protective role of quercetin in attenuating Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci 224:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.055
Zhang B, Lam EWF, Sun Y (2019a) Senescent cells: a new Achilles’ heel to exploit for cancer medicine? Aging Cell 18:e12875. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12875
Zhang P, Kishimoto Y, Grammatikakis I, Gottimukkala K, Cutler RG, Zhang S, Abdelmohsen K, Bohr VA, Misra SJ, Gorospe M, Mattson MP (2019b) Senolytic therapy alleviates Abeta-associated oligodendrocyte progenitor cell senescence and cognitive deficits in an Alzheimer’s Disease model. Nat Neurosci 22:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0372-9
Zhang L, Pitcher LE, Prahalad V, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD (2021) Recent advances in the discovery of senolytics. Mech Ageing Dev 200:111587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2021.111587
Zhu XH, Lu M, Lee BY, Ugurbil K, Chen W (2015a) In vivo NAD assay reveals the intracellular NAD contents and redox state in healthy human brain and their age dependences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:2876–2881. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417921112
Zhu Y, Tchkonia T, Pirtskhalava T, Gower AC, Ding H, Giorgadze N, Palmer AK, Ikeno Y, Hubbard GB, Lenburg M, O’Hara SP, LaRusso NF, Miller JD, Roos CM, Verzosa GC, LeBrasseur NK, Wren JD, Farr JN, Khosla S, Stout MB, McGowan SJ, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Gurkar AU, Zhao J, Colangelo D, Dorronsoro A, Ling YY, Barghouthy AS, Navarro DC, Sano T, Robbins PD, Niedernhofer LJ, Kirkland JL (2015b) The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: from transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell 14:644–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12344
Zhu Y, Tchkonia T, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Dai HM, Ling YY, Stout MB, Pirtskhalava T, Giorgadze N, Johnson KO, Giles CB, Wren JD, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD, Kirkland JL (2016) Identification of a novel senolytic agent, navitoclax, targeting the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic factors. Aging Cell 15:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12445
Zhu Y, Doornebal EJ, Pirtskhalava T, Giorgadze N, Wentworth M, Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg H, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL (2017) New agents that target senescent cells: the flavone, fisetin, and the BCL-X(L) inhibitors, A1331852 and A1155463. Aging 9:955–963. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101202
Funding
This work was financially supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant no. 30920041104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL Literature review, and writing of the original draft; SL Prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3 and 4; Tables 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5; KM and JK Conceptualization, supervision, and final reviewing and editing; All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Li, S., Ma, K. et al. Application potential of senolytics in clinical treatment. Biogerontology (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-023-10084-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-023-10084-5