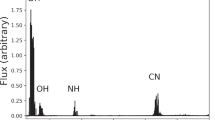
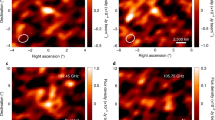
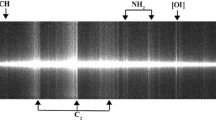
Abstract
This paper presents a prospect for the observations of comets with ALMA. Thanks to unprecedented sensitivity, angular resolution and instantaneous uv-coverage, key measurements on a number of topics related to the chemical and physical properties of the coma and the nucleus will be obtained. These include (1) the identification of new molecular species and measurements of key isotopic ratios, (2) measurements of the composition of short-period comets coming from the trans-Neptunian scattered disc, to investigate chemical diversity within the whole comet population, (3) imaging of gas jets and their relationship with dust features, (4) the study of extended sources of gas in the coma, and (5) the study of the physical and outgassing properties of the nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenhoff, W.J., et al.: Coordinated radio continuum observations of comets Hyakutake and Hale–Bopp from 22 to 860 GHz. Astron. Astrophys. 348, 1020–1034 (1999)
Altwegg, K., Bockelée-Morvan, D.: Isotopic abundances in comets. Space Sci. Rev., 139–154 (2003)
Biver, N.: Comets with ALMA. In: The Dusty and Molecular Universe: A Prelude to Herschel and ALMA, ESA SP-577, pp. 151–156 (2005)
Biver, N., et al.: Chemical composition diversity among 24 comets observed at radio wavelengths. Earth Moon, Planets 90, 323–333 (2002)
Biver, N., et al.: The 1995–2002 long-term monitoring of comet C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp) at radio wavelengths. Earth Moon, Planets 90, 5–14 (2002)
Bockelée-Morvan, D., et al.: New constraints on the origin of HNC. Asteroids, Comets, Meteors, Buzios, 7–12 August 2005
Bockelée-Morvan, D., et al.: New molecules found in comet C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp). Investing the link between cometary and interstellar material. Astron. Astrophys. 353, 1101–1114 (2000)
Bockelée-Morvan, D., et al.: The composition of cometary volatiles. In: Comets II, pp. 391–423. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (2004)
Boissier, J., et al.: Molecular spatial distributions observed in comet Hale–Bopp with IRAM Plateau de Bure interferometer. Astrophys. Space Sci. (2007, this volume)
Brownlee, D., et al.: Comet 81P/Wild 2 under a microscope. Science, 314, 1711–1716 (2007)
Ceccarelli, C., et al.: Extreme deuteration and hot corinos: the earliest chemical signatures of low-mass star formation. In: Protostars and Planets V, pp. 47–62. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (2007)
Crovisier, J., et al.: Ethylene glycol in comet C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp). Astron. Astrophys. 418, L35 (2004)
Crovisier, J., et al.: The composition of ices in comet C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp) from radio spectroscopy. Further results and upper limits on undetected species. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 1141–1157 (2004)
Fray, N., et al.: Heliocentric evolution of the degradation of polyoxymethylene: application to the origin of formaldehyde (H2CO) extended source in comet C/1995 O1 (Hale–Bopp). Icarus 184, 239–254 (2006)
Gibb, E., et al.: Methane in Oort cloud comets. Icarus 165, 391–406 (2003)
Henry, F., et al.: Observations of rotating jets of carbon monoxide in comet Hale–Bopp with the IRAM Interferometer. Earth Moon, Planets 90, 57–60 (2002)
Irvine, W.M., et al.: Comets: a link between interstellar and nebular chemistry. In: Protostars and Planets IV, pp. 1159–1200. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (2000)
Lamy, P., et al.: The sizes, shapes, albedos, and colors of cometary nuclei. In: Comets II, pp. 223–264. University of Arizona Press, Tucson (2004)
Rodgers, S.D., Charnley, S.B.: HNC and HCN in comets. Astrophys. J. 501, L227 (1998)
Rodgers, S.D., Charnley, S.B.: On the origin of HNC in Comet Lee. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 323, 84–92 (2001)
Snyder, L.E., et al.: BIMA array photodissociation measurements of HCN and CS in comet Hale–Bopp (C/1995 O1). Astron. J. 121, 1147–1154 (2001)
Wink, J., et al.: Evidences for extended sources and temporal modulations in molecular observations of C/1995 O1(Hale–Bopp) at the IRAM interferometer. Earth Moon, Planets 78, 63 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bockelée-Morvan, D. Cometary science with ALMA. Astrophys Space Sci 313, 183–189 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-007-9641-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-007-9641-2