Abstract
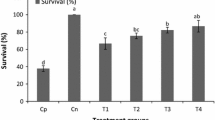
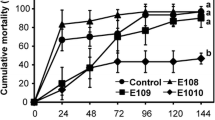
The aim of the present study was to investigate the influence of dietary supplementation with Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on the productive, intestinal histomorphometry, haemato-immunological aspects, as well as evaluated the resistance of juvenile Pseudoplatystoma sp. after challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila. Inclusion levels of the commercial probiotic were set at 0 (control), 1, 2, 3 and 4% of CALSPORIN® kg feed−1 with six replicates. Blood samples were collected on day 0, 10 and 20 for hematological analysis, and on the 20th day, samples were collected for intestinal histomorphometry, zootechnical and survival analyses. The results showed that probiotic supplementation with B. subtilis significantly improved intestinal morphology in fish from groups 1% and 2% and phagocytic activity in all supplemented groups, regardless of the applied dose. In addition, on the 20th day, improvements in non-specific immunity were observed, such as an increase in the number of monocytes (groups 2, 3 and 4%), eosinophils (group 3%), leukocytes (1%) and lymphocytes (group 4%) of the fish that received the supplemented feed. It was also possible to verify that the probiotic caused significant changes in the haemogram between the sampling periods on 0, 10th and 20th day, showing activation of specialized cells of the fish’s non-specific defense mechanism. At the end of the experimental period, supplementation of B. subtilis improved the productive indexes and survival of Pseudoplatystoma sp. after bacterial challenge.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly SM, Ahmed YA, Ghareeb AA, Mohamed MF (2008) Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:128–136
Amend DF (1981) Potency testing of fish vaccines. Dev Biol Stand 49:447–454
Balcázar JL, De Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Cunningham D, Vendrell D, Muzquiz JL (2006) The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet Microbiol 114(3–4):173–186
Boleli IC, Maiorka A, Macari M (2000) Estrutura funcional do trato digestório. In: Macari M, Furlan RL, Gonzalés EP (eds) Fisiologia aviária aplicada a frangos de corte. FUNEP/UNESP, Jaboticabal, pp 75–96c
Campos JL (2005) O cultivo do pintado. In: Baldisserotto B, Gomes LC (eds) Espécies nativas para piscicultura no Brasil. Ed. UFSM, Santa Maria, pp 327–342
Collier HB (1944) Standardization of blood haemoglobin determinations. Can Med Assoc J 50(6):550–552
Dawood MA, Koshio S, Abdel-Daim MM, Van Doan H (2019) Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev Aquac 11(3):907–924
Di J, Chu Z, Zhang S, Huang J, Du H, Wei Q (2019) Evaluation of the potential probiotic Bacillus subtilis isolated from two ancient sturgeons on growth performance, serum immunity and disease resistance of Acipenser dabryanus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 93:711–719
Dias DC, Furlaneto FPB, Ayroza LMS, Tachibana L, Romagosa E, Ranzani-Paiva MJT (2012) Probiotic in feeding of juvenile matrinxã (Brycon amazonicus): economic viability. Acta Scientiarum. Anim Sci 34(3):239–243
FAO (2018). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018-Meeting the sustainable development goals. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Farias THV, Levy-Pereira N, de Oliveira AL, de Carla DD, Tachibana L, Pilarski F, Ranzani-Paiva MJT (2016) Probiotic feeding improves the immunity of pacus, Piaractus mesopotamicus, during Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Anim Feed Sci Technol 211:137–144
Fazio F (2019) Fish hematology analysis as an important tool of aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 500:237–242
Gatesoupe FJ (1999) The use of probiotics in aquaculture. Aquaculture 180:147–165
Goldenfarb PB, Bowyer FP, Hall E, Brosious E (1971) Reproducibility in the hematology laboratory: the microhematocrit determination. Am J Clin Pathol 56(1):35–39
Green DH, Wakeley PR, Page EA, Barnes A, Baccigalupi L, Ricca E, Cutting SM (1999) Characterization of two Bacillus probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4288–4291
Hayatgheib N, Moreau E, Calvez S, Lepelletier D, Pouliquen H (2020) A review of functional feeds and the control of Aeromonas infections in freshwater fish. Aquacult Int 28:1083–1123
He S, Zhang Y, Xu L, Yang Y, Marubashi T, Zhou Z, Yao B (2013) Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on the production, intestinal cytokine expression and autochthonous bacteria of hybrid tilapia Oreochromis niloticus♀× Oreochromis aureus♂. Aquaculture 412:125–130
Hong HA, Duc LH, Cutting SM (2005) The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:813–835
Honorato CA, Ushizima TT, Santamaria FM, Flores-Quintana CI, Marcondes VM, Nascimento CA (2015) Desempenho produtivo e econômica de surubins (Pseudoplatystoma sp) alimentados com níveis de proteína e estocados em tanque-rede. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 67(5):1408–1414
Hrube TC, Smith SA (1998) Hematology of fish. In: Schalm’s veterinary hematology, 5th edn, pp 1120–1125
Inoue L, Hisano H, Ishikawa M, Rotta M, Senhorini J (2009) Princípios básicos para produção de alevinos de surubins (Pintado e Cachara). Embrapa Pantanal-Documentos (INFOTECA-E)
Interaminense JA, Vogeley JL, Gouveia CK, Portela RS, Oliveira JP, Silva SM, Bezerra RS (2019) Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis and Shewanella algae in expression profile of immune-related genes from hemolymph of Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 86:253–259
Kavitha M, Raja M, Perumal P (2018) Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquacult Rep 11:59–69
Kiron V (2012) Fish immune system and its nutritional modulation for preventive health care. Anim Feed Sci Tech 173(1–2):111–133
Kuebutornye FK, Abarike ED, Lu Y (2019) A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol 87:820–828
Kuebutornye FK, Abarike ED, Lu Y, Hlordzi V, Sakyi ME, Afriyie G, Wang Z, Li Y, Xie CX (2020) Mechanisms and the role of probiotic Bacillus in mitigating fish pathogens in aquaculture. Fish Physiol Biochem:1–23
Kumar R, Mukherjee SC, Ranjan R, Kayak SK (2008) Enhanced innate immune parameters in Labeo rohita (Ham.) following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 24:168–172
Liu CH, Chiu CH, Wang SW, Cheng W (2012) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, enhances the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33(4):699–706
Maiorka A, Boleli IC, Macari M (2002) Desenvolvimento e reparo da mucosa intestinal. In: Macari M, Furlan RL, Gonzales E (eds) Fisiologia aviária aplicada a frangos de corte. Jaboticabal, FUNEP/UNESP pp, pp 143–148
Martino RC, Cyrino JEP, Portz L, Trugo LC (2002) Performance and fatty acid composition of surubim (Pseudoplatystoma coruscans) fed diets with animal and plant lipids. Aquaculture 209(1–4):233–246
Mouriño JLP, do Vale Pereira G, do Nascimento Vieira F, Jatobá AB, Ushizima TT, da Silva BC, Seiffert WQ, GFA J, Martins ML (2016) Isolation of probiotic bacteria from the hybrid south American catfish Pseudoplatystoma reticulatum × Pseudoplatystoma corruscans (Siluriformes: Pimelodidae): a haematological approach. Aquacut Rep 3:166–171
Nakandakare IB, Iwashita MKP, Dias DDC, Tachibana L, Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Romagosa E (2013) Growth performance and intestinal histomorphology of Nile tilapia juveniles fed probiotics. Acta Sci Anim Sci 35(4):365–370
Nakandakare IB, Iwashita MKP, Danielle de Carla DIAS, Tachibana L, Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Romagosa E (2018) Incorporação de probióticos na dieta para juvenis de tilapias-do-Nilo: parâmetros hematológicos, imunológicos e microbiológicos. Bol Inst Pesca 39(2):121–135
Ochoa-Solano JL, Olmos-Soto J (2006) The functional property of Bacillus for shrimp feeds. Food Microbiol 23:519–525
Olmos SJ (2003) Molecular characterization and phylogenetic identification of marine microorganisms. In: X Congreso Nacional de Biotecnología y Bioingeniería. Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico
Olmos J, Acosta M, Mendoza G, Pitones V (2020) Bacillus subtilis, an ideal probiotic bacterium to shrimp and fish aquaculture that increase feed digestibility, prevent microbial diseases, and avoid water pollution. Arch Microbiol 202(3):427–435
Owatari MS, Jesus GFA, Cardoso L, Ferreira TH, Ferrarezi JVS, de Pádua PU, Mouriño JLP (2019) Different via to apply the Gamaxine® commercial biopromoter to Nile tilapia evaluating the immune system responses to Streptococcus agalactiae Ib. Aquaculture 503:254–266
Pal RR, Baidya AK, Mamou G, Bhattacharya S, Socol Y, Kobi S, Rosenshine I (2019) Pathogenic E. coli extracts nutrients from infected host cells utilizing injectisome components. Cell 177(3):683–696
Petri R (2000) Uso de exclusão competitiva na avicultura no Brasil. II Simpósio de sanidade avícola, Santa Maria
Raida MK, Larsen JL, Nilsen ME, Buchmann K (2003) Enhanced resistance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), against Yersinia ruckeri challenge following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis and B. licheniformis (BIOPLUS2B). J Fish Dis 26:495–498
Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Silva-Souza AT (2004) Hematologia de peixes brasileiros. Sanidade de organismos aquáticos São Paulo: Varela pp 89–120
Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Santos AA, de Carla Dias D, Seriani R, Egami MI (2008) Hematological and phagocytic response of the fat snook, Centropomus parallelus, reared in net cages, before and after inoculation with Sacharomyces ceresivisiae. Bioikos 22(1):29–35
Romanova E, Spirina E, Romanov V, Lyubomirova V, Shadyeva L (2020) Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on catfish in industrial aquaculture. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 175, p. 02013). EDP Sciences
Schamber CR (2008) Exigência de fósforo para a tilápia do Nilo (Oreochromis niloticus) na terminação. Universidade Estadual de Maringá (2008)
Silva JRMC, Staines NA, Hernandez-Blazquez FJ, PortoNeto LR, Borges JCS (2002) Phagocytosis and giant cell formation at 0°C by macrophage of Notothenia coriiceps. J Fish Biol 60:466–478
Silva JRMC, Porto-Neto LR, Borges JCS, Jensch-Junior BE (2005) Germicide capacity of macrophages in the Antartic fish Notothenia coriiceps (Richardson, 1844) at 0°C. Polar Biol 28(4):326–328
Silva LCR, Furuya WM, Natali MRM, Schamber CR, Santos LD, Vidal LVO (2010) Desempenho e morfometria intestinal de juvenis de tilápia-do-nilo alimentados com dietas suplementadas com L-glutamina e L-glutamato. R Bras Zootec 39(6):1175–1179
Silva BC, Mouriño JLP, Vieira FN, Jatobá A, Seiffert WQ, Martins ML (2012) Haemorrhagic septicaemia in the hybrid surubim (Pseudoplatystoma corruscans x Pseudoplatystoma fasciatum) caused by Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac Res 43:908–916
Silva EF, Soares MA, Calazans NF, Vogeley JL, Do Valle BC, Soares R, Peixoto S (2013) Effect of probiotic (Bacillus spp.) addition during larvae and postlarvae culture of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac Res 44:13–21
Sipaúba-Tavares LH, Ligeiro SR, Durigan JG (1995) Variação de alguns parâmetros limnológicos em um viveiro de piscicultura em função da luz. Acta Limnol Bras 7:138–150
Sonnenschein AL, Losick R, Hoch JA (1993) Bacillus subtilis and others gram-positive Bacteria: biochemistry, physiology and molecular genetics. American Society for Microbiology, Washington
Sugita H, Hirose Y, Matsuo N, Deguchi Y (1998) Production of the antibacterial substance by Bacillus sp. strain NM 12, an intestinal bacterium of Japanese coastal fish. Aquaculture 165:269–280
Tang Y, Han L, Chen X, Xie M, Kong W, Wu Z (2019) Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus subtilis affects antioxidant defenses and immune response in grass carp under Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Probiotics Antimicro 11(2):545–558
Tavares GC, de Queiroz GA, Assis GBN, Leibowitz MP, Teixeira JP, Figueiredo HCP, Leal CAG (2018) Disease outbreaks in farmed Amazon catfish (Leiarius marmoratus x Pseudoplatystoma corruscans) caused by Streptococcus agalactiae, S. iniae, and S. dysgalactiae. Aquaculture 495:384–392
Tavares-Dias M, Martins ML (2017) An overall estimation of losses caused by diseases in the Brazilian fish farms. J Parasit Dis 41(4):913–918
Tavares-Dias M, Moraes FR (2003) Características hematológicas da Tilapia rendalli Boulenger, 1896 (Osteichthyes: Cichlidae) capturada em “pesque-pague” de Franca, São Paulo, Brasil. Biosci J 19(1):107–114
Telli GS, Ranzani-Paiva MJT, de Carla Dias D, Sussel FR, Ishikawa CM, Tachibana L (2014) Dietary administration of Bacillus subtilis on hematology and non-specific immunity of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus raised at different stocking densities. Fish Shellfish Immunol 39(2):305–311
Tournut JR (1998) Probiotics. Reunião Anual Soc Bras Zootec 35:179–199
Veiga PT, Owatari MS, Nunes AL, Rodrigues RA, Kasai RYD, Fernandes CE, de Campos CM (2020) Bacillus subtilis C-3102 improves biomass gain, innate defense, and intestinal absorption surface of native Brazilian hybrid Surubim (Pseudoplatystoma corruscans x P. reticulatum). Aquacult Int 28:1183–1193
Yılmaz S, Ergun S, Yigit M, Çelik EŞ (2020) Effect of combination of dietary Bacillus subtilis and trans-cinnamic acid on innate immune responses and resistance of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss to Yersinia ruckeri. Aquac Res 51(2):441–454
Zhang D, Wu Z, Chen X, Wang H, Guo D (2019) Effect of Bacillus subtilis on intestinal apoptosis of grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella orally challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Sci 85(1):187–197
Zhao Y, Zhang W, Xu W, Mai K, Zhang Y, Liufu Z (2012) Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus subtilis T13 on growth, immunity and disease resistance against Vibrio splendidus infection in juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32(5):750–755
Zhou S, Song D, Zhou X, Mao X, Zhou X, Wang S, Qin Q (2019) Characterization of Bacillus subtilis from gastrointestinal tract of hybrid Hulong grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × E. lanceolatus) and its effects as probiotic additives. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:1115–1124
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Council for Scientific Development (CNPq) for their financial support to the project entitled “Probiotic and immunostimulant in the production of surubim” (CNPq 552395/2011-0), grant to M.L. Martins (CNPq 306635/2018-6) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior Brasil (CAPES) Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
- Short term of probiotic feeding evaluation in the diet of Brazilian native catfish Pseudoplatystoma sp.
- B. subtilis causes significant improvements in non-specific fish immunity.
- Probiotic feeding increases resistance to A. hydrophila.
- Short-term supplementation leads to productive improvements in Pseudoplatystoma sp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nunes, A.L., Owatari, M.S., Rodrigues, R.A. et al. Effects of Bacillus subtilis C-3102-supplemented diet on growth, non-specific immunity, intestinal morphometry and resistance of hybrid juvenile Pseudoplatystoma sp. challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquacult Int 28, 2345–2361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00586-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-020-00586-1