Abstract
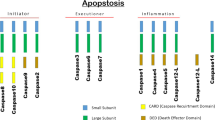
The death domain (DD), which is a versatle protein interaction module, is the prime mediator of the interactions necessary for apoptosis, innate immunity and the necrosis signaling pathway. Because DD mediated signaling events are associated with critical human diseases, studies in these areas are of great biological importance. Accordingly, many biochemical and structural studies of DD have been conducted in the past decade to investigate apoptotic and innate immune signaling. Evaluation of the molecular structure of DD and their interactions with partners have shown the underlying molecular basis for the assembly of DD mediated complexes and for the regulation of apoptosis and innate immunity. This review summarizes the structure and function of various DDs and DD:DD complexes involved in those signaling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park HH, Lo YC, Lin SC, Wang L, Yang JK, Wu H (2007) The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling of apoptosis and inflammation. Ann Rev Immunol 25:561–586
Weber CH, Vincenz C (2001) The death domain superfamily: a tale of two interfaces? Trends Biochem Sci 26:475–481
Kohl A, Grutter MG (2004) Fire and death: the pyrin domain joins the death-domain superfamily. C R Biol 327:1077–1086
Reed JC, Doctor KS, Godzik A (2004) The domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE 239:re9
Jang TH, Zheng C, Wu H, Jeon JH, Park HH (2010) In vitro reconstitution of the interactions in the PIDDosome. Apoptosis 15:1444–1452
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K et al (1997) TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kB. Immunity 7:831–836
Hsu H, Xiong J, Goeddel DV (1995) The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kB activation. Cell 81:495–504
Hsu H, Shu H-B, Pan M-G, Goeddel DV (1996) TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 84:299–308
Duan H, Dixit VM (1997) RAIDD is a new ‘death’ adaptor molecule. Nature 385:86–89
Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X (1996) IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 271:1128–1131
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Yu G et al (1996) Signal transduction by DR3, a death domain-containing receptor related to TNF-R1 and CD95. Science 274:990–992
Cleveland JL, Ihle JN (1995) Contenders in FasL/TNF death signaling. Cell 81:479–482
Wajant H (2002) The Fas signaling pathway: more than a paradigm. Science 296:1635–1636
Pop C, Salvesen GS (2009) Human caspases: activation, specificity and regulation. J Biol Chem 284:21777–21781
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X (1997) Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90:405–413
Tinel A, Tschopp J (2004) The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress. Science 304:843–846
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1999) Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10964–10967
Muzio M, Stockwell BR, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1998) An induced proximity model for caspase-8 activation. JBC 273:2926–2930
Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H, Zhivotovsky B (2010) The unpredictable caspase-2: what can it do? Trends Cell Biol 20:150–159
Olsson M, Vakifahmetoglu H, Abruzzo PM, Hogstrand K, Grandien A, Zhivotovsky B (2009) DISC-mediated activation of caspase-2 in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 28:1949–1959
Bergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G et al (1998) Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 12:1304–1314
Tinel A, Janssens S, Lippens S et al (2007) Autoproteolysis of PIDD marks the bifurcation between pro-death caspase-2 and pro-survival NF-kappaB pathway. EMBO J 26:197–208
Janssens S, Tinel A, Lippens S, Tschopp J (2005) PIDD mediates NF-kappaB activation in response to DNA damage. Cell 123:1079–1092
Shi M, Vivian CJ, Lee KJ et al (2009) DNA-PKcs-PIDDosome: a nuclear caspase-2-activating complex with role in G2/M checkpoint maintenance. Cell 136:508–520
Lin Y, Ma W, Benchimol S (2000) Pidd, a new death-domain-containing protein, is induced by p53 and promotes apoptosis. Nat Genet 26:122–127
Fitzgerald KA, Palsson-McDermott EM, Bowie AG et al (2001) Mal (MyD88-adapter-like) is required for Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction. Nature 413:78–83
Muzio M, Ni J, Feng P, Dixit VM (1997) IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 278:1612–1615
Wesche H, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Li S, Cao Z (1997) MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 7:837–847
Kawai T, Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ 13:816–825
Wang Q, Dziarski R, Kirschning CJ, Muzio M, Gupta D (2001) Micrococci and peptidoglycan activate TLR2→MyD88→IRAK→TRAF→NIK→IKK→NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway that induces transcription of interleukin-8. Infect Immun 69:2270–2276
Xiao T, Towb P, Wasserman SA, Sprang SR (1999) Three-dimensional structure of a complex between the death domains of Pelle and Tube. Cell 99:545–555
Salvesen GS, Riedl SJ (2009) Structure of the Fas/FADD complex: a conditional death domain complex mediating signaling by receptor clustering. Cell Cycle 8:2723–2727
Jeong EJ, Bang S, Lee TH, Park YI, Sim WS, Kim KS (1999) The solution structure of FADD death domain. Structural basis of death domain interactions of Fas and FADD. J Biol Chem 274:16337–16342
Sukits SF, Lin LL, Hsu S, Malakian K, Powers R, Xu GY (2001) Solution structure of the tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 death domain. J Mol Biol 310:895–906
Park HH, Wu H (2006) Crystal structure of RAIDD death domain implicates potential mechanism of PIDDosome assembly. J Mol Biol 357:358–364
Scott FL, Stec B, Pop C et al (2009) The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering. Nature 457:1019–1022
Park HH, Logette E, Rauser S et al (2007) Death domain assembly mechanism revealed by crystal structure of the oligomeric PIDDosome core complex. Cell 128:533–546
Lin SC, Lo YC, Wu H. Helical assembly in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature 465: 885-890
Liepinsh E, Ilag LL, Otting G, Ibanez CF (1997) NMR structure of the death domain of the p75 neurotrophin receptor. EMBO J 16:4999–5005
Lasker MV, Gajjar MM, Nair SK (2005) Cutting edge: molecular structure of the IL-1R-associated kinase-4 death domain and its implications for TLR signaling. J Immunol 175:4175–4179
Huang B, Eberstadt M, Olejniczak ET, Meadows RP, Fesik SW (1996) NMR structure and mutagenesis of the Fas (APO-1/CD95) death domain. Nature 384:638–641
Park HH, Wu H (2007) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the oligomeric death-domain complex between PIDD and RAIDD. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 63:229–232
Holm L, Sander C (1995) Dali: a network tool for protein structure comparison. Trends Biochem Sci 20:478–480
Qin H, Srinivasula SM, Wu G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES, Shi Y (1999) Structural basis of procaspase-9 recruitment by the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1. Nature 399:549–557
Lawrence MC, Colman PM (1993) Shape complementarity at protein/protein interfaces. J Mol Biol 234:946–950
Belvin MP, Anderson KV (1996) A conserved signaling pathway: the Drosophila toll-dorsal pathway. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:393–416
Sun H, Towb P, Chiem DN, Foster BA, Wasserman SA (2004) Regulated assembly of the Toll signaling complex drives Drosophila dorsoventral patterning. EMBO J 23:100–110
Grosshans J, Schnorrer F, Nusslein-Volhard C (1999) Oligomerisation of Tube and Pelle leads to nuclear localisation of dorsal. Mech Dev 81:127–138
Sun H, Bristow BN, Qu G, Wasserman SA (2002) A heterotrimeric death domain complex in Toll signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12871–12876
Wang L, Yang JK, Kabaleeswaran V et al (2010) The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure reveals the basis of DISC assembly and disease mutations. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1324–1329
Esposito D, Sankar A, Morgner N, Robinson CV, Rittinger K, Driscoll PC (2010) Solution NMR investigation of the CD95/FADD homotypic death domain complex suggests lack of engagement of the CD95 C terminus. Structure 18:1378–1390
Park A, Baichwal VR (1996) Systematic mutational analysis of the death domain of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-associated protein TRADD. J Biol Chem 271:9858–9862
Micheau O, Tschopp J (2003) Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114:181–190
Stanger BZ, Leder P, Lee TH, Kim E, Seed B (1995) RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell 81:513–523
Hsu H, Huang J, Shu HB, Baichwal V, Goeddel DV (1996) TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 4:387–396
Gajate C, Mollinedo F (2005) Cytoskeleton-mediated death receptor and ligand concentration in lipid rafts forms apoptosis-promoting clusters in cancer chemotherapy. J Biol Chem 280:11641–11647
Darnay BG, Aggarwal BB (1997) Early events in TNF signaling: a story of associations and dissociations. J Leukoc Biol 61:559–566
Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM et al (1997) The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 276:111–113
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505–512
Juo P, Kuo CJ, Yuan J, Blenis J (1998) Essential requirement for caspase-8/FLICE in the initiation of the Fas-induced apoptotic cascade. Curr Biol 8:1001–1008
Kitson J, Raven T, Jiang YP et al (1996) A death-domain-containing receptor that mediates apoptosis. Nature 384:372–375
Chaudhary PM, Eby M, Jasmin A, Bookwalter A, Murray J, Hood L (1997) Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity 7:821–830
Jin Z, Li Y, Pitti R et al (2009) Cullin3-based polyubiquitination and p62-dependent aggregation of caspase-8 mediate extrinsic apoptosis signaling. Cell 137:721–735
Sprick MR, Weigand MA, Rieser E et al (2000) FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2. Immunity 12:599–609
Pan G, Bauer JH, Haridas V et al (1998) Identification and functional characterization of DR6, a novel death domain-containing TNF receptor. FEBS Lett 431:351–356
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D (1996) Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell 85:803–815
Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Wang L et al (1997) CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase-2, and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP. Cancer Res 57:615–619
Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L et al (2000) Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor. Nat Cell Biol 2:346–351
Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H (2002) IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:5567–5572
Berglund H, Olerenshaw D, Sankar A, Federwisch M, McDonald NQ, Driscoll PC (2000) The three-dimensional solution structure and dynamic properties of the human FADD death domain. J Mol Biol 302:171–188
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0020962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.H. Structural analyses of death domains and their interactions. Apoptosis 16, 209–220 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0571-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0571-z