Abstract
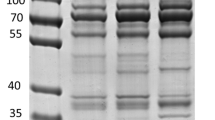
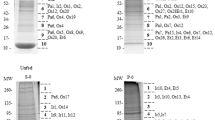
Antimicrobial midgut proteins and peptides that result from blood digestion in feeding American dog ticks Dermacentor variabilis (Say) were identified. Midgut extracts from these ticks showed antimicrobial activity against Micrococcus luteus, regardless of whether they were challenged with peptidoglycan, blood meal components, rabbit blood, Bacillus subtilis, Escherischia coli or Borrelia burgdorferi. However, no peptide band co-migrating with defensin was found in midgut extracts from the challenged ticks. Partial purification of the midgut extracts using C18 Sep Paks and gel electrophoresis showed the presence of 4 distinct bands with rMW 4.1, 5.3, 5.7 and 8.0 kDa identified by tryptic digestion-mass fingerprinting as digestive fragments of rabbit α-, β-7, γ-chain hemoglobin, and rabbit ubiquitin. No evidence of varisin, a defensin previously identified in the hemolymph of D. variabilis, was found in the tryptic digest, although varisin was found in a hemocyte lysate using the same methods. However, varisin transcript was detected in midgut cell lysates. Also present in all midgut samples was a cluster of 3 overlapping bands with rMW 13.0, 14.1 and 14.7 kDa which were identified by tryptic-digestion LC-MS and MALDI-TOF as rabbit α- and β-chain hemoglobin (undigested) and transtherytin. Lysozyme transcript was detected in midgut cell extracts but the peptide was not. Studies done on other tick species demonstrated that hemoglobin digestion resulted in antimicrobial fragments. Antimicrobial hemoglobin fragments (including fragments larger than any reported previously) also were found in D. variabilis, as well as ubiquitin, a peptide known to occur as part of an antimicrobial complex in vertebrate leukocytes. In addition, we noted that Borrelia burgdorferi spirochetes were not lysed in the midgut lumen, which would be expected if defensin and lysozyme were active in this location. In this respect, the midgut’s response to microbial challenge differs from that of the hemolymph. In summary, the midgut’s antimicrobial activity appears to be primarily a byproduct of hemoglobin digestion rather than expression of immune peptides and proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.D. Agyei N.W. Runham N. Blackstock (1991) ArticleTitleHistochemical localization of acid phosphatase and non-specific esterase in the midguts of two species of tick, Boophilus microplus Rhipicephalus appendiculatusas determined by light microscopy Parasitol. Res. 77 IssueID7 629–634 Occurrence Handle1724321
B. Beerntsen A.A. James B.M. Christensen (2000) ArticleTitleGenetics of mosquito vector competence Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64 115–137 Occurrence Handle10704476
N. Boulanger R. Brun L. Ehret-Sabatier C. Kunz P. Bulet (2002) ArticleTitleImmunopeptides in the defense reactions of Glossina morsitans to bacterial and Trypanosoma brucei brucei infections Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 32 369–375 Occurrence Handle11886771
S.M. Ceraul D.E. Sonenshine W.L. Hynes (2002) ArticleTitleInvestigations into the resistance of the tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Say) (Acari: Ixodidae) following challenge with the bacteriumEscherichi coli (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae) J. Med. Entomol. 39 376–383 Occurrence Handle11931039
S.M. Ceraul D.E. Sonenshine R.E. Ratzlaff W.L. Hynes (2003) ArticleTitleAn arthropod defensin expressed by the hemocytes of the American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 33 1099–1103 Occurrence Handle14563361
S.L. Cohen B.T. Chait (1997) ArticleTitleMass spectrometry of whole proteins eluted from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels Anal. Biochem. 247 257–267 Occurrence Handle10.1006/abio.1997.2072 Occurrence Handle9177686
L.B. Coons R. Rosell-Davis B.I. Tarnowski (1986) Bloodmeal digestion ticks J.R. Sauer J.A. Hair (Eds) Morphology, Physiology and Behavioral Biology of Ticks Ellis Horwood ChichesterUK 248–279
A.C. Fogaca P.I. da Silva SuffixJr. M.T. Miranda A.G. Bianchi A. Miranda P.E. Ribolla S. Daffre (1999) ArticleTitleAntimicrobial activity of a bovine hemoglobin fragment in the tick Boophilus microplus J. Biol. Chem. 274 25330–25334 Occurrence Handle10464258
J.P. Gillespie M.R. Kanost T. Trenczek (1997) ArticleTitleBiological mediators of insect immunity Annu. Rev. Entomol. 42 611–643 Occurrence Handle9017902
J.M. Gough D.H. Kemp (1995) ArticleTitleAcid phosphatase in midgut digestive cells in partially fed females of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus J. Parasitol. 81 341–349 Occurrence Handle7776118
L. Grunclova H. Fouguier V. Hypga P. Kopacek (2003) ArticleTitleLysozyme from the gut of the soft tick, Ornithodoros moubatathe sequencephylogeny and post-feeding regulation Develop. Comp. Immunol. 27 661–660 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0145-305X(03)00039-9
P.S. Hiemstra M.T. den Barselaar P.H. Nibbering R. van Furth (1999) ArticleTitleUbiquicidin, a novel murine microbicidal protein present in the cytosolic fraction of macrophages J. Leukoc. Biol. 66 426–428
R. Johns D.E. Sonenshine W.L. Hynes (2000) ArticleTitleResponses of the tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) to hemocoelic inoculation of Borrelia burgdorferi (Spirochetales) J. Med. Entomol. 37 265–270 Occurrence Handle10730498
R. Johns D.E. Sonenshine W.L. Hynes (2001a) ArticleTitleIdentification of a defensin from the hemolymph of the American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 31 857–865 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0965-1748(01)00031-5
R. Johns J. Ohnishi A. Broadwater D.E. Sonenshine A. deSilva W.L. Hynes (2001b) ArticleTitleContrasts in tick immune responses to Borrelia burgdorferi challenge: immunotolerance in Ixodes scapularis (L.) versus immunocompetence in Dermacentor variabilis J. Med. Entomol. 38 99–107
P. Kopacek R. Vogt L. Jindrak C. Weise I. Safarik (1999) ArticleTitlePurification and characterization of the lysozyme from the gut of the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 29 195–205
V. Kovar P. Kopacek L. Grubhoffer (2000) ArticleTitleIsolation and characterization of Dorin M, a lectin from plasma of the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30 195–205 Occurrence Handle10732987
M. Lebendiker (2004) Native acidic gel protocol Alexander Silberman Institute of Life Sciences Hebrew University, Israel
C.A. Lowenberger S. Kamal J. Chiles S. Paskewitz P. Bulet J.A. Hoffman B. Christensen (1999) ArticleTitleMosquito–Plasmodium interactions in response to immune activation of the vector Exp. Parasitol. 91 59–69 Occurrence Handle9920043
K.R. Macaluso D.E. Sonenshine C.M. Ceraul A.F. Azad (2001) ArticleTitleInfection and transovarial transmission of rickettsiae in Dermacentor variabilis ticks acquired by artificial feeding Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 1L 45–53 Occurrence Handle10.1089/153036601750137660
K.R. Macaluso D.E. Sonenshine S.M. Ceraul A.F. Azad (2002) ArticleTitleRickettsial infection in Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) inhibits transovarial transmission of a second Rickettsia J. Med. Entomol. 39 809–813 Occurrence Handle12495176
A. Mulenga O. Misao C. Sugimoto (2003) ArticleTitleThree serine proteinases from midguts of the hard tick Phipicephalus appendiculatus; cDNA cloning and preliminary characterization Exp. Appl. Acarol. 29 151–164 Occurrence Handle14580067
Y. Nakajima A. van Naters-Yasui D. Taylor M. Yamakawa (2002) ArticleTitleAntibacterial peptide defensin is involved in midgut immunity of the soft tick, Ornithodoros moubata Insect Mol. Biol. 11 611–618 Occurrence Handle12421419
Y. Nakajima K. Ogihara D. Taylor M. Yamakawa (2003) ArticleTitleAntibacterial hemoglobin fragments from the midgut of the soft tick, Ornithodoros moubata (Acari: Argasidae) J. Med. Entomol. 40 78–81 Occurrence Handle12597657
C.A. Parish H. Jiang Y. Tokiwa N. Berova K. Nakanishi D. McCabe W. Zuckerman M.M. Xi J.E. Gabay (2001) ArticleTitleBroad spectrum antimicrobial activity of hemoglobin Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9 377–382 Occurrence Handle11249130
J. Rao J.C. Herr P. Reddi M.J. Wolkowitz L.A. Bush N.E. Sherman M. Black C.J. Flickinger (2003) ArticleTitleCloning and characterization of a novel sperm associated iso-antigen (E-3) with defensin/lectin-like motifs exclusively expressed in rat epididymidis Biol. Reprod. 68 290–301 Occurrence Handle12493725
Y. Rechav M. Zyzak L.J. Fielden J.E. Childs (1999) ArticleTitleComparison of methods for introducing and producing artificial infection of ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) with Ehrlichia chaffeensis J. Med. Entomol. 36 414–419 Occurrence Handle10467766
A.M. Richman G. Dimopoulos D. Deelye F.C. Kafatos (1997) ArticleTitle Plasmodium activates the innate response of Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes EMBO J. 16 6114–6119 Occurrence Handle9321391
J.M. Ribeiro (1988) ArticleTitleThe midgut hemolysin of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) J. Parasitol. 74 532–537 Occurrence Handle3397814
D.E. Sonenshine (1991) Biology of Ticks, Vol. 1 Oxford University Press New York
D.E. Sonenshine (1993) Biology of Ticks, Vol. 2 Oxford University Press New York
D.E. Sonenshine P.J. Homsher J.S. VandeBerg D. Dawson (1981) ArticleTitleFine structure of the foveal glands and foveae dorsales of the American dog tick, Dermacentor variabilis (Say) J. Parasitol. 67 627–646 Occurrence Handle7299576
D.E. Sonenshine S.M. Ceraul W.L. Hynes K.R. Macaluso A.F. Azad (2002) ArticleTitleExpression of defensin-like peptides in tick hemolymph and midgut in response to challenge with Borrelia burgdorferi Bacillus subtilis Exp. Appl. Acarol. 28 127–134 Occurrence Handle14570122
I. Stojilkovic B.D. Evavold V. Kumar (2001) ArticleTitleAntimicrobial properties of porphyrins Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 10 309–320 Occurrence Handle11178343
J.A. Vaughan A.F. Azad (1993) ArticleTitlePatterns of erythrocyte digestion by bloodsucking insects: constraints on vector competence J. Med. Entomol. 30 214–216 Occurrence Handle8094460
J. Vizioli A.M. Richman J.S. Uttenweiler C. Blass P. Bulet (2001) ArticleTitleThe defensin peptide of the malaria vector mosquitoAnopheles gambiae: antimicrobial activities and expression in adult mosquitoes Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 31 241–248 Occurrence Handle11167093
K. Zhu J.W. Dillwith A.S. Bowman J.R. Sauer (1997) ArticleTitleIdentification of hemolytic activity in saliva of the lone star tick (Acari: Ixodidae) J. Med. Entomol. 34 160–166 Occurrence Handle9103758
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonenshine, D., Hynes, W., Ceraul, S. et al. Host Blood Proteins and Peptides in the Midgut of the Tick Dermacentor variabilis Contributeto Bacterial Control. Exp Appl Acarol 36, 207–223 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-005-2564-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-005-2564-0