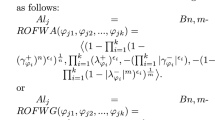Abstract
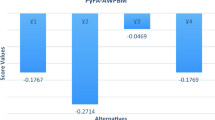
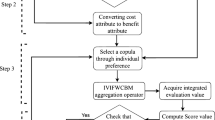
The MULTIMOORA is a relatively new multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) technique containing three major parts. It has partial and complete aggregation information. The MULTIMOORA procedure contains three major parts: the full multiplicative shape, ratio system, and reference point. Furthermore, the Muirhead mean (MM) operator can easily capture the interaction between any number of preferences. The main feature of this model is to evaluate the novel theory of complex Pythagorean fuzzy uncertain linguistic (CPFUL) settings and utilize their useful properties (“algebraic laws, score value, and accuracy value”). Additionally, we combined the main theory of MM operators with information taken from the theory of CPFUL to diagnose the major idea of the CPFUL Muirhead mean (CPFULMM), CPFUL weighted Muirhead mean (CPFULWMM), CPFUL dual Muirhead mean (CPFULDMM), and CPFUL dual weighted Muirhead mean (CPFULDWMM) operators. We then evaluated their valuable properties (“idempotency, Boundedness, and monotonicity”). Moreover, to enhance the worth and feasibility of the diagnosed approach, we elaborated the extension of the MULTIMOORA method under CPFUL information. We then diagnosed a procedure of the MADM scenario whilst considering the evaluated operators using the CPFUL set theory. Lastly, to compare the diagnosed information with some old operators, we used numerical examples to illustrate the flexibility and feasibility of the presented information.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this manuscript are artificial and can be used without permission from the authors if the present article is appropriately cited.
References
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Bal M, Ahmad KD, Hajjari AA, Ali R (2022) A short note on the kernel subgroup of intuitionistic fuzzy groups. J Neutroso Fuzzy Syst (JNFS) 2(1):14–20
Gohain B, Chutia R, Dutta P (2022) Distance measure on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application in decision-making, pattern recognition, and clustering problems. Int J Intell Syst 37(3):2458–2501
Jebadass JR, Balasubramaniam P (2022) Low light enhancement algorithm for color images using intuitionistic fuzzy sets with histogram equalization. Multimed Tools Appl 81(6):8093–8106
Garg H (2016) A new generalized improved score function of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and applications in expert systems. Appl Soft Comput 38:988–999
Yager RR (2013) Pythagorean fuzzy subsets. In 2013 joint IFSA world congress and NAFIPS annual meeting (IFSA/NAFIPS) (pp. 57-61). IEEE
Khan MJ, Ali MI, Kumam P, Kumam W, Aslam M, Alcantud JCR (2022) Improved generalized dissimilarity measure-based VIKOR method for Pythagorean fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 37(3):1807–1845
Sarkar B, Biswas A (2022) A multi-criteria decision making approach for strategy formulation using Pythagorean fuzzy logic. Expert Syst 39(1):e12802
Bhunia S, Ghorai G, Xin Q, Gulzar M (2022) On the algebraic attributes of (α, β)-Pythagorean fuzzy subrings and (α, β)-Pythagorean fuzzy ideals of rings. IEEE Access 10:11048–11056
Garg H (2018) Some methods for strategic decision-making problems with immediate probabilities in Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Int J Intell Syst 33(4):687–712
Ramot D, Milo R, Friedman M, Kandel A (2002) Complex fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10(2):171–186
Alkouri, A. M. D. J. S ,& Salleh, A. R. (2012) Complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets. In AIP conference proceedings (Vol. 1482, no. 1, pp. 464-470). American Institute of Physics
Garg H, Rani D (2019) Complex interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their aggregation operators. Fundamenta Informa 164(1):61–101
Rani D, Garg H (2017) Distance measures between the complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to the decision-making process. Int J Uncertain Quantif 7(5):423–439
Garg H, Rani D (2019) A robust correlation coefficient measure of complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications in decision-making. Appl Intell 49(2):496–512
Garg H, Rani D (2019) Novel aggregation operators and ranking method for complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to decision-making process. Artif Intell Rev:1–26
Ullah K, Mahmood T, Ali Z, Jan N (2020) On some distance measures of complex Pythagorean fuzzy sets and their applications in pattern recognition. Comp Intel Syst 6(1):15–27
Akram M, Naz S (2019) A novel decision-making approach under complex Pythagorean fuzzy environment. Mathema Compu App 24(3):73
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf Sci 8(3):199–249
Herrera F, Martínez L (2000) A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(6):746–752
Baležentis A, Baležentis T, Valkauskas R (2010) Evaluating situation of Lithuania in the European Union: structural indicators and MULTIMOORA method. Technol Econ Dev Econ 16(4):578–602
Hafezalkotob A, Hafezalkotob A (2016) Extended MULTIMOORA method based on Shannon entropy weight for materials selection. J Indust Engin Intern 12(1):1–13
Liu HC, Fan XJ, Li P, Chen YZ (2014) Evaluating the risk of failure modes with extended MULTIMOORA method under fuzzy environment. Eng Appl Artif Intell 34:168–177
Baležentis A, Baležentis T, Brauers WK (2012) Personnel selection based on computing with words and fuzzy MULTIMOORA. Expert Syst Appl 39(9):7961–7967
Liu Z, Liu P (2017) Intuitionistic uncertain linguistic partitioned Bonferroni means and their application to multiple attribute decision-making. Int J Syst Sci 48(5):1092–1105
Liu P, Liu Z, Zhang X (2014) Some intuitionistic uncertain linguistic Heronian mean operators and their application to group decision making. Appl Math Comput 230:570–586
Liu PD, Zhang X (2012) Intuitionistic uncertain linguistic aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. Syst Engin-Theory Prac 32(12):2704–2711
Lu M, Wei GW (2017) Pythagorean uncertain linguistic aggregation operators for multiple attribute decision making. Int J Knowl-based Intel Engin Syst 21(3):165–179
Liu Z, Liu P, Liu W, Pang J (2017) Pythagorean uncertain linguistic partitioned Bonferroni mean operators and their application in multi-attribute decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(3):2779–2790
Garg H, Rani D (2019) Generalized geometric aggregation operators based on t-norm operations for complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their application to decision-making. Cognitive Computation, 1–20
Garg H, Rani D (2020) Robust averaging–geometric aggregation operators for complex intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications to MCDM process. Arab J Sci Eng 45(3):2017–2033
Alkan Ö, Albayrak ÖK (2020) Ranking of renewable energy sources for regions in Turkey by fuzzy entropy based fuzzy COPRAS and fuzzy MULTIMOORA. Renew Energy 162:712–726
Fattahi R, Khalilzadeh M (2018) Risk evaluation using a novel hybrid method based on FMEA, extended MULTIMOORA, and AHP methods under fuzzy environment. Saf Sci 102:290–300
Zhang C, Chen C, Streimikiene D, Balezentis T (2019) Intuitionistic fuzzy MULTIMOORA approach for multi-criteria assessment of the energy storage technologies. Appl Soft Comput 79:410–423
Zavadskas EK, Antucheviciene J, Razavi Hajiagha SH, Hashemi SS (2015). The interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy MULTIMOORA method for group decision making in engineering Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015
Zhao H, You JX, Liu HC (2017) Failure mode and effect analysis using MULTIMOORA method with continuous weighted entropy under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Soft Comput 21(18):5355–5367
Lv L, Li H, Wang L, Xia Q, Ji L (2019) Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) with extended MULTIMOORA method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set: application in operational risk evaluation for infrastructure. Information 10(10):313
Huang C, Lin M, Xu Z (2020) Pythagorean fuzzy MULTIMOORA method based on distance measure and score function: its application in multicriteria decision making process. Knowl Inf Syst 62(11):4373–4406
Li XH, Huang L, Li Q, Liu HC (2020) Passenger satisfaction evaluation of public transportation using pythagorean fuzzy MULTIMOORA method under large group environment. Sustainability 12(12):4996
Liang D, Darko AP, Zeng J (2020) Interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy power average-based MULTIMOORA method for multi-criteria decision-making. J Exper Theore Artificial Intel 32(5):845–874
Liu P, Li D (2017) Some Muirhead mean operators for intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and their applications to group decision making. PLoS One 12(1):e0168767
Qin Y, Cui X, Huang M, Zhong Y, Tang Z, Shi P (2020) Linguistic interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy archimedean power muirhead mean operators for multiattribute group decision-making Complexity, 2020
Xu W, Shang X, Wang J, Li W (2019) A novel approach to multi-attribute group decision-making based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy power Muirhead mean. Symmetry 11(3):441
Liu Y, Liu J, Qin Y (2020) Pythagorean fuzzy linguistic Muirhead mean operators and their applications to multiattribute decision-making. Int J Intell Syst 35(2):300–332
Tang X, Wei G, Gao H (2019) Models for multiple attribute decision making with interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy muirhead mean operators and their application to green suppliers selection. Informatica 30(1):153–186
Li L, Zhang R, Wang J, Zhu X, Xing Y (2018) Pythagorean fuzzy power Muirhead mean operators with their application to multi-attribute decision making. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(2):2035–2050
Tang X, Wei G, Gao H (2019) Pythagorean fuzzy Muirhead mean operators in multiple attribute decision making for evaluating of emerging technology commercialization. Eco research-Ekonomska istraživanja 32(1):1667–1696
Zhu J, Li Y (2018) Pythagorean fuzzy Muirhead mean operators and their application in multiple-criteria group decision-making. Information 9(6):142
Cao Y, Li H, Su L (2020) Decision-making for project delivery system with related-indicators based on pythagorean fuzzy weighted muirhead mean operator. Information 11(9):451
Xu Y, Shang X, Wang J (2018) Pythagorean fuzzy interaction Muirhead means with their application to multi-attribute group decision-making. Information 9(7):157
Ali Z, Mahmood T (2020) Maclaurin symmetric mean operators and their applications in the environment of complex q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets. Comput Appl Math 39:1–27
Mahmood T, Ali Z (2021) Entropy measure and TOPSIS method based on correlation coefficient using complex q-rung orthopair fuzzy information and its application to multi-attribute decision making. Soft Comput 25(2):1249–1275
Ali Z, Mahmood T, Yang MS (2020) Complex T-spherical fuzzy aggregation operators with application to multi-attribute decision making. Symmetry 12(8):1311
Ali Z, Mahmood T, Yang MS (2020) TOPSIS method based on complex spherical fuzzy sets with Bonferroni mean operators. Mathematics 8(10):1739
Mahmood T, Ullah K, Khan Q, Jan N (2019) An approach toward decision-making and medical diagnosis problems using the concept of spherical fuzzy sets. Neural Comput & Applic 31(11):7041–7053
Umetani, S., & Murakami, S. (2022). Coordinate descent heuristics for the irregular strip packing problem of rasterized shapes. European journal of operational research. 303(3), 1009-1026, 2022
Juang CF, Chang CW, Hung TH (2021) Hand palm tracking in monocular images by fuzzy rule-based fusion of explainable fuzzy features with robot imitation application. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(12):3594–3606
Dong Y, Li X, Dezert J, Zhou R, Zhu C, Wei L, Ge SS (2021) Evidential reasoning with hesitant fuzzy belief structures for human activity recognition. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(12):3607–3619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, X., Ali, Z., Mahmood, T. et al. An approach for combining MULTIMOORA method and Muirhead mean operators based on the complex Pythagorean fuzzy uncertain linguistic representation model. Appl Intell 53, 17561–17592 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04408-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04408-0