Abstract
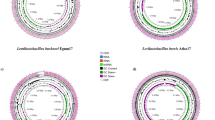
A white-colony-forming, facultative anaerobic, motile and Gram-stain-negative bacterium, designated G-1-2-2 T was isolated from soil of agriculture field near Kyonggi University, Republic of Korea. Strain G-1-2-2 T synthesized the polyhydroxybutyrate and could grow at 10–35 °C. The phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that, strain G-1-2-2 T formed a lineage within the family Comamonadaceae and clustered as a member of the genus Ramlibacter. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain G-1-2-2 T showed high sequence similarities with Ramlibacter ginsenosidimutans BXN5-27 T (97.9%), Ramlibacter monticola G-3-2 T (97.9%) and Ramlibacter alkalitolerans CJ661T (97.5%). The sole respiratory quinone was ubiquinone-8 (Q-8). The major polar lipids were phosphatidylethanolamine, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol, and an unidentified phospholipid. The principal cellular fatty acids were C16:0, cyclo-C17:0, summed feature 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c) and summed feature 8 (C18:1ω7c and/or C18:1ω6c). The genome of strain G-1-2-2 T was 7,200,642 bp long with 13 contigs, 6,647 protein-coding genes, and DNA G + C content of 68.9%. The average nucleotide identity and in silico DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain G-1-2-2 T and close members were ≤ 81.2 and 24.1%, respectively. The genome of strain G-1-2-2 T showed eight putative biosynthetic gene clusters responsible for various secondary metabolites. Genome mining revealed the presence of atoB, atoB2, phaS, phbB, phbC, and bhbD genes in the genome which are responsible for polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis. Based on these data, strain G-1-2-2 T represents a novel species in the genus Ramlibacter, for which the name Ramlibacter agri sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is G-1-2-2 T (= KACC 21616 T = NBRC 114389 T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Blin K, Shaw S, Steinke K et al (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W81–W87
Catone MV, Ruiz JA, Castellanos M et al (2014) High polyhydroxybutyrate production in Pseudomonas extremaustralis is associated with differential expression of horizontally acquired and core genome polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase genes. PLoS One 9:e98873
Chaudhary DK, Kim J (2017) Ramlibacter monticola sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4468–4474
Dahal RH, Kim J (2018) Fluviicola kyonggii sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from forest soil and emended description of the genus Fluviicola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1885–1889
Dahal RH, Chaudhary DK, Kim J (2018) Pinisolibacter ravus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from pine forest soil and allocation of the genera Ancalomicrobium and Pinisolibacter to the family Ancalomicrobiaceae fam. nov., and emendation of the genus Ancalomicrobium Staley 1968. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1955–1962
Doetsch RN (1981) Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: Gerdhardt P, Murray RGE, Costilow RN et al (eds) Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American society for microbiology, Washington, pp 21–33
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S et al (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2461–2470
Getachew A, Woldesenbet F (2016) Production of biodegradable plastic by polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) accumulating bacteria using low cost agricultural waste material. BMC Res Notes 9:1–9
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucl Acids Res 36:W181–W184
Heulin T, Barakat M, Christen R et al (2003) Ramlibacter tataouinensis gen. nov., sp. nov., and Ramlibacter henchirensis sp. nov., cyst-producing bacteria isolated from subdesert soil in Tunisia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:589–594
Kim HM, Han DM, Chun BH et al (2021) Ramlibacter algicola sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater alga Cryptomonas obovoidea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71:005010
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1988) 4 lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA et al (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108
Lee DH, Cha CJ (2017) Ramlibacter alkalitolerans sp. nov., alkali-tolerant bacterium isolated from soil of ginseng. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4619–4623
Lee HJ, Lee SH, Lee SS et al (2014) Ramlibacter solisilvae sp. nov., isolated from forest soil, and emended description of the genus Ramlibacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1317–1322
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha S-M et al (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2053–2057
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Sard JS, Carbasse S et al (2021) TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucl Acids Res 50:D801
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M et al (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Mostafa YS, Alrumman SA, Alamri SA et al (2020) (2020) Bioplastic (poly-3-hydroxybutyrate) production by the marine bacterium Pseudodonghicola xiamenensis through date syrup valorization and structural assessment of the biopolymer. Sci Reports 101(10):1–13
Muneer F, Rasul I, Azeem F et al (2020) Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs): efficient replacement of synthetic polymers. J Polym Environ 28:2301–2323
Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH et al (2018) UBCG: Up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:281–285
Parte AC, Carbasse JS, Meier-Kolthoff JP et al (2020) List of Prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:5607–5612
Props R, Monsieurs P, Vandamme P et al (2019) Gene expansion and positive selection as bacterial adaptations to oligotrophic conditions. mSphere. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphereDirect.00011-19
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:19126–19131
Sasser M (1990) Bacterial identification by gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid methyl esters (GC-FAME). MIDI Tech Note 101 Newark, MIDI Inc;1990
Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucl Acids Res 33:W686–W689
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American society for microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Spiekermann P, Rehm BHA, Kalscheuer R et al (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171:73–80
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A et al (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucl Acids Res 44:6614–6624
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Lim J et al (2017a) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S et al (2017b) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214
Zhang XJ, Da FG, Yao Q et al (2019) Ramlibacter humi sp. nov., isolated from tropical forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:3460–3464
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Aharon Oren (The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel) for his expert suggestions concerning the correct species epithet and etymology.
Funding
This paper was supported by the Semyung University Research Grant of 2020. This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2019R1F1A1058501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.H.D., JM.K., D.K.C. conceived, designed and conducted all the experiments. D.U.K. and T.T.N.L. interpreted the data. J.K. and H.J. coordinated and supervised the study. R.H.D., J.K., D.K.C. and D.U.K. analysed all the data and prepared the manuscript. All the authors read, discussed, edited and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Data availability
The genome sequence and 16 s rRNA gene sequence are publicly available in NCBI database.
Ethical Statement
This study does not describe any experimental work related to human.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahal, R.H., Kim, J., Chaudhary, D.K. et al. Genome mining revealed polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis by Ramlibacter agri sp. nov., isolated from agriculture soil in Korea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 115, 563–572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-022-01721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-022-01721-z