Abstract
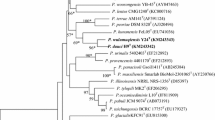
Strain R33T, an endophyte recovered from Herbertus sendtneri, was identified as representing a novel species of the genus Paenibacillus by using a polyphasic taxonomic approach. The novel strain was observed to be a Gram-stain positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, motile and endospore-forming bacterium. The major polar lipids of strain R33T were identified as diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, along with lesser amounts of phosphatidylglycerol, three unidentified aminophospholipids, two unidentified phospholipids and two unidentified lipids. The predominant isoprenoid quinone was identified as MK-7. The major fatty acids (>8.0 %) were found to be anteiso-C15:0 (40.0 %), C16:1 ω11c (9.4 %), C16:1 ω7c alcohol (8.5 %) and C16:0 (8.2 %). The diamino acid found in the cell-wall peptidoglycan was meso-diaminopimelic acid. The G+C content of genomic DNA was determined to be 56.9 mol%. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities of strain R33T to other Paenibacillus species ranged from 91.6 to 97.2 %, with high similarities to Paenibacillus humicus PC-147T and Paenibacillus pasadenensis SAFN-007T. The phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequences and the partial rpoB gene confirmed that strain R33T belongs to the genus Paenibacillus. However, strain R33T shows differential molecular characteristics compared to other related Paenibacillus species based on 16S rDNA-RFLP analyses; the DNA–DNA relatedness values between strain R33T and P. humicus PC-147T, and that between strain R33T and P. pasadenensis SAFN-007T, were 35.0 ± 2.0 and 41.4 ± 0.9 %, respectively. Based on its phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic properties, strain R33T is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Paenibacillus, for which the name Paenibacillus herberti is proposed (type strain R33T = CGMCC 1.15042T = DSM 29849T).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ash C, Priest FG, Collins MD (1993) Molecular identification of ribosomal RNA group 3 Bacilli (Ash, Farrow, Wallbanks and Collins) using a PCR probe test-proposal for the creation of a new genus Paenibacillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 64:253–260
Baik KS, Choe HN, Park SC, Kim EM, Seong CN (2011) Paenibacillus wooponensis sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2763–2768
Cao Y, Chen F, Li Y, Wei S, Wang G (2015) Paenibacillus ferrarius sp. nov., isolated from iron mineral soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:165–170
Chen L, Wang L, Sheng X-F (2015) Paenibacillus qingshengii sp. nov., isolated from lead-zinc tailing in Nanjing. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol doi:10.1099/ijs.0.000232
Daane LL, Harjono I, Barns SM, Launen LA, Palleroni NJ, Haggblom MM (2002) PAH-degradation by Paenibacillus spp. and description of Paenibacillus naphthalenovorans sp. nov., a naphthalene-degrading bacterium from the rhizosphere of salt marsh plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:131–139
Dong X-Z, Cai M-Y (2001) Determination of biochemical properties. Manual for the systematic identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing, pp 370–398 (In Chinese)
Elo S, Suominen I, Kampfer P, Juhanoja J, Salkinoja-Salonen M, Haahtela K (2001) Paenibacillus borealis sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species isolated from spruce forest humus in Finland. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:535–545
Gillis M, Deley J, Decleene M (1970) Determination of molecular weight of bacterial genome DNA from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:143–153
Han L-L, He J-Z, Zheng Y-M, Zeng J, Zhang L-M (2015) Paenibacillus tibetensis sp. nov., a novel psychrophilic bacterium isolated from alpine swamp meadow soil in Tibet, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol doi:10.1099/ijs.0.000141
Hong Y-Y, Ma Y-C, Zhou Y-G, Gao F, Liu H-C, Chen S-F (2009) Paenibacillus sonchi sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species isolated from the rhizosphere of Sonchus oleraceus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2656–2661
Kaempfer P, Falsen E, Lodders N, Martin K, Kassmannhuber J, Busse H-J (2012) Paenibacillus chartarius sp. nov., isolated from a paper mill. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1342–1347
Khianngam S, Tanasupawat S, Akaracharanya A, Kim KK, Lee KC, Lee J-S (2011) Paenibacillus xylanisolvens sp. nov., a xylan-degrading bacterium from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:160–164
Kim KK, Lee KC, Yu H, Ryoo S, Park Y, Lee J-S (2010) Paenibacillus sputi sp. nov., isolated from the sputum of a patient with pulmonary disease. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2371–2376
Kim O-S et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kim T-S, Han J-H, Joung Y, Kim SB (2015) Paenibacillus oenotherae sp. Nov. and Paenibacillus hemerocallicola sp. Nov., isolated from the root of Herbaceous Plants. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol doi:10.1099/ijs.0.000329
Kong BH et al (2013) Paenibacillus typhae sp. nov., isolated from roots of Typha angustifolia L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1037–1044
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Logan NA et al (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2114–2121
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Nakamura LK (1987) Bacillus alginolyticus sp. nov. and Bacillus chondroitinus sp. nov., 2 alginate-degrading species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:284–286
Osman S, Satomi M, Venkateswaran K (2006) Paenibacillus pasadenensis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus barengoltzii sp. nov., isolated from a spacecraft assembly facility. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1509–1514
Park D-S, Jeong W-J, Lee KH, Oh H-W, Kim B-C, Bae KS, Park H-Y (2009) Paenibacillus pectinilyticus sp. nov., isolated from the gut of Diestrammena apicalis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1342–1347
Rivas R, Garcia-Fraile P, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Velazquez E (2006) Paenibacillus cellulosilyticus sp. nov., a cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacterium isolated from the bract phyllosphere of Phoenix dactylifera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2777–2781
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method-a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Indentification of bacteria y gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC News Lett 20:1–6
Schumann P (2011) Peptidoglycan Structure. In: Rainey F, Oren A (eds) Methods in Microbiology, vol 38: taxonomy of prokaryotes, vol 38. Academic Press, London, pp 101–129
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Nakamura LK, Komagata K (1997) Emended description of Paenibacillus amylolyticus and description of Paenibacillus illinoisensis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus chibensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:299–306
Smibert RM, Kreg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Stackebrandt E et al (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Sukweenadhi J, Kim Y-J, Lee KJ, Koh S-C, Van-An H, Ngoc-Lan N, Yang D-C (2014) Paenibacillus yonginensis sp nov., a potential plant growth promoting bacterium isolated from humus soil of Yongin forest. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 106:935–945
Takeda M, Suzuki I, Koizumi JI (2005) Paenibacillus hodogayensis sp. nov., capable of degrading the polysaccharide produced by Sphaerotilus natans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:737–741
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RM, Kreig NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf G, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. Snyder ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 330–393
Traiwan J, Park M-H, Kim W (2011) Paenibacillus puldeungensis sp. nov., isolated from a grassy sandbank. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:670–673
Vaz-Moreira I, Faria C, Nobre MF, Schumann P, Nunes OC, Manaia CM (2007) Paenibacillus humicus sp. nov., isolated from poultry litter compost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2267–2271
Velaquez E, de Miguel T, Poza M, Rivas R, Rossello-Mora R, Villa TG (2004) Paenibacillus favisporus sp. nov., a xylanolytic bacterium isolated from cow faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:59–64
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Scientific Research Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31470136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, G.N., Zhou, X., Zhao, R. et al. Paenibacillus herberti sp. nov., an endophyte isolated from Herbertus sendtneri . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 587–596 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0514-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0514-3