Abstract
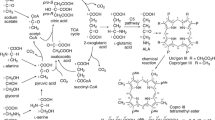
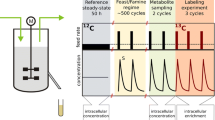
The advantage of using 13C-labelled glucose in metabolic studies is that it is an important carbon and energy source for almost all biotechnologically and medically important organisms. On the other hand, the disadvantage is its relatively high cost in the labelling experiments. Looking for cheaper alternatives we found that 13C-[2] acetate or 13C-[1,2] acetate is a prospective compound for such experiments. Acetate is well incorporated by many organisms, including mammalian and insect cell cultures as preferred source of acetyl-CoA. Our experimental results using 13C NMR demonstrated that acetate was efficiently incorporated into glutamate and alanine secreted by the insect cell culture. Using D-stat culture of Saccharomyces uvarum on glucose/13C-acetate mineral media we demonstrated that the labelling patterns of proteinogenic amino acids can be well predicted on the basis of specific substrate consumption rates using the modified scheme of yeast metabolism and stoichiometric modelling. According to this scheme aspartate and alanine in S. uvarum under the experimental conditions used is synthesised in the mitochondria. Synthesis of alanine in the mitochondria was also demonstrated for Spodoptera frugiperda. For both organisms malic enzyme was also operative. For S. uvarum it was shown that the activity of malic enzyme is sufficient for supporting the mitochondrial biosynthetic reactions with NADPH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BDF:
-
biosynthetically directed fractional labelling
- FCS:
-
foetal calf serum
- IEAM:
-
yeast extract free medium
- MEM:
-
minimal essential medium
- MFA:
-
metabolic flux analysis
- oxac :
-
cytosolic oxaloacetate
- oxam :
-
mitochondrial oxaloacetate
- PP pathway:
-
pentose phosphate pathway
- Pyrc :
-
cytosolic pyruvate
- Pyrm :
-
mitochondrial pyruvate
- TCA:
-
tricarboxylic acid
References
Adamberg K., Kask S., Laht T.M. and Paalme T. (2003). The effect of temperature and pH on the growth of lactic acid bacteria: a pH-auxostat study. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 85:171–183
Barton J.K., Den Hollander J.A., Hopfield J.J. and Shulman R.G. (1982). 13C Nuclear magnetic resonance study of trehalose mobilization in yeast spores. J. Bacteriol. 151:177–185
Bedard C., Tom R. and Kamen A. (1993). Growth, nutrient consumption, and end-product accumulation in Sf-9 and BTI-EAA insect cell cultures: insights into growth limitation and metabolism. Biotechnol. Prog. 9:615–624
Cannizzaro C., Christensen B., Nielsen J. and Von Stockar U.(2004). Metabolic network analysis on Phaffia rhodozyma yeast using 13C-labeled glucose and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Metab. Eng. 6:340–351
Chance E., Seeholzer S., Kobayashi K. and Williamson J. (1983). Mathematical analysis of isotope labeling in the citric acid cycle with applications to 13C NMR studies in perfused rat harts. J. Biol. Chem. 258:13785–13794
Christensen B. and Nielsen J. (1999). Metabolic network analysis. A powerful tool in metabolic engineering. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 66:210–231
Christensen B., Gombert A.K. and Nielsen J. (2002). Analysis of flux estimates based on 13C-labelling experiments. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:2795–2800
Cortassa S., Aon J.C. and Aon M.A. (1995). Fluxes of carbon, phosphorylation, and redox intermediates during growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on different carbon sources. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 47:193–208
Dallies N., François J. and Paquet V. (1998). A New method for quantitative determination of polysaccharides in the yeast cell wall. Application to the cell wall defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 14:1297–1306
Dauner M. and Sauer U. (2001). Stoichiometric growth model for riboflavin-producing Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 76:132–143
DeLuna A., Avendaño A., Riego L. and González A. (2001). NADP-Glutamate Dehydrogenase Isoenzymes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 276(47):43775–43783
DeLuna A., Qezada H., Gómez-Puyou A., González A. (2005). Asparaginyl deamidation in two glutamate dehydrogenase isoenzymes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 328:1083–1090
Dickinson J.R., Dawes I.W., Boyd A.S. and Baxter R.L. (1983). 13C NMR studies of acetate metabolism during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80(19):5847–51
Dos Santos M.M., Gombert A.K., Christensen B., Olsson L. and Nielsen J. (2003). Identification of in vivo enzyme activities in the cometabolism of glucose and acetate by Saccharomyces cerevisiae by using 13C-labeled substrates. Eucaryotic Cell 2(3):599–608
Dos Santos M.M., Raghevendran V., Kötter P., Olsson L. and Nielsen J. (2004). Manipulation of malic enzyme in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for increasing production capacity aerobically in different cellular compartments. Metab. Eng. 6:352–363
Doverskog M., Jacobsson U., Chapman B.E., Kuchel P. and Häggström L. (2000). Determination of NADH-dependent glutamate synthase (GOGAT) in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cells by a selective 1H/15N NMR in vitro assay. J. Biotechnol. Apr 14;79(1):87–97
Drews M., Doverskog M., Öhman L., Chapman B.E., Jacobsson U., Kuchel P.W. and Häggström L. (2000). Pathways of glutamine metabolism in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cells: evidence for the presence of the nitrogen assimilation system, and a metabolic switch by 1H/15N NMR. J. Biotechnol. 78:23–37
Drews, M., Nisamedtinov, I. and Paalme, T. 2003. Application of quasi-steady-state cultures. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Congress on Bioreactor Technology in Cell, Tissue Culture and Biomedical Applications. BioBien Innovations, Piikiö, Finland, pp. 218–225
Falco S.C., Dumas K.S. and Livak K.J. (1985). Nucleotide sequence of the yeast ILV2 gene which encodes acetolactate synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 13(11):4011–4027
Ferreira J.C., Thevelein J.M., Hohmann S., Paschoalin V.M.F., Trugo L.C. and Panek A.D. (1997). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1335:40–50
Gerhardt P., Murray R.G.E., Wood W.A. and Krieg N.R. (1994). Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Mirobiology, Washington, D.C
Haselbeck R.J. and McAlister-Henn L. (1991). Isolation, nucleotide sequence, and disruption of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene encoding mitochondrial NADP(H)-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 266(4):2339–2345
Huh W.K., Falvo J.V., Gerke L.C., Carroll A.S., Howson R.W., Weissman J.S. and O’Shea E.K. (2003). Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425(6959):686–691
Kasemets K., Drews M., Nisamedtinov I., Adamberg K. and Paalme T. (2003). Modification of A-stat for the characterization of microorganisms. J. Microbiol. Methods 55(1):187–200
Kumar A., Agarwal S., Heyman J.A., Matson S., Heidtman M., Piccirillo S., Umansky L., Drawid A., Jansen R., Liu Y., Cheung K.H., Miller P., Gerstein M., Roeder G.S. and Snyder M. (2002). Subcellular localization of the yeast proteome. Genes Dev. 16(6):707–719
Kylie F., Mackenzie K., Singh K. and Brown A.D. (1987). Water stress plating hypersensitivity of yeasts: protective role of trehalose in Saccharomyces cerevisae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 134:1661–1666
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (http://www.kegg. com/)
Maaheimo H., Fiaux J., Çakar Z.P., Bailey J. E., Sauer U. and Szyperski T. (2001). Central carbon metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae explored by biosynthetic 13C labeling of common amino acids. Eur. J. Biochem. 268:2464–2479
Magasanik, B. 2003. Ammonia Assimilation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryotic cell. Oct.: 827–829
Michal G. (1998). Biochemical Pathways: An Atlas of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York
Paalme T., Olivson A. and Vilu R. (1982). 13C-NMR study of CO2-fixation during the heterotrophic growth in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 782:311–319
Paalme T., Olivson A. and Vilu R. (1982). 13C-NMR study of the glucose synthesis pathways in the bacterium Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 720:303–310
Paalme T., Elken R., Vilu R. and Korhola M. (1997). The growth efficiency of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on glucose/ethanol media with smooth change in the dilution rate (A-stat). Enzyme Microb. Technol. 20:174–181
Pang S.S. and Duggleby R.G. (1999). Expression, purification, characterization, and reconstitution of the large and small subunits of yeast acetohydroxyacid synthase. Biochemistry 38(16):5222–5231
Radin N.S. (1981). Extraction of tissue lipids with a solvent of low toxicity. Methods Enzymol. 72:5–7
Saccharomyces Genome Database (http://www.yeastgenome.-org/)
Sickmann A., Reinders J., Wagner Y., Joppich C., Zahedi R., Meyer H.E., Schonfisch B., Perschil I., Chacinska A., Guiard B., Rehling P., Pfanner N. and Meisinger C. (2003). The proteome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100(23):13207–13212
Szyperski T., Bailey J.E. and Wütrich K. (1996). Detecting and dissecting metabolic fluxes using biosynthetic fractional 13C labeling and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Tibtech. 14:453–458
Tran-Dinh S., Fermendjian S., Sala E., Mermet-Bouvier R., Cohen M. and Fromageot P. (1973). 13C-Enriched amino acids. Chemical shifts, coupling constants J c–c and conformation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96(5):1484–1492
Tran-Dinh S., Bouet F., Huynh Q. and Herve M. (1996). Mathematical models for determining metabolic fluxes through the citric acid and glyoxylate cycles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 242:770–778
Vallino J.J. and Stephanopoulos G. (1993). Metabolic flux distributions in Corynebacterium glutamicum during growth and lysine overproduction. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41:633–646
Varma A. and Palsson P.O. (1994). Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60(10):3724–3731
Vilu, R., Paalme, T. and Vanatalu, K. 1990. In: Directed Design of Cells-Producers (in Russian). Microbial Conversion, Riga, pp. 14–21
Walker T.E., Han C.H., Kollman V.H., London R.E. and Matwiyoff N.A. (1982). 13C Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the biosynthesis by Microbacterium ammoniaphilum of L-glutamate selectively enriched with carbon-13. J. Biol. Chem. 3:1189–1195
Weiss S.A., Smith G.C., Kalter S.S. and Vaughn J.L. (1981). Improved method for the production of insect cell cultures in large volume. In Vitro. 17 (6):495–502
Wiechert W. and De Graaf A. (1996). Bidirectional reaction steps in metabolic networks: I. Modeling and simulation of carbon isotope labeling experiments. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 55:101–117
Wiechert W. (2001). 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metab. Eng. 3:195–206
Wütrich K. (1976). NMR in Biological Research: Peptides and Proteins. North-Holland, American Elsevier
Acknowledgements
This work was founded through Estonian Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 5129 and 5160).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix A
Appendix B
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paalme, T., Nisamedtinov, I., Abner, K. et al. Application of 13C-[2] - and 13C-[1,2] acetate in metabolic labelling studies of yeast and insect cells. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 89, 443–457 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9053-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-005-9053-7