Abstract
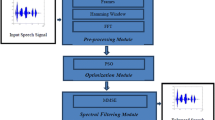
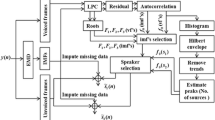
In this research a new way introduced for solving the underdetermined blind speech signal separation problem when the number of observation is less than the sources for which the ICA is no longer applicable, which enhance the time complexity for separation of signal. To resolve that, Improved Sparse Component Analysis (ISCA) is introduced to exploit the sparse nature of TF domain, which adopt a two-step processing that contains mixing matrix estimation followed by separation of source. This ISCA is based on fuzzy c-means with Particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm for mixed matrix Estimation. In our work PSO is used to separate the accurate voice signal from the random mixed signal by finding the best optima solution in the cluster part. Then the source signal separation is carried out based on the shortest path. These initial processing is done and verified by Mat lab and hardware description language is generated using HDL coder and it is synthesized using Xilinx ISE. The final result illustrates that the proposed system has an improved performance in terms of SNR, Efficiency and Accuracy.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dupont, S., & Luettin, J. (2000). Audio-visual speech modeling for continuous speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2(3), 141–151.
Liutkus, A., Badeau, R., & Richard, G. (2011). Gaussian processes for underdetermined source separation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 59(7), 3155–3167.
Vincent, E., Araki, S., Theis, F., Nolte, G., Bofill, P., Sawada, H., et al. (2012). The signal separation evaluation Campaign (2007–2010): Achievements and remaining challenges. Signal Processing Journal, 92(8), 1928–1936.
Kokkinakis, K., & Asoke Nandi, K. (2006). Multichannel blind deconvolution for source separation in convolutive mixtures of speech. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 14(1), 200–212.
Daniel, W. E., Schobben, C., & Sommen, P. (2002). A frequency domain blind signal separation method based on decorrelation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 50(8), 1855–1865.
Koldovsky, Z., & Tichavsky, P. (2011). Time-domain blind separation of audio sources on the basis of a complete ICA decomposition of an observation space. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19(2), 406–416.
Yilmaz, O., & Rickard, S. (2004). Blind separation of speech mixtures via time-frequency masking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(7), 1830–1847.
Gribonval, R., Benaroya, L., Vincent, E., & Févotte, C. (2003). Proposals for performance measurement in source separation. In Proceedings of 4th international symposium on independent component analysis and blind signal separation (ICA2003) (pp. 763–768).
Lin, Q.-H., Yin, F.-L., Mei, T.-M., & Liang, H. (2006). A blind source separation based method for speech encryption. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 53(6), 1320–1328.
Rojas, F., Puntonet, C. G., Górriz, J. M., & Valenzuela, O. (2005). Assessing the performance of several fitness functions in a genetic algorithm for nonlinear separation of sources. Advances in natural computation (pp. 863–872). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
André Takahata, K., Everton Nadalin, Z., Ferrari, R., Duarte, L. T., Suyama, R., Renato Lopes, R., et al. (2012). Unsupervised processing of geophysical signals: A review of some key aspects of blind de convolution and blind source separation. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 29(4), 27–35.
Fuentes, B., Badeau, R., & Richard, G. (2012). Blind harmonic adaptive decomposition applied to supervised source separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 2654–2658).
Diago Sorianoa, C., Suyamab, R., & Attux, R. (2011). Blind extraction of chaotic sources from mixtures with stochastic signals based on recurrence quantification analysis. Conference on Digital Signal Processing, 21, 417–426.
Virtanen, T. (2007). Monaural sound source separation by nonnegative matrix factorization with temporal continuity and sparseness criteria. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 15(3), 1066–1074.
Sawada, H., Mukai, R., Araki, S., & Makino, S. (2004). A robust and precise method for solving the permutation problem of frequency-domain blind source separation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 12(5), 530–538.
Araki, S., Sawada, H., Mukai, R., & Makino, S. (2007). Underdetermined blind sparse source separation for arbitrarily arranged multiple sensors. Signal Processing, 87(8), 1833–1847.
Bofill, P., & Zibulevsky, M. (2001). Underdetermined blind source separation using sparse representations. Signal Processing, 81(11), 2353–2362.
Abrard, F., & Deville, Y. (2005). A time-frequency blind signal separation method applicable to underdetermined mixtures of dependent sources. Signal Processing, 85(7), 1389–1403.
Puigt, M., & Deville, Y. (2005). Time–frequency ratio-based blind separation methods for attenuated and time-delayed sources. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 19(6), 1348–1379.
Reju, V. G., Koh, S. N., & Soon, I. Y. (2009). An algorithm for mixing estimation in instantaneous blind source separation. Signal Processing, 89(9), 1762–1773.
Sha, Z.-C., Huang, Z.-T., Zhou, Yi-Yu., & Wang, F.-H. (2013). Frequency-hopping signals sorting based on underdetermined blind source separation. IET Communications, 7(14), 1456–1464.
Xie, S., Yang, L., Yang, J.-M., Zhou, G., & Xiang, Y. (2012). Time-Frequency Approach to Underdetermined Blind Source Separation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 23(2), 306–316.
Bao, G., Zhongfu Ye, X., & Zhou, Y. (2013). A compressed sensing approach to blind separation of speech mixture based on a two-layer sparsity model. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 21(5), 899–906.
Alshabrawy, O. S. & Hassanien, A. E. (2014). Underdetermined blind separation of mixtures of an unknown number of sources with additive white and pink noises. In Proceedings of the Fifth international conference on innovations in bio-inspired computing and applications IBICA 2014 (pp. 241–250). Cham: Springer.
Zhang, L., Yang, J., Kaiwang, L., & Zhang, Q. (2014). Modified subspace method based on convex model for underdetermined blind speech separation. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 60(2), 225–232.
Abrard, F., & Deville, Y. (2005). A time-frequency blind signal separation method applicable to underdetermined mixtures of dependent sources. Signal Process, 85(7), 1389–1403.
Puigt, M., & Deville, Y. (2005). Time–frequency ratio-based blind separation methods for attenuated and time-delayed sources. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 19(6), 1348–1379.
Araki, S., Sawada H. & Makino, S. (2007). Blind speech separation in a meeting situation with maximum SNR beamformers. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, 2007. ICASSP 2007 (pp. 1–41).
Pavlidi, D., Griffin, A., Puigt, M., & Mouchtaris, A. (2013). Real-time multiple sound source localization and counting using a circular microphone array. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 21(10), 2193–2206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velammal, M.N., Kumar, P.N. “A speech recognizer” a tool to recognize the high clarity speech signal based on existing speech using ISCA. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 98, 41–58 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1275-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1275-5