Abstract
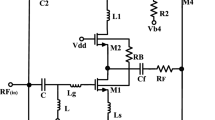
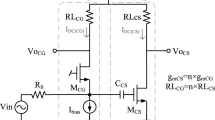
A wideband CG–CS-based balun-LNA is proposed, with high linearity (IIP2 and IIP3) for multi-standard radio applications. By taking advantage of the common-gate transistor’s noise and distortion cancellation property in CG–CS-based balun topology, this balun-LNA just focuses on CS-stage’s noise and linearity improvement. Post-distortion technique with a p-MOSFET as auxiliary transistor is adopted to suppress the 2nd and 3rd nonlinear terms of the main transistor in CS-stage, and then across 0.2–4.35 GHz, above 34 dBm IIP2 and 7.5 dBm IIP3 with typical process corner is achieved. In addition, in order to reduce the considerable substrate noise from the main transistor in CS-stage, a large resistor is connected between its bulk and source terminal, which reduces the substrate noise contribution from 7.68 to 0.2 % and improves the noise figure (NF) at 1 GHz about 0.38 dB. This balun-LNA was designed in 0.18-μm CMOS, operates from 0.2 to 4.35 GHz, and dissipates 17.8 mW with 1.5-V supply. With typical process corner, this amplifier provides 17.2-dB maximum voltage gain and 2.5–3.2 dB NF.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Im, D., Nam, I., Kim, H.-T., & Lee, K. (2009). A wideband CMOS low noise amplifier employing noise and IM2 distortion cancellation for a digital TV tuner. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44, 686–698.
Blaakmeer, S. C., Klumperink, E. A. M., Leenaerts, D. M. W., & Nauta, B. (2008). Wideband balun-LNA with simultaneous output balancing, noise-canceling and distortion-canceling. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43, 1341–1350.
Tae Wook, K., Bonkee, K., & Kwyro, L. (2004). Highly linear receiver front-end adopting MOSFET transconductance linearization by multiple gated transistors. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39, 223–229.
Zhang, H., Fan, X., & Sinencio, E. S. (2009). A low-power, linearized, ultra-wideband LNA design technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44, 320–330.
Kim, N., Aparin, V., Barnett, K., & Persico, C. (2006). A cellular-band CDMA 0.25-um CMOS LNA linearized using active post-distortion. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41, 1530–1534.
Kim, T.-S., & Kim, B.-S. (2006). Post-linearization of cascode CMOS low noise amplifier using folded PMOS IMD sinker. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 16, 182–184.
Bagheri, R., Mirzaei, A., Chehrazi, S., Heidari, M. E., Lee, M., Mikhemar, M., et al. (2006). An 800-MHz–6-GHz software-defined wireless receiver in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41, 2860–2876.
Tin S. F., & Mayaram, K. (1999). Substrate network modeling for CMOS RF circuit simulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits, 1999. (pp. 583–586).
Donggu, I., Ilku, N., & Kwyro, L. (2010). A CMOS active feedback balun-LNA with high IIP2 for wideband digital TV receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 58, 3566–3579.
Wang, H., Zhang, L., & Yu, Z. (2010). A wideband inductorless LNA with local feedback and noise cancelling for low-power low-voltage applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 57, 1993–2005.
Kim, J., & Silva-Martinez, J. (2012). Wideband inductorless balun-LNA employing feedback for low-power low-voltage applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 60, 2833–2842.
Li, Z., Sun, L., & Huang, L. (2014). A 6–9 GHz UWB balun-LNA employing current-reuse with preamplifier and CCC buffer. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 79, 291–299.
Geddada, H. M., Silva-Martinez, J., & Taylor, S. (2011). Inductorless wideband CMOS LNAs with nonlinearity cancellation. In IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), 2011 (pp. 1–4).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Information Science Laboratory Center of USTC for EDA tools support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, D., Qian, W., Khan, M. et al. 0.2–4.35 GHz highly linear CMOS balun-LNA with substrate noise optimization. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 83, 285–293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0533-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-015-0533-z