Abstract
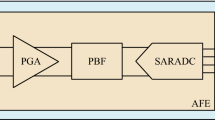
This paper presents a pipelined analog to digital converter (ADC) with reconfigurable resolution and sampling rate for biomedical applications. Significant power saving is achieved by turning off the sample-and-hold stage and the first two pipeline stages of the ADC instead of turning off the last two stages. The reconfiguration scheme allows having three modes of operation with variable resolutions and sampling rates. Reconfigurable operational transconductance amplifiers and an interference elimination technique have been employed to optimize power-speed-accuracy performance in biomedical instrumentation. The proposed ADC exhibits a 56.9 dB SNDR with 35.4 mW power consumption in 10-bit, 40 MS/s mode and 49.2 dB SNDR with only 7.9 mW power consumption in 8-bit, 2.5 MS/s mode. The area of the core layout is 1.9 mm2 in a 0.35 μm bulk-CMOS process.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo Elneel, N., Aksoy, E., & Schroeder, D. (2010). A power-adaptable A/D converter with integrated data compression. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 64, 249–259.
Rodriguez-Perez, A., Delgado-Restituto, M., Medeiro, F., Rodriguez-Vazquez, A. (2009). A low-power reconfigurable ADC for biomedical sensor interfaces, IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, 2009. BioCAS 2009. pp. 253–256.
Verma, N., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2007). An ultra low energy 12-bit rate-resolution scalable SAR ADC for wireless sensor nodes. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42, 1196–1205.
Malla, P., Lakdawala, H., Kornegay, K., Soumyanath, K. (2008). A 28mW spectrum-sensing reconfigurable 20 MHz 72 dB-SNR 70 dB-SNDR DT ΔΣ ADC for 802.11n/WiMAX receivers, ISSCC 2008. Digest of Technical Papers. IEEE International, pp. 496–631.
Castro-López, R., Morgado, A., Guerra, O., Río, R., Rosa, J. M., Pérez-Verdú, B., et al. (2009). Systematic top-down design of reconfigurable ΣΔ modulators for multi-standard transceivers. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 58, 227–241.
Ke, Y., Craninckx, J., & Gielen, G. (2008). A design approach for power-optimized fully reconfigurable ΣΔ A/D converter for 4G radios. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 55, 229–233.
Gustafsson, E.M.I., Rusu, A., Ismail, M., (2008). Design of a reconfigurable ADC for UWB/Bluetooth radios. 2008 Joint 6th International IEEE Northeast Workshop on Circuits and Systems and TAISA Conference, pp. 205–208.
Ahmed, I., & Johns, D. A. (2008). A high bandwidth power scalable sub-sampling 10-bit pipelined ADC with embedded sample and hold. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43, 1638–1647.
Chandrashekar, K., Corsi, M., Fattaruso, J., & Bakkaloglu, B. (2010). A 20-MS/s to 40-MS/s reconfigurable pipeline ADC implemented with parallel OTA scaling. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 57, 602–606.
Huang, M. C., & Liu, S. I. (2010). A 10-MS/s-to-100-kS/s power-scalable fully differential CBSC 10-bit pipelined ADC with adaptive biasing. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 57, 11–15.
Jang, J. E., Miao, Y. K. & Lee, Y. P. (2010). High-bandwidth power-scalable 10-bit pipelined ADC using bandwidth-reconfigurable operational amplifier, Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS) (pp. 4029–4032).
O’Driscoll, S., Meng, T.H. (2009). Adaptive resolution ADC array for neural implant, Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2009. pp. 1053–1056.
Bonfini, G., Brogna, A. S., Garbossa, C., Colombini, L., Bacci, M., Chicca, S., et al. (2004). An ultralow-power switched opamp-based 10-B integrated ADC for implantable biomedical applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 51, 174–177.
Agah, A., Vleugels, K., Griffin, P.B., Ronaghi, M., Plummer, J.D., Wooley, B.A. (2007). A high-resolution low-power oversampling ADC with extended-range for bio-sensor arrays, 2007 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits. pp. 244–245.
To, G. (2007). Development of the telemetrical intraoperative soft tissue tension monitoring system in total knee replacement with MEMS and ASIC technologies. Master of Science Thesis.
Qu, W., Islam, S. K., Mahfouz, M. R., Haider, M. R., To, G., & Mostafa, S. (2010). Microcantilever array pressure measurement system for biomedical instrumentation. IEEE Sensors Journal, 10, 321–330.
Huque, M. A., Haider, M. R., Zhang, M., Oh, T., Islam, S.K. (2007). A low power, low voltage current read-out circuit for implantable electro-chemical sensors, 2007 IEEE Sensors. pp. 64–67.
To, G., Qu, W., Mahfouz, M.R. (2006). ASIC design for wireless surgical MEMS device and instrumentation, 28th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. pp. 5892–5895.
Liu, H., & Hassoun, M. (2002). A 9-b 40-MSample/s reconfigurable pipeline analog-to-digital converter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 49, 449–456.
Mortezapour, S., Lee, E.K.F. (2001). A reconfigurable pipelined data converter, The 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 314–317 vol. 4.
Anderson, M., Norling, K., Dreyfert, A., Yuan, J. (2005). A reconfigurable pipelined ADC in 0.18 μm CMOS, Digest of Technical Papers, 2005 symposium on VLSI circuits, pp. 326–329.
Nikolaidis, T., Varagis, A., Fragopoulos, D., Sinnis, B. S., Venios, N. (2004). Reconfigurable pipeline analog/digital converter for WCDMA/GSM operation. Workshop on Multi-mode multi-band re-configurable systems for 3rd enhanced generation mobile phones.
Audoglio, W., Zuffetti, E., Cesura, G., Castello, R. (2006). A 6-10 bits reconfigurable 20 MS/s digitally enhanced pipelined ADC for multi-standard wireless terminals. Proceedings of the 32nd European, pp. 496–499.
Abo, A. (1992). Design for reliability of low-voltage, switched-capacitor circuits. Doctor of philosophy Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA.
Chiu, Y., Gray, P. R., & Nikolic, B. (2004). A 14-b 12-MS/s CMOS pipeline ADC with over 100-dB SFDR. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39, 2139–2151.
Enz, C. C., & Cheng, Y. (2000). MOS transistor modeling for RF IC design. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 35, 186–201.
Silveira, F., Flandre, D., & Jespers, P. G. A. (1996). A gm/ID based methodology for the design of CMOS analog circuits and its application to the synthesis of a silicon-on-insulator micropower OTA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31, 1314–1319.
Murmann, B., & Boser, B. E. (2004). Digitally assisted pipeline ADCs: Theory and implementation. New York: Springer. ISBN 1402078390.
Lewis, S. H., Fetterman, H. S., Gross, G. F, Jr, Ramachandran, R., & Viswanathan, T. R. (1992). A 10-b 20-Msample/s analog-to-digital converter. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 27, 351–358.
Goodenough, F. (1996). Analog technology of all varieties dominate ISSCC. Electronic Design, 44, 96–111.
P. Setty, J.B. (1998). A 5.75 b 350 M sample/s or 6.75 b 150 M sample/s reconfigurable flash ADC for a PRML read channel. 148–149, 428.
Andersen, T. N., & Hernes, B. (2005). A cost-efficient high-speed 12-bit pipeline ADC in 0.18-μm digital CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40, 1506–1513.
Iizuka, K., Matsui, H., Ueda, M., & Daito, M. (2006). A 14-bit digitally self-calibrated pipelined ADC with adaptive bias optimization for arbitrary speeds up to 40 MS/s. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41, 883–890.
Ahmed, I., & Johns, D. A. (2005). A 50-MS/s (35 mW) to 1-kS/s (15 μW) power scalable 10-bit pipelined ADC using rapid power-on opamps and minimal bias current variation. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40, 2446–2455.
Gulati, K., & Lee, H. S. (2001). A low-power reconfigurable analog-to-digital converter. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36, 1900–1911.
Gielen, G., Goris, E. (2005). Reconfigurable front-end architectures and A/D converters for flexible wireless transceivers for 4G radios, 2005 IEEE 7th CAS Symposium on Emerging Technologies: Circuits and Systems for 4G Mobile Wireless Communications, ETW’05. pp. 13–18.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Center of Musculoskeletal Research at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, W., Islam, S.K., Mahbub, I. et al. An energy-efficient reconfigurable analog-to-digital converter for orthopedic implants. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 78, 233–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0217-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0217-5