Abstract
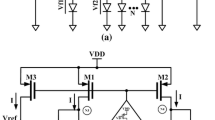
In this paper a low-voltage low-power threshold voltage monitor for CMOS process sensing is presented. This circuit works in weak inversion and it can be used as an elementary circuit block for on-chip compensation of the intra-die or inter-die threshold voltage variations in low-power analog and mixed-signal SoC, since it is robust to temperature and power supply voltage variations (similar to the bandgap voltage reference). The proposed threshold voltage monitor has been successfully verified in a standard 0.35-μm n-well CMOS TSMC process. Experimental results have confirmed that the circuit generates an average reference voltage of 758 mV (very close to the typical threshold voltage when extrapolated to absolute zero) for a 950 mV power supply voltage, with a variation of 39 ppm/°C for the −20 to 80°C temperature range.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
It can be not sufficient for saturation and a bigger value may be necessary to obtain it.
References
Intel Pentium III Processor. Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, Aug. 2010 [Online]. Avaliable: www.intel.com.
Power Management Guide 2010. Texas Instruments, Inc., Dallas, TX, Aug. 2010 [Online]. Avaliable: www.ti.com.
Chi, B., Yao, J., Chiang, P., & Wang, Z. (2009). A fast-settling wideband-IF ASK baseband circuit for a wireless endoscope capsule. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Part II: Express Briefs, 56(4), 275–279.
Pelgrom, M. J. M., Duinmaijer, A. C. J., & Welbers, A. P. G. (1989). Matching properties of MOS transistors. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 24(5), 1433–1439.
Kinget, P. R. (2005). Device mismatch and tradeoffs in the design of analog circuits. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(6), 1212–1224.
Eisele, M., Berthold, J., Schmitt-Landsiedel, D., & Mahnkopf, R. (1997). The impact of intra-die device parameter variations on path delays and on the design for yield of low voltage digital circuits. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 5(4), 360–368.
Tschanz, J. W., Narendra, S., Nair, R., & De, V. (2003). Effectiveness of adaptive supply voltage and body bias for reducing impact of parameter variations in low power and high performance microprocessors. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(5), 826–829
Olivieri, M., Scotti, G., & Trifiletti, A. (2005). A novel yield optimization technique for digital CMOS circuits design by means of process parameters run-time estimation and body bias active control. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 13(5), 630–638.
Allen, P. E. & Holberg, D. R. (2002). CMOS analog circuits design, (2nd ed.). New York, USA: Oxford University Press, Inc.
Tsividis, Y. P. (1999). Operation and modeling of the MOS transistor (2nd ed.). New York, USA: Oxford University Press, Inc.
Ferreira, L. H. C. (2008). An ultra-low-voltage ultra-low-power CMOS threshold voltage reference. PhD thesis, Federal University of Itajubá, Sep. 2008. in Portuguese.
Ferreira, L. H. C., Pimenta, T. C., & Moreno, R. L. (2008). A CMOS threshold voltage reference source for very-low-voltage applications. Microelectronics Journal, 39(12), 1867–1873.
Croon, J. A., Rosmeulen, M., Decoutere, S., Sansen, W., & Maes, H. E. (2002). An easy-to-use mismatch model for the MOS transistor. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(8), 1056–1064.
MOSIS Technical Documents. The MOSIS Service, Marina DelRay, CA, Aug. 2010 [Online]. Avaliable: www.mosis.org.
Ueno, K., Hirose, T., Asai, T., & Amemiya, Y. (2009). A 300-nW, 15-ppm/°C, 20-ppm/V CMOS voltage reference circuit consisting of subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(7), 2047–2054.
Huang, P., Lin, H., & Lin, Y. (2006). A simple subthreshold CMOS voltage reference circuit with channel-length modulation compensation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Part II: Express Briefs, 53(9), 882–885.
Acknowledgment
The author would like to thank Prof. Dr. Sameer Sonkusale (Tufts University, MA, USA) for his helpful suggestions on this paper, and MOSIS for helping to fabricate the chips. This work was partially supported by CAPES Foundation, a research agency of the Brazilian Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, L.H.C. A low-voltage low-power threshold voltage monitor for CMOS process sensing. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 68, 51–57 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9572-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9572-7