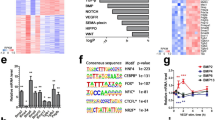
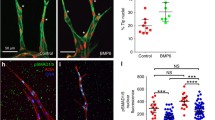
Abstract
The Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 (BMP4) regulates multiple biological processes, including vascular development and angiogenesis. Here, we investigated the role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2) in mediating the angiogenic activity of BMP4. BMP4 induces a rapid relocation and phosphorylation of VEGFR2 on the endothelial cell membrane. These effects occur in the absence of a direct interaction of BMP4 and/or BMP receptors with VEGFR2. At variance, BMP4, by interacting with the BMPRI-II hetero-complex, induces c-Src phosphorylation which, in turn, activates VEGFR2, leading to an angiogenic response. Accordingly, the BMPR inhibitor dorsomorphin prevents c-Src activation and specific inhibition of c-Src significantly reduces downstream VEGFR2 phosphorylation and the angiogenic activity exerted by BMP4 in a chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane assay. Together, our data indicate that the pro-angiogenic activity exerted by BMP4 in endothelial cells is mediated by a BMPR-mediated intracellular transactivation of VEGFR2 via c-Src.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146:873–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.039
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10144
Li X, Claesson-Welsh L, Shibuya M (2008) VEGF receptor signal transduction. Methods Enzymol 443:261–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(08)02013-2
Grillo E, Ravelli C, Corsini M, Ballmer-Hofer K, Zammataro L et al (2016) Monomeric gremlin is a novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antagonist. Oncotarget 7:35353–35368. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9286
Ryu JM, Baek YB, Shin MS, Park JH, Park SH et al (2014) Sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced Flk-1 transactivation stimulates mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation through S1P1/S1P3-dependent beta-arrestin/c-Src pathways. Stem Cell Res 12:69–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2013.08.013
Petreaca ML, Yao M, Liu Y, Defea K, Martins-Green M (2007) Transactivation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 by interleukin-8 (IL-8/CXCL8) is required for IL-8/CXCL8-induced endothelial permeability. Mol Biol Cell 18:5014–5023. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-01-0004
Fujita Y, Yoshizumi M, Izawa Y, Ali N, Ohnishi H et al (2006) Transactivation of fetal liver kinase-1/kinase-insert domain-containing receptor by lysophosphatidylcholine induces vascular endothelial cell proliferation. Endocrinology 147:1377–1385. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0644
Garcia-Martin A, Acitores A, Maycas M, Villanueva-Penacarrillo ML, Esbrit P (2013) Src kinases mediate VEGFR2 transactivation by the osteostatin domain of PTHrP to modulate osteoblastic function. J Cell Biochem 114:1404–1413. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24482
Garcia-Martin A, Ardura JA, Maycas M, Lozano D, Lopez-Herradon A et al (2014) Functional roles of the nuclear localization signal of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) in osteoblastic cells. Mol Endocrinol 28:925–934. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2013-1225
Little SC, Mullins MC (2009) Bone morphogenetic protein heterodimers assemble heteromeric type I receptor complexes to pattern the dorsoventral axis. Nat Cell Biol 11:637–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1870
Kondo M (2007) Bone morphogenetic proteins in the early development of zebrafish. FEBS J 274:2960–2967. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05838.x
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M et al (2014) Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis 1:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2014.07.005
Benn A, Hiepen C, Osterland M, Schutte C, Zwijsen A et al (2017) Role of bone morphogenetic proteins in sprouting angiogenesis: differential BMP receptor-dependent signaling pathways balance stalk vs. tip cell competence. FASEB J 31:4720–4733. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700193RR
Benn A, Bredow C, Casanova I, Vukicevic S, Knaus P (2016) VE-cadherin facilitates BMP-induced endothelial cell permeability and signaling. J Cell Sci 129:206–218. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.179960
Helbing T, Arnold L, Wiltgen G, Hirschbihl E, Gabelmann V et al (2017) Endothelial BMP4 regulates leukocyte diapedesis and promotes inflammation. Inflammation 40:1862–1874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0627-0
Raida M, Clement JH, Leek RD, Ameri K, Bicknell R et al (2005) Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) and induction of tumor angiogenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131:741–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-005-0024-1
Stabile H, Mitola S, Moroni E, Belleri M, Nicoli S et al (2007) Bone morphogenic protein antagonist Drm/gremlin is a novel proangiogenic factor. Blood 109:1834–1840. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-06-032276
Langenfeld EM, Langenfeld J (2004) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates angiogenesis in developing tumors. Mol Cancer Res 2:141–149
Johnson DW, Berg JN, Baldwin MA, Gallione CJ, Marondel I et al (1996) Mutations in the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat Genet 13:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0696-189
McAllister KA, Grogg KM, Johnson DW, Gallione CJ, Baldwin MA et al (1994) Endoglin, a TGF-beta binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1. Nat Genet 8:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1294-345
Harrison RE, Berger R, Haworth SG, Tulloh R, Mache CJ et al (2005) Transforming growth factor-beta receptor mutations and pulmonary arterial hypertension in childhood. Circulation 111:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000153798.78540.87
David L, Mallet C, Keramidas M, Lamande N, Gasc JM et al (2008) Bone morphogenetic protein-9 is a circulating vascular quiescence factor. Circ Res 102:914–922. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.165530
Marcelo KL, Goldie LC, Hirschi KK (2013) Regulation of endothelial cell differentiation and specification. Circ Res 112:1272–1287. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300506
Sieber C, Kopf J, Hiepen C, Knaus P (2009) Recent advances in BMP receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:343–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.10.007
Kiyono M, Shibuya M (2006) Inhibitory Smad transcription factors protect arterial endothelial cells from apoptosis induced by BMP4. Oncogene 25:7131–7137. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209700
Wong CM, Zhang Y, Huang Y (2014) Bone morphogenic protein-4-induced oxidant signaling via protein carbonylation for endothelial dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 75:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.035
Xu J, Zhu D, Sonoda S, He S, Spee C et al (2012) Over-expression of BMP4 inhibits experimental choroidal neovascularization by modulating VEGF and MMP-9. Angiogenesis 15:213–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9254-4
Rothhammer T, Bataille F, Spruss T, Eissner G, Bosserhoff AK (2007) Functional implication of BMP4 expression on angiogenesis in malignant melanoma. Oncogene 26:4158–4170. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210182
Yao Y, Watson AD, Ji S, Bostrom KI (2009) Heat shock protein 70 enhances vascular bone morphogenetic protein-4 signaling by binding matrix Gla protein. Circ Res 105:575–584. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.202333
Suzuki Y, Montagne K, Nishihara A, Watabe T, Miyazono K (2008) BMPs promote proliferation and migration of endothelial cells via stimulation of VEGF-A/VEGFR2 and angiopoietin-1/Tie2 signalling. J Biochem 143:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvm215
Rezzola S, Nawaz IM, Cancarini A, Ravelli C, Calza S et al (2017) 3D endothelial cell spheroid/human vitreous humor assay for the characterization of anti-angiogenic inhibitors for the treatment of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Angiogenesis 20:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9575-4
Mitola S, Moroni E, Ravelli C, Andres G, Belleri M et al (2008) Angiopoietin-1 mediates the proangiogenic activity of the bone morphogenic protein antagonist Drm. Blood 112:1154–1157. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-09-111450
Urbinati C, Ravelli C, Tanghetti E, Belleri M, Giacopuzzi E et al (2012) Substrate-immobilized HIV-1 Tat drives VEGFR2/alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin complex formation and polarization in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:e25–34. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.242396
Rezzola S, Corsini M, Chiodelli P, Cancarini A, Nawaz IM et al (2017) Inflammation and N-formyl peptide receptors mediate the angiogenic activity of human vitreous humour in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 60:719–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-016-4204-0
Sun L, Tran N, Tang F, App H, Hirth P et al (1998) Synthesis and biological evaluations of 3-substituted indolin-2-ones: a novel class of tyrosine kinase inhibitors that exhibit selectivity toward particular receptor tyrosine kinases. J Med Chem 41:2588–2603. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm980123i
Fong TA, Shawver LK, Sun L, Tang C, App H et al (1999) SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res 59:99–106
Ravelli C, Grillo E, Corsini M, Coltrini D, Presta M et al (2015) beta3 integrin promotes long-lasting activation and polarization of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by immobilized ligand. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:2161–2171. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306230
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X et al (2001) Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 108:1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI13505
Wu T, Zhang B, Ye F, Xiao Z (2013) A potential role for caveolin-1 in VEGF-induced fibronectin upregulation in mesangial cells: involvement of VEGFR2 and Src. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304:F820–830. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00294.2012
Duval M, Le Boeuf F, Huot J, Gratton JP (2007) Src-mediated phosphorylation of Hsp90 in response to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is required for VEGF receptor-2 signaling to endothelial NO synthase. Mol Biol Cell 18:4659–4668. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0467
Tanimoto T, Jin ZG, Berk BC (2002) Transactivation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor Flk-1/KDR is involved in sphingosine 1-phosphate-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt and endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS). J Biol Chem 277:42997–43001. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204764200
Hurst LA, Dunmore BJ, Long L, Crosby A, Al-Lamki R et al (2017) TNFalpha drives pulmonary arterial hypertension by suppressing the BMP type-II receptor and altering NOTCH signalling. Nat Commun 8:14079. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14079
Delle Monache S, Sanita P, Calgani A, Schenone S, Botta L et al (2014) Src inhibition potentiates antitumoral effect of paclitaxel by blocking tumor-induced angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 328:20–31
Zhang P, Li J, Tan Z, Wang C, Liu T et al (2008) Short-term BMP-4 treatment initiates mesoderm induction in human embryonic stem cells. Blood 111:1933–1941. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-02-074120
Goumans M-J, Zwijsen A, Ten Dijke P, Bailly S (2018) Bone morphogenetic proteins in vascular homeostasis and disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspec Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a031989
Miyazono K, Maeda S, Imamura T (2005) BMP receptor signaling: transcriptional targets, regulation of signals, and signaling cross-talk. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:251–263
Zhang YE (2009) Non-smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res 19:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.328
Wong WK, Knowles JA, Morse JH (2005) Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II C-terminus interacts with c-Src: implication for a role in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2005-0103OC
Sun Z, Li X, Massena S, Kutschera S, Padhan N et al (2012) VEGFR2 induces c-Src signaling and vascular permeability in vivo via the adaptor protein TSAd. J Exp Med 209:1363–1377. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20111343
Gao M, Zhan YQ, Yu M, Ge CH, Li CY et al (2014) Hepassocin activates the EGFR/ERK cascade and induces proliferation of L02 cells through the Src-dependent pathway. Cell Signal 26:2161–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.04.013
Yang CM, Lin CC, Lee IT, Hsu CK, Tai YC et al (2015) c-Src-dependent transactivation of EGFR mediates CORM-2-induced HO-1 expression in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 230:2351–2361. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24912
Warren CM, Ziyad S, Briot A, Der A, Iruela-Arispe ML (2014) A ligand-independent VEGFR2 signaling pathway limits angiogenic responses in diabetes. Sci Signal 7:ra1. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004235
Jin ZG, Ueba H, Tanimoto T, Lungu AO, Frame MD et al (2003) Ligand-independent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by fluid shear stress regulates activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ Res 93:354–363. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000089257.94002.96
Zhang R, Xu Y, Ekman N, Wu Z, Wu J et al (2003) Etk/Bmx transactivates vascular endothelial growth factor 2 and recruits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to mediate the tumor necrosis factor-induced angiogenic pathway. J Biol Chem 278:51267–51276. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M310678200
Chou MT, Wang J, Fujita DJ (2002) Src kinase becomes preferentially associated with the VEGFR, KDR/Flk-1, following VEGF stimulation of vascular endothelial cells. BMC Biochem 3:32
Eliceiri BP, Paul R, Schwartzberg PL, Hood JD, Leng J et al (1999) Selective requirement for Src kinases during VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Mol Cell 4:915–924
Csiszar A, Labinskyy N, Jo H, Ballabh P, Ungvari Z (2008) Differential proinflammatory and prooxidant effects of bone morphogenetic protein-4 in coronary and pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H569–577. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00180.2008
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (IG AIRC grant n° IG 17276 and AIRC grant n° IG 14395) to S.M and M.P.; S.R., M.DS. and E.G. were supported by AIRC fellowships; MPP Lab was supported by Fondazione Cariplo and Regione Lombardia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 6345 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezzola, S., Di Somma, M., Corsini, M. et al. VEGFR2 activation mediates the pro-angiogenic activity of BMP4. Angiogenesis 22, 521–533 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-019-09676-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-019-09676-y