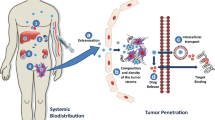
Abstract
Conventional drug delivery systems for solid tumors are composed of a nano-carrier that releases its therapeutic load. These two-stage nanoparticles utilize the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect to enable preferential delivery to tumor tissue. However, the size-dependency of the EPR, the limited penetration of nanoparticles into the tumor as well as the rapid binding of the particles or the released cytotoxic agents to cancer cells and stromal components inhibit the uniform distribution of the drug and the efficacy of the treatment. Here, we employ mathematical modeling to study the effect of particle size, drug release rate and binding affinity on the distribution and efficacy of nanoparticles to derive optimal design rules. Furthermore, we introduce a new multi-stage delivery system. The system consists of a 20-nm primary nanoparticle, which releases 5-nm secondary particles, which in turn release the chemotherapeutic drug. We found that tuning the drug release kinetics and binding affinities leads to improved delivery of the drug. Our results also indicate that multi-stage nanoparticles are superior over two-stage nano-carriers provided they have a faster drug release rate and for high binding affinity drugs. Furthermore, our results suggest that smaller nanoparticles achieve better treatment outcome.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baish, J. W., Y. Gazit, D. A. Berk, M. Nozue, L. T. Baxter, and R. K. Jain. Role of tumor vascular architecture in nutrient and drug delivery: an invasion percolation-based network model. Microvasc. Res. 51:327–346, 1996.
Baxter, L. T., and R. K. Jain. Transport of fluid and macromolecules in tumors. I. Role of interstitial pressure and convection. Microvasc. Res. 37:77–104, 1989.
Baxter, L. T., and R. K. Jain. Pharmacokinetic analysis of the microscopic distribution of enzyme-conjugated antibodies and prodrugs: comparison with experimental data. Br. J. Cancer 73:447–456, 1996.
Chauhan, V. P., and R. K. Jain. Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Mater. 12:958–962, 2013.
Chauhan, V. P., T. Stylianopoulos, Y. Boucher, and R. K. Jain. Delivery of molecular and nanomedicine to tumors: transport barriers and strategies. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2:281–298, 2011.
Chauhan, V. P., T. Stylianopoulos, J. D. Martin, Z. Popovic, O. Chen, W. S. Kamoun, M. G. Bawendi, D. Fukumura, and R. K. Jain. Normalization of tumour blood vessels improves the delivery of nanomedicines in a size-dependent manner. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7:383–388, 2012.
Choi, H. S., W. Liu, P. Misra, E. Tanaka, J. P. Zimmer, B. Itty Ipe, M. G. Bawendi, and J. V. Frangioni. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 25:1165–1170, 2007.
Eikenberry, S. A tumor cord model for doxorubicin delivery and dose optimization in solid tumors. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 6:16, 2009.
El-Kareh, A. W., and T. W. Secomb. Two-mechanism peak concentration model for cellular pharmacodynamics of Doxorubicin. Neoplasia 7:705–713, 2005.
Halford, S., D. Yip, C. S. Karapetis, A. H. Strickland, A. Steger, H. T. Khawaja, and P. G. Harper. A phase II study evaluating the tolerability and efficacy of CAELYX (liposomal doxorubicin, Doxil) in the treatment of unresectable pancreatic carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 12:1399–1402, 2001.
Jain, R. K., and T. Stylianopoulos. Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7:653–664, 2010.
Lammers, T., W. E. Hennink, and G. Storm. Tumour-targeted nanomedicines: principles and practice. Br. J. Cancer 99:392–397, 2008.
Mok, W., T. Stylianopoulos, Y. Boucher, and R. K. Jain. Mathematical modeling of herpes simplex virus distribution in solid tumors: implications for cancer gene therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 15:2352–2360, 2009.
Perrault, S. D., C. Walkey, T. Jennings, H. C. Fischer, and W. C. Chan. Mediating tumor targeting efficiency of nanoparticles through design. Nano Lett. 9:1909–1915, 2009.
Pirollo, K. F., and E. H. Chang. Does a targeting ligand influence nanoparticle tumor localization or uptake? Trends Biotechnol. 26:552–558, 2008.
Pluen, A., Y. Boucher, S. Ramanujan, T. D. McKee, T. Gohongi, E. di Tomaso, E. B. Brown, Y. Izumi, R. B. Campbell, D. A. Berk, and R. K. Jain. Role of tumor-host interactions in interstitial diffusion of macromolecules: cranial vs. subcutaneous tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:4628–4633, 2001.
Plummer, R., R. H. Wilson, H. Calvert, A. V. Boddy, M. Griffin, J. Sludden, M. J. Tilby, M. Eatock, D. G. Pearson, C. J. Ottley, Y. Matsumura, K. Kataoka, and T. Nishiya. A Phase I clinical study of cisplatin-incorporated polymeric micelles (NC-6004) in patients with solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 104:593–598, 2011.
Popovic, Z., W. Liu, V. P. Chauhan, J. Lee, C. Wong, A. B. Greytak, N. Insin, D. G. Nocera, D. Fukumura, R. K. Jain, and M. G. Bawendi. A nanoparticle size series for in vivo fluorescence imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49:8649–8652, 2010.
Pozrikidis, C., and D. A. Farrow. A model of fluid flow in solid tumors. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:181–194, 2003.
Pries, A. R., A. J. Cornelissen, A. A. Sloot, M. Hinkeldey, M. R. Dreher, M. Hopfner, M. W. Dewhirst, and T. W. Secomb. Structural adaptation and heterogeneity of normal and tumor microvascular networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5:e1000394, 2009.
Pries, A. R., M. Hopfner, F. le Noble, M. W. Dewhirst, and T. W. Secomb. The shunt problem: control of functional shunting in normal and tumour vasculature. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10:587–593, 2010.
Ruoslahti, E., S. N. Bhatia, and M. J. Sailor. Targeting of drugs and nanoparticles to tumors. J. Cell Biol. 188:759–768, 2010.
Sarin, H. Physiologic upper limits of pore size of different blood capillary types and another perspective on the dual pore theory of microvascular permeability. J. Angiogenes. Res. 2:14, 2010.
Schmidt, M. M., and K. D. Wittrup. A modeling analysis of the effects of molecular size and binding affinity on tumor targeting. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8:2861–2871, 2009.
Sevick, E. M., and R. K. Jain. Viscous resistance to blood flow in solid tumors: effect of hematocrit on intratumor blood viscosity. Cancer Res. 49:3513–3519, 1989.
Stylianopoulos, T. EPR-effect: utilizing size-dependent nanoparticle delivery to solid tumors. Ther. Deliv. 4:421–423, 2013.
Stylianopoulos, T., and R. K. Jain. Combining two strategies to improve perfusion and drug delivery in solid tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110:18632–18637, 2013.
Stylianopoulos, T., K. Soteriou, D. Fukumura, and R. K. Jain. Cationic nanoparticles have superior transvascular flux into solid tumors: insights from a mathematical model. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 41(1):68–77, 2013.
Sun, C., R. K. Jain, and L. L. Munn. Non-uniform plasma leakage affects local hematocrit and blood flow: implications for inflammation and tumor perfusion. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35:2121–2129, 2007.
Torchilin, V. P. Targeted pharmaceutical nanocarriers for cancer therapy and imaging. AAPS J. 9:E128–E147, 2007.
Von Hoff, D. D., T. J. Ervin, F. P. Arena, E. G. Chiorean, J. R. Infante, M. J. Moore, T. E. Seay, S. Tjulandin, W. W. Ma, M. N. Saleh, M. Harris, M. Reni, R. K. Ramanathan, J. Tabernero, M. Hidalgo, E. V. Cutsem, D. Goldstein, X. Wei, L. J. Iglesias, and M. F. Renschler. Results of a randomized phase III trial (MPACT) of weekly nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine alone for patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas with PET and CA19-9 correlates. J. Clin. Oncol. 31(suppl; abstr 4005), 2013.
Weiss, G. J., J. Chao, J. D. Neidhart, R. K. Ramanathan, D. Bassett, J. A. Neidhart, C. H. Choi, W. Chow, V. Chung, S. J. Forman, E. Garmey, J. Hwang, D. L. Kalinoski, M. Koczywas, J. Longmate, R. J. Melton, R. Morgan, J. Oliver, J. J. Peterkin, J. L. Ryan, T. Schluep, T. W. Synold, P. Twardowski, M. E. Davis, and Y. Yen. First-in-human phase 1/2a trial of CRLX101, a cyclodextrin-containing polymer-camptothecin nanopharmaceutical in patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies. Invest. New Drugs 31(4):986–1000, 2013.
Wong, C., T. Stylianopoulos, J. Cui, J. Martin, V. P. Chauhan, W. Jiang, Z. Popovic, R. K. Jain, M. G. Bawendi, and D. Fukumura. Multistage nanoparticle delivery system for deep penetration into tumor tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108:2426–2431, 2011.
Yuan, F., M. Leunig, S. K. Huang, D. A. Berk, D. Papahadjopoulos, and R. K. Jain. Microvascular permeability and interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth) liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res. 54:3352–3356, 1994.
Zhou, J., T. R. Patel, M. Fu, J. P. Bertram, and W. M. Saltzman. Octa-functional PLGA nanoparticles for targeted and efficient siRNA delivery to tumors. Biomaterials 33:583–591, 2012.
Zhu, H., R. K. Jain, and L. T. Baxter. Tumor pretargeting for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy. J. Nucl. Med. 39:65–76, 1998.
Acknowledgments
Simulations were performed at the high performance computer systems of the Cancer Biophysics laboratory at the University of Cyprus and of the Partners Healthcare System at Massachusetts General Hospital. This work was supported by the European Commission with a Marie-Curie Reintegration Grant (FP7-PIRG08-GA-2010-276894) to TS and the National Cancer Institute (P01-CA080124, R01-CA126642, R01-CA115767, R01-CA096915, R01-CA085140, T32-CA073479, Federal Share Income Grant), and a DoD Breast Cancer Research Innovator award (W81XWH-10-1-0016) to RKJ.
Conflict of interest
R.K.J. received research grants from Dyax, MedImmune and Roche; consultant fees from Enlight, Ophthotech, SynDevRx, and Zyngenia; owns equity in Enlight, Ophthotech, SynDevRx, and XTuit, serves on the Board of Directors of XTuit and Board of Trustees of Tekla Healthcare Investors, Tekla Life Sciences Investors and Tekla Healthcare Opportunities Fund. No reagents or funding from these companies was used in these studies. Therefore, there is no significant financial or other competing interest in the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Konstantinos Konstantopoulos oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stylianopoulos, T., Economides, EA., Baish, J.W. et al. Towards Optimal Design of Cancer Nanomedicines: Multi-stage Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 2291–2300 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1276-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1276-9