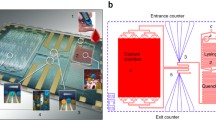
Abstract
Cost-effective, high-performance diagnostic instruments are vital to providing the society with accessible, affordable, and high-quality healthcare. Here we present an integrated, “microfluidic drifting” based flow cytometry chip as a potential inexpensive, fast, and reliable diagnostic tool. It is capable of analyzing human blood for cell counting and diagnosis of diseases. Our device achieves a throughput of ~3754 events/s. Calibration with Flow-Check calibration beads indicated good congruency with a commercially available benchtop flow cytometer. Moreover, subjection to a stringent 8-peak rainbow calibration particle test demonstrated its ability to perform high-resolution immunological studies with separation resolution of 4.28 between the two dimmest fluorescent populations. Counting accuracy at different polystyrene bead concentrations showed strong correlation (r = 0.9991) with hemocytometer results. Finally, reliable quantification of CD4+ cells in healthy human blood via staining with monoclonal antibodies was demonstrated. These results demonstrate the potential of our microfluidic flow cytometry chip as an inexpensive yet high-performance point-of-care device for mobile medicine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., P. Li, P.-H. Huang, Y. Xie, J. D. Mai, L. Wang, N.-T. Nguyen, and T. J. Huang. Rare cell isolation and analysis in microfluidics. Lab Chip 14:626–645, 2014.
Chen, Y., A. A. Nawaz, Y. Zhao, P.-H. Huang, J. P. McCoy, S. J. Levine, L. Wang, and T. J. Huang. Standing surface acoustic wave (SSAW)-based microfluidic cytometer. Lab Chip 14:916–923, 2014.
Cheng, X., Y. Liu, D. Irimia, U. Demirci, L. Yang, L. Zamir, W. R. Rodríguez, M. Toner, and R. Bashir. Cell detection and counting through cell lysate impedance spectroscopy in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:746–755, 2007.
Chin, C. D., Y. K. Cheung, T. Laksanasopin, M. M. Modena, S. Y. Chin, A. A. Sridhara, D. Steinmiller, V. Linder, J. Mushingantahe, G. Umviligihozo, E. Karita, L. Mwambarangwe, S. L. Braunstein, J. van de Wijgert, R. Sahabo, J. E. Justman, W. El-Sadr, and S. K. Sia. Mobile device for disease diagnosis and data tracking in resource-limited settings. Clin. Chem. 59:629–640, 2013.
Chiu, Y.-J., S. H. Cho, Z. Mei, V. Lien, T.-F. Wu, and Y.-H. Lo. Universally applicable three-dimensional hydrodynamic microfluidic flow focusing. Lab Chip 13:1803–1809, 2013.
Eyal, S., and S. R. Quake. Velocity-independent microfluidic flow cytometry. Electrophoresis 23:2653–2657, 2002.
Goddard, G. R., C. K. Sanders, J. C. Martin, G. Kaduchak, and S. W. Graves. Analytical performance of an ultrasonic particle focusing flow cytometer. Anal. Chem. 79:8740–8746, 2007.
Godin, J., C.-H. Chen, S. H. Cho, W. Qiao, F. Tsai, and Y.-H. Lo. Microfluidics and photonics for Bio-System-on-a-Chip: a review of advancements in technology towards a microfluidic flow cytometry chip. J. Biophotonics 1:355–376, 2008.
Godin, J., V. Lien, and Y.-H. Lo. Demonstration of two-dimensional fluidic lens for integration into microfluidic flow cytometers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89:061106, 2006.
Godin, J., and Y.-H. Lo. Two-parameter angular light scatter collection for microfluidic flow cytometry by unique waveguide structures. Biomed. Opt. Express 1:1472–1479, 2010.
Gossett, D. R., and D. Di Carlo. Particle focusing mechanisms in curving confined flows. Anal. Chem. 81:8459–8465, 2009.
Gottwald, E., B. Lahni, G. Lüdke, T. Preckel, and C. Buhlmann. Intracellular HSP72 detection in HL60 cells using a flow cytometry system based on microfluidic analysis. Biotechniques 35:358–362, 364, 366–367, 2003.
Grafton, M., L. M. Reece, P. P. Irazoqui, B. Jung, H. D. Summers, R. Bashir, and J. F. Leary. Design of a multi-stage microfluidics system for high-speed flow cytometry and closed system cell sorting for cytomics. Proc. SPIE 6859:1–10, 2008.
Jayat, C., and M. H. Ratinaud. Cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry: principles and applications. Biol. Cell 78:15–25, 1993.
Kiesel, P., M. Beck, and N. Johnson. Monitoring CD4 in whole blood with an opto-fluidic detector based on spatially modulated fluorescence emission. Cytometry A 79:317–324, 2011.
Kummrow, A., J. Theisen, M. Frankowski, A. Tuchscheerer, H. Yildirim, K. Brattke, M. Schmidt, and J. Neukammer. Microfluidic structures for flow cytometric analysis of hydrodynamically focussed blood cells fabricated by ultraprecision micromachining. Lab Chip 9:972–981, 2009.
Laerum, O. D., and R. Bjerknes. Flow Cytometry in Hematology. London: Academic Press, 1992.
Lapsley, M. I., L. Wang, and T. J. Huang. On-chip flow cytometry: where is it now and where is it going? Biomark. Med. 7:75–78, 2013.
Lee, G.-B., C.-H. Lin, and G.-L. Chang. Micro flow cytometers with buried SU-8/SOG optical waveguides. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 103:165–170, 2003.
Maleki, T., T. Fricke, J. Quesenberry, P. Todd, and J. F. Leary. Point-of-care, portable microfluidic blood analyzer system. Proc. SPIE 8251:1–3, 2012.
Mao, X., and T. J. Huang. Microfluidic diagnostics for the developing world. Lab Chip 12:1412–1416, 2012.
Mao, X., S.-C. S. Lin, C. Dong, and T. J. Huang. Single-layer planar on-chip flow cytometer using microfluidic drifting based three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing. Lab Chip 9:1583–1589, 2009.
Mao, X., S.-C. S. Lin, M. I. Lapsley, J. Shi, B. K. Juluri, and T. J. Huang. Tunable Liquid Gradient Refractive Index (L-GRIN) lens with two degrees of freedom. Lab Chip 9:2050–2058, 2009.
Mao, X., A. A. Nawaz, S.-C. S. Lin, M. I. Lapsley, Y. Zhao, J. P. McCoy, W. S. El-Deiry, and T. J. Huang. An integrated, multiparametric flow cytometry chip using “microfluidic drifting” based three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing. Biomicrofluidics 6:24113–241139, 2012.
Mao, X., J. R. Waldeisen, B. K. Juluri, and T. J. Huang. Hydrodynamically tunable optofluidic cylindrical microlens. Lab Chip 7:1303–1308, 2007.
Morris, K. Mobile phones connecting efforts to tackle infectious disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 9:274, 2009.
Nawaz, A. A., X. Zhang, X. Mao, J. Rufo, S.-C. S. Lin, F. Guo, Y. Zhao, M. Lapsley, P. Li, J. P. McCoy, S. J. Levine, and T. J. Huang. Sub-micrometer-precision, three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing via “microfluidic drifting”. Lab Chip 14:415–423, 2014.
Oakey, J., R. W. Applegate, E. Arellano, D. Di Carlo, S. W. Graves, and M. Toner. Particle focusing in staged inertial microfluidic devices for flow cytometry. Anal. Chem. 82:3862–3867, 2010.
Pop-Eleches, C., H. Thirumurthy, J. P. Habyarimana, J. G. Zivin, M. P. Goldstein, D. de Walque, L. MacKeen, J. Haberer, S. Kimaiyo, J. Sidle, D. Ngare, and D. R. Bangsberg. Mobile phone technologies improve adherence to antiretroviral treatment in a resource-limited setting: a randomized controlled trial of text message reminders. AIDS 25:825–834, 2011.
Shapiro, H. M. Practical Flow Cytometry. New York: Wiley-Liss, 2003.
Shapiro, H. M., and N. G. Perlmutter. Violet laser diodes as light sources for cytometry. Cytometry 44:133–136, 2001.
Shi, J., X. Mao, D. Ahmed, A. Colletti, and T. J. Huang. Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 8:221–223, 2008.
Shi, J., S. Yazdi, S.-C. S. Lin, X. Ding, I.-K. Chiang, K. Sharp, and T. J. Huang. Three-dimensional continuous particle focusing in a microfluidic channel via standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 11:2319–2324, 2011.
Skommer, J., J. Akagi, K. Takeda, Y. Fujimura, K. Khoshmanesh, and D. Wlodkowic. Multiparameter Lab-on-a-Chip flow cytometry of the cell cycle. Biosens. Bioelectron. 42:586–591, 2013.
Telford, W. G., T. S. Hawley, and R. G. Hawley. Analysis of violet-excited fluorochromes by flow cytometry using a violet laser diode. Cytometry A 54:48–55, 2003.
Tudos, A. J., G. J. Besselink, and R. B. Schasfoort. Trends in miniaturized total analysis systems for point-of-care testing in clinical chemistry. Lab Chip 1:83–95, 2001.
Wang, J., B. Fei, R. L. Geahlen, and C. Lu. Quantitative analysis of protein translocations by microfluidic total internal reflection fluorescence flow cytometry. Lab Chip 10:2673–2679, 2010.
Wang, J., Y. Zhan, N. Bao, and C. Lu. Quantitative measurement of quantum dot uptake at the cell population level using microfluidic evanescent-wave-based flow cytometry. Lab Chip 12:1441–1445, 2012.
Wang, J.-H., L. Cheng, C.-H. Wang, W.-S. Ling, S.-W. Wang, and G.-B. Lee. An integrated chip capable of performing sample pretreatment and nucleic acid amplification for HIV-1 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 41:484–491, 2013.
Wang, S., F. Inci, G. De Libero, A. Singhal, and U. Demirci. Point-of-care assays for tuberculosis: role of nanotechnology/microfluidics. Biotechnol. Adv. 31:438–449, 2013.
Wei, F., R. Lam, S. Cheng, S. Lu, D. Ho, and N. Li. Rapid detection of melamine in whole milk mediated by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96:133702, 2010.
Woods, J., and R. Hoffman. Evaluating fluorescence sensitivity on flow cytometers: an overview. Cytometry A 33:256–259, 1998.
Xia, Y., and G. M. Whitesides. Soft Lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28:153–184, 1998.
Yager, P., G. J. Domingo, and J. Gerdes. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 10:107–144, 2008.
Zhao, C., Y. Liu, Y. Zhao, N. Fang, and T. J. Huang. A reconfigurable plasmofluidic lens. Nat. Commun. 4:2305, 2013.
Acknowledgments
We thank Joseph Rufo and Adem Ozcelik for helpful discussions. This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Director’s New Innovator Award (1DP2OD007209-01), National Science Foundation, and the Penn State Center for Nanoscale Science (MRSEC) under grant DMR-0820404. Components of this work were conducted at the Penn State node of the NSF-funded National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network (NNIN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Tingrui Pan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, A.A., Nissly, R.H., Li, P. et al. Immunological Analyses of Whole Blood via “Microfluidic Drifting” Based Flow Cytometric Chip. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 2303–2313 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1041-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1041-5