Abstract
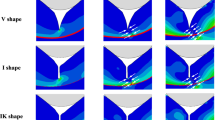
This study investigates micro-crack propagation at the enamel/adhesive interface using finite element (FE) submodeling and element death techniques. A three-dimensional (3D) FE macro-model of the enamel/adhesive/ceramic subjected to shear bond testing was generated and analyzed. A 3D micro-model with interfacial bonding structure was constructed at the upper enamel/adhesive interface where the stress concentration was found from the macro-model results. The morphology of this interfacial bonding structure (i.e., resin tag) was assigned based on resin tag geometry and enamel rod arrangement from a scanning electron microscopy micrograph. The boundary conditions for the micro-model were determined from the macro-model results. A custom iterative code combined with the element death technique was used to calculate the micro-crack propagation. Parallel experiments were performed to validate this FE simulation. The stress concentration within the adhesive occurred mainly at the upper corner near the enamel/adhesive interface and the resin tag base. A simulated fracture path was found at the resin tag base along the enamel/adhesive interface. A morphological observation of the fracture patterns obtained from in vitro testing corresponded with the simulation results. This study shows that the FE submodeling and element death techniques could be used to simulate the 3D micro-stress pattern and the crack propagation noted at the enamel/adhesive interface.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSYS 11.0 manual.
Berkovitz, B. K. B., G. R. Holland, and B. J. Moxham. Oral Anatomy, Histology and Embryology. London: Mosby, pp. 101–118, 2002.
Betamar, N., G. Cardew, and R. van Noort. Influence of specimen designs on the microtensile bond strength of dentin. J. Adhes. Dent. 9:159–168, 2007.
Betamar, N., G. Cardew, and R. van Noort. The effect of variations in hourglass specimen design on microtensile bond strength to dentin. J. Adhes. Dent. 9:427–436, 2007.
Chang, K. H., S. Magdum, S. C. Khera, and V. K. Goel. An advanced approach for computer modeling and prototyping of the human tooth. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31:621–631, 2003.
Cormier, N. G., B. S. Smallwood, G. B. Sinclair, and G. Meda. Aggressive submodelling of stress concentrations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 46:889–909, 1999.
Craig, R. G., F. A. Peyton, and D. W. Johnson. Compressive properties of enamel, dental cements, and gold. J. Dent. Res. 40:936–945, 1961.
DeHoff, P. H., K. J. Anusavice, and Z. Wang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the shear bond test. Dent. Mater. 11:126–131, 1995.
Dos Santos, K. T., R. H. Sundfeld, C. A. Garbin, R. S. de Alexandre, M. L. Sundefeld, and B. N. Ceolim. Length of resin tags in pit-and-fissure sealants: all-in-one self-etching adhesive vs phosphoric acid etching. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 29:186–192, 2008.
Erickson, R. L., W. W. Barkmeier, and M. A. Latta. The role of etching in bonding to enamel: a comparison of self-etching and etch-and-rinse adhesive systems. Dent. Mater. 25:1459–1467, 2009.
Fennis, W. M. M., R. H. Kuijs, M. Barink, C. M. Kreulen, N. Verdonschot, and N. H. J. Creugers. Can internal stresses explain the fracture resistance of cusp-replacing composite restorations? Eur. J. Oral Sci. 113:443–448, 2005.
Gökçe, B., M. E. Çömlekoğlu, B. Özpinar, M. Türkün, and A. D. Kaya. Effect of antioxidant treatment on bond strength of a luting resin to bleached enamel. J. Dent. 36:780–785, 2008.
Guess, P. C., and C. F. J. Stappert. Midterm results of a 5-year prospective clinical investigation of extended ceramic veneers. Dent. Mater. 24:804–813, 2008.
Gupta, S., F. C. van der Helm, and F. van Keulen. Stress analysis of cemented glenoid prostheses in total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Biomech. 37:1777–1786, 2004.
Gupta, S., F. C. van der Helm, and F. van Keulen. The possibilities of uncemented glenoid component—a finite element study. Clin. Biomech. 19:292–302, 2004.
Hipólito, V. D., M. F. Goes, M. R. O. Carrilho, D. C. N. Chan, M. Daronch, and M. A. C. Sinhoreti. SEM evaluation of contemporary self-etching primers applied to ground and unground enamel. J. Adhes. Dent. 7:203–211, 2005.
Ichim, I., Q. Li, W. Li, M. V. Swain, and J. Kieser. Modelling of fracture behaviour in biomaterials. Biomaterials 28:1317–1326, 2007.
Kulkarni, M. G., P. H. Geubelle, and K. Matous. Multi-scale modeling of heterogeneous adhesives: effect of particle decohesion. Mech. Mater. 41:573–583, 2009.
Liu, H. L., C. L. Lin, M. T. Sun, and Y. H. Chang. Numerical investigation of macro and micro-mechanics of a ceramic veneer bonded with various cement thicknesses using the typical and submodeling finite element approaches. J. Dent. 37:141–148, 2009.
Liu, J. M., J. T. Liu, and T. Sawa. Strength and failure of bulky adhesive joints with adhesively-bonded columns. J. Adhes. Sci. Tech. 18:1613–1623, 2004.
Lührs, A. K., S. Guhr, H. Günay, and W. Geurtsen. Shear bond strength of self-adhesive resins compared to resin cements with etch and rinse adhesives to enamel and dentin in vitro. Clin. Oral Invest. 14:193–199, 2010.
Matous, K., M. G. Kulkarni, and P. H. Geubelle. Multiscale cohesive failure modeling of heterogeneous adhesives. J. Mech. Phys. Solid 56:1511–1533, 2008.
Misra, A., P. Spencer, O. Marangos, Y. Wang, and J. L. Katz. Micromechanical analysis of dentin/adhesive interface by the finite element method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B: Appl. Biomater. 15:56–65, 2004.
Özcan, M., and A. Mese. Effect of ultrasonic versus manual cementation on the fracture strength of resin composite laminates. Oper. Dent. 34:437–442, 2009.
Pérez, M. A., J. M. García-Aznar, and M. Doblaré. Does increased bone–cement interface strength have negative consequences for bulk cement integrity? A finite element study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37:454–466, 2009.
Peumans, M., B. Van Meerbeek, P. Lambrechts, and G. Vanherle. Porcelain veneers: a review of the literature. J. Dent. 28:163–177, 2000.
Placido, E., J. B. C. Meira, R. G. Lima, A. Muench, R. M. Souza, and R. Y. Ballester. Shear versus micro-shear bond strength test: a finite element stress analysis. Dent. Mater. 23:1086–1092, 2007.
Ritter, A. V., E. Ghaname, and L. A. F. Pimenta. Dentin and enamel bond strengths of dual-cure composite luting agents used with dual-cure dental adhesives. J. Dent. 37:59–64, 2009.
Seghi, R. R., I. Denry, and F. Brajevic. Effects of ion exchange on hardness and fracture toughness of dental ceramics. Int. J. Prosthodont. 5:309–314, 1992.
Shaini, F. J., A. C. Shortall, and P. M. Marquis. Clinical performance of porcelain laminate veneers. A retrospective evaluation over a period of 6.5 years. J. Oral Rehabil. 24:553–559, 1997.
Sieweke, M., U. Salomon-Sieweke, P. Zofel, and V. Stachniss. Longevity of oroincisal ceramic veneers on canines—a retrospective study. J. Adhes. Dent. 2:229–234, 2000.
Simmons, C. A., S. A. Meguid, and R. M. Pilliar. Mechanical regulation of localized and appositional bone formation around bone-interfacing implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55:63–71, 2001.
Stacey, G. D. A shear stress analysis of the bonding of porcelain veneers to enamel. J. Prosthet. Dent. 70:395–402, 1993.
Swift, E. J., and M. J. Friedman. Critical appraisal. Porcelain veneer outcomes, part I. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 18:54–57, 2006.
Troedson, M., and T. Derand. Effect of margin design, cement polymerization, and angle of loading on stress in porcelain veneers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 82:518–524, 1999.
van Landuyt, K. L., P. Kanumilli, J. De Munck, M. Peumans, P. Lambrechts, and B. van Meerbeek. Bond strength of a mild self-etch adhesive with and without prior acid-etching. J. Dent. 34:77–85, 2006.
Versluis, A., D. Tantbirojn, and W. H. Douglas. Why do shear bond tests pull out dentin? J. Dent. Res. 76:1298–1307, 1997.
Yuan, Y., Y. Shimada, S. Ichinose, A. Sadr, and J. Tagami. Effects of dentin characteristics on interfacial nanoleakage. J. Dent. Res. 86:1001–1006, 2007.
Zhao, R., K. Wyss, and C. A. Simmons. Comparison of analytical and inverse finite element approaches to estimate cell viscoelastic properties by micropipette aspiration. J. Biomech. 42:2768–2773, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Mona Kamal Marei oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HL., Lin, CL., Sun, MT. et al. 3D Micro-Crack Propagation Simulation at Enamel/Adhesive Interface Using FE Submodeling and Element Death Techniques. Ann Biomed Eng 38, 2004–2012 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0047-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-010-0047-x