Abstract
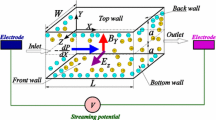
In a microfluidic system, flow slip velocity on a solid wall can be the same order of magnitude as the average velocity in a microchannel. The flow-electricity interaction in a complex microfluidic system subjected to joint action of wall slip and electro-viscous effect is an important topic. This paper presents an analytic solution of pressure-driven liquid flow velocity and flow-induced electric field in a two-dimensional microchannel made of different materials with wall slip and electro-viscous effects. The Poisson- Boltzmann equation and the Navier-Stokes equation are solved for the analytic solutions. The analytic solutions agree well with the numerical solutions. It was found that the wall slip amplifies the flow-induced electric field and enhances the electro-viscous effect on flow. Thus the electro-viscous effect can be significant in a relatively wide microchannel with relatively large κh, the ratio of channel width to thickness of electric double layer, in comparison with the channel without wall slip.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baudry J., Charlaix E., Tonck A., Mazuyer D.: Experimental evidence for a large slip effect at a non-wetting fluid-solid interface. Langmui 17, 5232–5236 (2001)
Pit R., Hervet H., Léger L.: Direct experimental evidence of slip in hexadecane: solid interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(5), 980–983 (2000)
Pit R., Hervet H., L’eger L.: Friction and slip of a simple liquid at a solid surface. Tribol. Lett. 7, 147–152 (1999)
Zhu Y.X., Granick S.: Limits of the hydrodynamic no-slip boundary condition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(11), 106102 (2002)
Barrat J.L.: Large slip effect at a non-wetting fluid-solid interface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4671–4674 (1999)
Tretheway D.C., Meinhart C.D.: Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys. Fluids 14(3), L9–L12 (2002)
Ou J., Perot B., Rothstein J.P.: Laminar drag reduction in microchannels using ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Phys. Fluids 16(12), 4635–4643 (2004)
Tretheway D.C., Meinhart C.D.: A generating mechanism for apparent fluid slip in hydrophobic microchannels. Phys. Fluids 16(5), 1509–1515 (2004)
Joseph P., Tabeling P.: Direct measurement of the apparent slip length. Phys. Rev. E 71, 035303(R) (2005)
Chun M.S., Lee T.S., Lee K.: Microflow of dilute colloidal suspension in narrow channel of microfluidic-chip under Newtonian fluid slip condition. K. Aust. Rheol. J. 17(4), 207–215 (2005)
Squires T.M.: Electrokinetic flows over inhomogeneously slipping surfaces. Phys. Fluids 20(9), 092105 (2008)
Muller V.M., Sergeeva I.P., Sobolev V.D., Churaev N.V.: Boundary efects in the theory of electrokinetic phenomena. Colloid J. USSR 48, 606–614 (1986)
Ajdari A., Bocquet L.: Giant amplification of interfacially driven transport by hydrodynamic slip: Diffusio-osmosis and beyond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(18), 186102 (2006)
Bazant M.Z., Vinogradova O.I.: Tensorial hydrodynamic slip. J. Fluid Mech. 613, 125–134 (2008)
Davidson C., Xuan X.C.: Electrokinetic energy conversion in slip microchannels. J. Power Sour. 179, 297–300 (2008)
Ren Y.Q., Stein D.: Slip-enhanced electrokinetic energy conversion in microfluidic channels. Microtechnology 19, 195707 (2008)
Brunet E., Ajdari A.: Generalized Onsager relations for electrokinetic effects in anisotropic and heterogeneous geometries. Phys. Rev. E 69, 016306 (2004)
Hunter R.J.: Zeta Potential in Colloidal Science, Principle and Application. Academic Press, New York (1981)
Lyklema J.: Fundamentals of Interface and Colloidal Science, vol. II. Academic Press, New York (1995)
Li D.Q.: Electrokinetics in Microfluidics. Elsevier Academic Press, New York (2004)
Yang C., Li D.Q., Masliyah J.H.: Modeling forced liquid convection in rectangular microchannels with electrokinetic effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 41, 4229–4249 (1998)
Ren L.Q., Qu W.L., Li D.Q.: Interfacial electrokinetic effects on liquid flow in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 44, 3125–3134 (2001)
Chun M.S., Lee S.Y., Yang S.M.: Estimation of Zeta-potential by electrokinetic analysis of ionic fluid flows through a divergent microchannel. J. Colloid Interface Sci 266, 120–126 (2003)
Kilic M.S., Bazant M.Z., Ajdari A.: Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. I. Double-layer charging. Phys. Rev. E 75, 021502 (2007)
Kilic M.S., Bazant M.Z., Ajdari A.: Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. II. Modified Poisson-Nernst-Planck equations. Phys. Rev. E 75, 021503 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10872076).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Wu, J. Flow behavior in microchannel made of different materials with wall slip velocity and electro-viscous effects. Acta Mech Sin 26, 73–80 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0286-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0286-y