Abstract
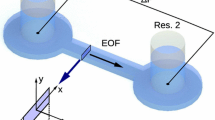
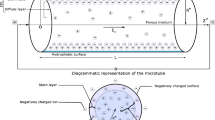
In electrokinetically driven microfluidic applications, reservoirs are indispensable and have finite sizes. During operation processes, as the liquid level in reservoirs keeps changing as time elapses, a backpressure is generated. Thus, the flow in microfluidic channels actually exhibits a combination of the electroosmotic flow and the time-dependent induced backpressure-driven flow. In this paper, a model is presented to describe the effect of the finite reservoir size on electroosmotic flow in a rectangular microchannel. Important parameters that describe the effect of finite reservoir size on flow characteristics are discussed. A new concept termed as “effective pumping period” is introduced to characterize the reservoir size effect. The proposed model identifies the mechanisms of the finite-reservoir size effects and is verified by experiment using the micro-PIV technique. The results reported in this study can be used for facilitating the design of microfluidic devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crabtree HJ, Cheong ECS, Tilroe DA, Backhouse CJ (2001) Microchip injection and separation anomalies due to pressure effects. Anal Chem 73:4079–4086
Deen WM (1998) Analysis of transport phenomena. Oxford University Press, New York
Einstein A (1905) Theory of Brownian movement. Dover, New York
Erickson D, Li D (2004) Integrated microfluidic devices. Anal Chim Acta 507:11–26
MacInnes JM, Du X, Allen RWK (2003) Prediction of electrokinetic and pressure flow in a microchannel T-junction. Phys Fluids 15:1992–2005
Marcos, Yang C, Ooi KT, Wong TN, Masliyah JH (2004) Frequency-dependent laminar electroosmotic flow in a closed-end rectangular microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:679–698
Marcos, Kang YJ, Ooi KT, Yang C, Wong TN (2005) Frequency-dependent velocity and vorticity fields of electro-osmotic flow in a closed-end cylindrical microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 15:301–312
Papanastasiou TC, Georgiou GC, Alexandrou AN (2000) Viscous fluid flow. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Probstein RF (1994) Physicochemical hydrodynamics, 2nd edn. Butterworths, Boston
Santiago JG (2001) Electroosmotic flows in microchannels with finite intertrial and pressure forces. Anal Chem 73:2353–2365
Santiago JG, Wereley ST, Meinhart CD, Beebe DJ, Adrian RJ (1998) A particle image velocimetry system for microfluidics. Exp Fluids 25:316–325
Tang GY, Yang C, Chai JC, Gong HQ (2003) Modeling of electroosmotic flow and capillary electrophoresis with the Joule heating effect: the Nernst–Planck equation versus the Boltzmann distribution. Langmuir 19:10975–10984
Yan DG, Yang C, Nguyen NT, Huang XY (2006) A method for simultaneously determining the zeta potentials of the channel surface and the tracer particles using microparticle image velocimetry technique. Electrophoresis 27:620–627
Yang R-J, Tseng T-I, Chang C-C (2005) End effects on electro-osmotic flows in micro-channels. J Micromech Microeng 15:254–262
Zhang Y, Gu X-J, Barber RW, Emerson DR (2004) An analysis of induced pressure fields in electroosmotic flows through microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:670–678
Acknowledgments
D.G. Yan wishes to acknowledge the PhD scholarship from Nanyang Technological University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, D.G., Yang, C. & Huang, X.Y. Effect of finite reservoir size on electroosmotic flow in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 3, 333–340 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0135-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-006-0135-2