Abstract
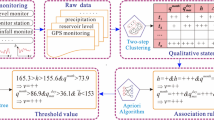
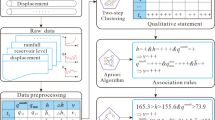
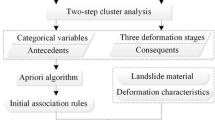
In this study, a data mining approach is proposed to investigate the hydrological causes of the Majiagou landslide, located in the Three Gorges Reservoir in China. It is possible to determine the cause-and-effect relationships between hydrological parameters and landslide movement. The data mining approach consists of two steps: first, hydrological indicators and landslide movements are discretized using the two-step cluster analysis; second, the association rule mining with the Apriori algorithm is employed to identify the contribution of each hydrological parameter to landslide movement. The results obtained suggest that deformation and later failure occurred first at the toe of the landslide and progressed upslope due to rising water level in the reservoir, prolonged heavy rainfall, and rapid drawdown in the reservoir. The proposed novel use of field data and data mining has the potential for providing procedures and solutions for an effective interpretation of landslide monitoring data.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal R, Imieliski T, Swami A (1993) Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proc. 1993 ACM-SIGMOD Int. Conf. Management of Data (SIGMOD'93), Washington, DC, pp. 207–216. doi:10.1145/170035.170072
Althuwaynee OF, Pradhan B, Park HJ, Lee JH (2014) A novel ensemble decision tree-based CHi-squared Automatic Interaction Detection (CHAID) and multivariate logistic regression models in landslide susceptibility mapping. Landslides 11:1063–1078. doi:10.1007/s10346-014-0466-0
Cheng CW, Lin CC, Leu SS (2010) Use of association rules to explore cause-effect relationships in occupational accidents in the Taiwan construction industry. Saf sci 48:436–444. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2009.12.005
Cruden DM, Varnes DJ (1996) Landslide types and processes. In: Turner AK, Schuster RL (eds) Special report 247: landslides investigation and mitigation. Transportation Research Board, US National Research Council, Washington, pp 36–75
Dai FC, Deng JH, Tham LG, Law KT, Lee CF (2004) A large landslide in Zigui County, Three Gorges area. Can Geotech J 41(6):1233–1240. doi:10.1139/t04-049
Du J, Yin KL, Lacasse S (2013) Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 10:203–218. doi:10.1007/s10346-012-0326-8
Ermini L, Catani F, Casagli N (2005) Artificial neural networks applied to landslide susceptibility assessment. Geomorphology 66:327–343. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.09.025
Falaschi F, Giacomelli F, Federici PR, Puccinelli A, D’Amato Avanzi G, Pochini A, Ribolini A (2009) Logistic regression versus artificial neural networks: landslide susceptibility evaluation in a sample area of the Serchio River valley, Italy. Nat Hazards 50(3):551–569. doi:10.1007/s11069-009-9356-5
Gao YL, Wang HD, Li G, Zhang JY, Yang XY (2009) Construction and application of a real-time monitoring system for landslides. In: Wang FW, Li TL (eds) Landslide disaster mitigation in Three Gorges Reservoir. Springer, China, pp 497–517. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-00132-1_24
Genevois R, Ghirotti M (2005) The 1963 Vaiont landslide. Giornale di Geologia Applicata 1:41–52. doi:10.1474/GGA.2005-01.0-05.0005
Griffiths JS (1999) Proving the occurrence and cause of a landslide in a legal context. B Eng Geol Environ 58:75–85. doi:10.1007/s100640050070
Han EH, Karypis G, Kumar V (1997) Min-Apriori: an algorithm for finding association rules in data with continuous attributes. Technical report, Department of Computer Science, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
Hu XL, Zhang M, Sun MJ, Huang KX, Song YJ (2013) Deformation characteristics and failure mode of the Zhujiadian landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. B Eng Geol Environ 74:1–12. doi:10.1007/s10064-013-0552-x
Huang HF, Yi W, Lu SQ, Yi QL, Zhang GD (2014) Use of monitoring data to interpret active landslide movements and hydrological triggers in Three Gorges Reservoir. J Perform Constr Fac: C4014005. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000682
Hui L, Shih CC, Keh HC, Yu PY, Cheng YC, Huang NC (2014) The application of association rules in clinical disease: the relationship between recovery after operation of endovascular aneurysm repairing and chronic. In: Peng WC, Wang HX, Bailey J, Tseng VS, Ho TB, Zhou ZH, Chen ALP (eds) Trends and applications in knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer, pp 712–721. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-13186-3_63
Jian WX, Wang ZJ, Yin KL (2009) Mechanism of the Anlesi landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng Geol 108:86–95. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.017
Karabatak M, Ince MC (2009) An expert system for detection of breast cancer based on association rules and neural network. Expert Syst Appl 36(2, Part2):3465–3469. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2008.02.064
Liang WJ, Zhuang DF, Jiang D, Pan JJ, Ren HY (2012) Assessment of debris flow hazards using a Bayesian network. Geomorphology 171–172:94–100. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.05.008
Liao CW, Perng YH (2008) Data mining for occupational injuries in the Taiwan construction industry. Saf Sci 46:1091–1102. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2007.04.007
Michailidou C, Maheras P, Arseni-Papadimititriou A, Kolyva-Machera F, Anagnostopoulou C (2009) A study of weather types at Athens and Thessaloniki and their relationship to circulation types for the cold-wet period, part I: two-step cluster analysis. Theor Appl Climatol 97:163–177. doi:10.1007/s00704-008-0057-x
Nahar J, Imam T, Tickle KS, Chen Y-PP (2013) Association rule mining to detect factors which contribute to heart disease in males and females. Expert Syst Appl 40(4):1086–1093. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2012.08.028
Nefeslioglu HA, Sezer E, Gokceoglu C, Bozkir AS, Duman TY (2010) Assessment of landslide susceptibility by decision trees in the metropolitan area of Istanbul, Turkey. Math Probl Eng. doi:10.1155/2010/901095
Ouyang Y, Luo SM, Cui LH, Wang Q, Zhang JE (2011) Estimation of real-time n load in surface water using dynamic data-driven application system. Ecol Eng 37:616–621. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2010.12.023
Popescu ME (1994) A suggested method for reporting landslide causes. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 50:71–74. doi:10.1007/BF02594958
Pourghasemi HR, Goli Jirandeh A, Pradhan B, Xu C, Gokceoglu C (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using support vector machine and GIS at the Golestan Province, Iran. J Earth Syst Sci 122:349–369. doi:10.1007/s12040-013-0282-2
Saito H, Nakayama D, Matsuyama H (2009) Comparison of landslide susceptibility based on a decision-tree model and actual landslide occurrence: the Akaishi Mountains, Japan. Geomorphology 109:108–121. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.02.026
Salciarini D, Godt JW, Savage WZ, Conversini P, Baum RL, Michael JA (2006) Modeling regional initiation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides in the eastern Umbria region of central Italy. Landslides 3:181–194. doi:10.1007/s10346-006-0037-0
Satish SM, Bharadhwaj S (2010) Information search behaviour among new car buyers: a two-step cluster analysis. IIMB Manag Rev 22(1-2):5–15. doi:10.1016/j.iimb.2010.03.005
Shi B, Jiang HT, Liu ZB, Fang HY (2002) Engineering geological characteristics of expansive soils in China. Eng Geol 67:63–71. doi:10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00145-X
Song YQ, Gong JH, Gao S, Wang DC, Cui TJ, Li Y, Wei BQ (2012) Susceptibility assessment of earthquake-induced landslides using Bayesian network: a case study in Beichuan, China. Comput Geosci 42:189–199. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2011.09.011
SPSS (2012) IBM SPSS modeler 15 algorithms guide. Chicago, USA
Terzaghi K (1950) Mechanisms of landslides. In: Application of geology to engineering practice, Geological Society of America, Berkey volume, pp 83–123
Tien Bui D, Pradhan B, Lofman O, Revhaug I, Dick OB (2012) Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Hoa Binh province of Vietnam: a comparison of the Levenberg-Marquardt and Bayesian regularized neural networks. Geomorphology 171–172:12–29. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.04.023
Tsai F, Lai JS, Chen WW, Lin TH (2013) Analysis of topographic and vegetative factors with data mining for landslide verification. Ecol Eng 61(Part C):669–677
Wang FW, Zhang YM, Huo ZT, Peng XM, Araiba K, Wang GH (2008) Movement of the Shuping landslide in the first four years after the initial impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam Reservoir, China. Landslides 5:321–329. doi:10.1007/s10346-008-0128-1
Wang XM, Niu RQ (2010) Landslide intelligent prediction using object-oriented method. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 30:1478–1486. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2010.06.017
Wen BP, Wang SJ, Wang EZ, Zhang JM (2004) Characteristics of rapid giant landslides in China. Landslides 1:247–261. doi:10.1007/s10346-004-0022-4
Witten IH, Frank E (2011) Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques, 3rd edn. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington
Xia M, Ren GM, Ma XL (2013) Deformation and mechanism of landslide influenced by the effects of reservoir water and rainfall, Three Gorges, China. Nat Hazards 68:467–482. doi:10.1007/s11069-013-0634-x
Yin YP, Wang HD, Gao YL, Li XC (2010) Real-time monitoring and early warning of landslides at relocated Wushan town, the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 7:339–349. doi:10.1007/s10346-010-0220-1
Acknowledgments
The author Junwei Ma thanks the China Scholarship Council for providing a scholarship for the research described in this paper, which was conducted as a Visiting Research Scholar at Purdue University. This study was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program “973” Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2011CB710604 and 2011CB710606), Key National Natural Science Foundation of China (41230637), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41572279, 41272305 and 41102195), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2012M521500 and 2014T70758), and Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2014CFB901). All supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Tang, H., Hu, X. et al. Identification of causal factors for the Majiagou landslide using modern data mining methods. Landslides 14, 311–322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0693-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0693-7