Abstract
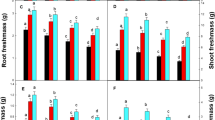
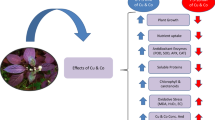
The present study was based on a hypothesis that excess copper (Cu) in the soil reduces the growth and seed yield of chicory plants and chicory plants have the potential to clean up the Cu-contaminated soil. A pot experiment was conducted to investigate the abovementioned hypothesis in which chicory plants were grown in the garden soil contaminated with three doses of copper (150, 450 and 750 mg Cu kg−1 soil) except control and the results were recorded to evaluate the effect of copper-induced toxicity on the vegetative and reproductive growth parameters of Cichorium intybus L. and its soil remediation potential. Results revealed that all Cu treatments decreased the vegetative and reproductive growth parameters of Cichorium intybus. Chlorophyll content (a, b and total) decreased significantly (P ≤ 0.05) while proline content in the fresh leaves and Cu accumulation in different plant organs increased significantly (P ≤ 0.05) on increasing Cu concentration in the soil. The pattern of Cu accumulation in different plant organs was shoot > root > seeds. Cu levels in the seeds obtained from 450 and 750 mg Cu kg−1 soil-treated plants exceeded the permissible limits of the world health organization (WHO). Biological concentration factor (BCF), biological accumulation coefficient (BAC) and translocation factor (TF) values showed that Cichorium intybus absorbed and accumulated a considerable amount of Cu and accumulation of Cu was found to be greater in the shoots than in the roots. Hence Cichorium intybus L. can be used for phytoextraction and is considered a potential candidate to clean up the Cu-contaminated soil.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 September 2023
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00925-1
References
Abbas ZK, Saggu S, Sakeran MI, Zidan N, Rehman H, Ansari AA (2015) Phytochemical, antioxidant and mineral composition of hydroalcoholic extract of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) leaves. Saudi J Biol Sci 22(3):322–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.11.015
Addis W, Abebaw A (2017) Determination of heavy metal concentration in soils used for cultivation of Allium sativum L. (garlic) in east Gojjam zone, Amhara region, Ethiopia. Cogent Chem 3(1):1419422. https://doi.org/10.1080/23312009.2017.1419422
Adrees M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbas F, Farid M, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Irshad MK, Bharwana SA (2015) The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8148–8162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4496-5
Aggarwal A, Sharma I, Tripathi BN, Munjal AK, Baunthiyal M, Sharma V (2011) Metal toxicity and photosynthesis. In: Photosynthesis: Overviews on recent progress & future perspectives, vol 16. IK International, New Delhi, pp 229–236
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.071
Aisa HA, Xin X, Tang D (2020) Chemical constituents and their pharmacological activities of plants from Cichorium genus. Chin Herb Med 12(3):224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2020.05.001
Aksoy A (2008) Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.): A possible biomonitor of metal pollution. Pak J Bot 40(2):791–797
Alaboudi KA, Ahmed B, Brodie G (2018) Phytoremediation of Pb and Cd contaminated soils by using sunflower (Helianthus annuus) plant. Ann Agric Sci 63(1):123–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2018.05.007
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity and bioaccumulation. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Allen SE, Grimshaw HM, Rowland AP (1986) Chemical analysis. In: Moore PD, Chapman SB (eds) Methods in plant ecology. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp 285–344
Amin H, Arain BA, Jahangir TM, Abbasi AR, Mangi J, Abbasi MS, Amin F (2021) Copper (Cu) tolerance and accumulation potential in four native plant species: A comparative study for effective phytoextraction technique. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes 5(1):53–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2019.1700671
Anjum SA, Ashraf U, Tanveer M, Khan I, Hussain S, Shahzad B, Zohaib A, Abbas F, Saleem MF, Ali I, Wang LC (2017) Drought induced changes in growth, osmolyte accumulation and antioxidant metabolism of three maize hybrids. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00069
Aprile A, De Bellis L (2020) Editorial for special issue “Heavy metals accumulation, toxicity, and detoxification in plants”. Int J Mol Sci 2(11):4103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114103
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzyme in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Ashraf S, Ali Q, Zahir ZA, Ashraf S, Asghar HN (2019) Phytoremediation: environmentally sustainable way for reclamation of heavy metal polluted soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:714–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.068
Badr N, Fawzy M, Al-Qahtani KM (2012) Phytoremediation: an ecological solution to heavy-metal-polluted soil and evaluation of plant removal ability. World Appl Sci J 16(9):1292–1301
Baker AJM (1981) Accumulators and excluders—strategies in the response of plants to heavy metals. J Plant Nutr 3(1–4):643–654. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168109362867
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M (2021) Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium and arsenic. Front Pharmacol 12:643972. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C (2003) Phytoremediation: principles and perspectives. Contrib Sci 2(3):333–344. https://doi.org/10.2436/CS.V0I0.310
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Bouazizi H, Jouili H, Geitmann A, Ferjani EE (2010) Copper toxicity in expanding leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris L.: antioxidant enzyme response and nutrient element uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1304–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.05.014
Chandrasekhar C, Ray JG (2017) Copper accumulation, localization and antioxidant response in Eclipta alba L. in relation to quantitative variation of the metal in soil. Acta Physiol Plant 39(9):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-017-2508-4
Choudhary S, Kaurav H, Chaudhary G (2021) Kasani beej (Cichorium intybus): Ayurvedic view, folk view, phytochemistry and modern therapeutic uses. Int J Res Appl Sci Biotechnol 8(2):114–125. https://doi.org/10.31033/ijrasb.8.2.14
Cosgrove DJ (2014) Plant cell growth and elongation. eLS. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0001688.pub2
Cosgrove DJ (2022) Plant cell growth and Cell Wall Enlargement. eLS. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0029421
Cui S, Zhou Q, Chao L (2007) Potential hyper-accumulation of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in endurant plants distributed in an old smeltery, northeast China. Environ Geol 51:1043–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0373-3
Das S, Vasudeva N, Sharma S (2016) Cichorium intybus: A concise report on its ethnomedicinal, botanical, and phytopharmacological aspects. Drug Dev Ther 7(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.4103/2394-6555.180157
El-Banna MF, Mosa A, Gao B, Yin X, Wang H, Ahmad Z (2019) Scavenging effect of oxidized biochar against the phytotoxicity of lead ions on hydroponically grown chicory: An anatomical and ultrastructural investigation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:363–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.011
El-Tayeb MA, El-Enany AE, Ahmed NL (2006) Salicylic acid-induced adaptive response to copper stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Plant Growth Regul 50(2):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-006-9118-2
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Bharwana SA, Rizwan M, Ishaque W, Farid M, Mahmood K, Iqbal Z (2016) Cadmium stress in cotton seedlings: Physiological, photosynthesis and oxidative damages alleviated by glycine betaine. S Afr J Bot 104(61):68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2015.11.006
Fitz WJ, Wenzel WW (2002) Arsenic transformation in the soil-rhizosphere-plant system, fundamentals and potential application of phytoremediation. J Biotechnol 99(3):259–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(02)00218-3
Ghani A, Naheed S (2011) Toxic effect of copper on growth, yield, photosynthetic pigments and mineral composition of wheat plants (Triticum aestivum L.). Pak J Chem 1:96–99. https://doi.org/10.15228/2011.v01.i02.p08
Ghasera KM, Rashid SA, Gupta K (2021) Heavy metals abundance and distribution in soil, groundwater and vegetables in parts of Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh, India: implication for human health risk assessment. Current Science 121(8):1056–1063. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v121/i8/1056-1063
Goswami S, Das S (2016) Copper phytoremediation potential of Calandula officinalis L. and the role of antioxidant enzymes in metal tolerance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.030
Habiba U, Ali S, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Rizwan M, Ibrahim M, Abbasi GH, Hayat T, Ali B (2015) EDTA enhanced plant growth, antioxidant defense system, and phytoextraction of copper by Brassica napus L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1534–1544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3431-5
Hosman ME, El-Feky SS, Elshahawy MI, Shaker EM (2017) Mechanism of phytoremediation potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) to Pb, Cd and Zn. Asian J Plant Sci Res 7(4):30–40
Htwe T, Onthong J, Duangpan S, Techato K, Chotikarn P, Sinutok S (2020) Effect of copper contamination on plant growth and metal contents in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.). Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 51(18):2349–2360. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1836200
Jangra SS, Madan VK (2018) Proximate, mineral and chemical composition of different parts of chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). J Pharmacog Phytochem 7(5):3311–3315
Kafle A, Timilsina A, Gautam A, Adhikari K, Bhattarai A, Aryal N (2022) Phytoremediation: Mechanisms, plant selection and enhancement by natural and synthetic agents. Environ Adv 8:100203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2022.100203
Kalai T, Khamassi K, da-Silva JAT, Gouia H, Ben-Kaab LB (2014) Cadmium and copper stress affect seedling growth and enzymatic activities in germinating barley seeds. Arch Agron Soil Sci 60(6):765–783. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2013.838001
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Huang L, Riaz M, Bashir S, Mustafa A, Abbasi GH, Xue B, Ali U (2019a) Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J Plant Growth Regul 39:266–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-019-09980-3
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Zong Y, Abbasi GH, Rafiq MT, Shaaban M, Mustafa A, Bashir S, Rafay M, Mehmood S, Ali M (2019b) Biochar alleviates Cd phytotoxicity by minimizing bioavailability and oxidative stress in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) cultivated in Cd-polluted soil. J Environ Manag 250:109500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109500
Ku HM, Tan CW, Su YS, Chiu C, Chen CT, Jan FJ (2012) The effect of water deficit and excess copper on proline metabolism in Nicotiana benthamiana. Biol Plant 56:337–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-012-0095-1
Kumar V, Pandita S, Sidhu GPS, Sharma A, Khanna K, Kaur P, Bali AS, Setia R (2021) Copper bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and tolerance in plants: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere 262:127810
Lange B, Van der Ent A, Baker AJM, Echevarria G, Mahy G, Malaisse F et al (2017) Copper and cobalt accumulation in plants: a critical assessment of the current state of knowledge. New Phytol 213(2):537–551. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14175
Li MS, Luo YP, Su ZY (2007) Heavy metal concentrations in soils and plant accumulation in a restored manganese mineland in Guangxi, South China. Environ Pollut 147(1):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.08.006
Li XY, Lin ML, Lu F, Zhou X, Xiong X, Chen LS, Huang ZR (2023) Physiological and ultrastructural responses to excessive-copper-induced toxicity in two differentially copper tolerant citrus species. Plants 12(2):351
Liao MT, Hedley MJ, Woolley DJ, Brooks RR, Nichols MA (2000) Copper uptake and translocation in chicory (Cichorium intybus L. cv. Grasslands Puna) and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. Rondy) plants grown in NFT system. I. Copper uptake and distribution in plants. Plant Soil 221:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004731415931
Lin D, Li G, Zhu Y, Liu H, Li L, Fahad S, Zhang X, Wei C, Jiao Q (2021) Predicting copper content in chicory leaves using hyperspectral data with continuous wavelet transforms and partial least squares. Comput Electron Agric 187:106293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106293
Liu J, Wang J, Lee S, Wen R (2018) Copper-caused oxidative stress triggers the activation of antioxidant enzymes via ZmMPK3 in maize leaves. PLoS ONE 13:603–612. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203612
Liu Z, Bai Y, Luo L, Wan J, Wang W, Zhao G (2021) Effects of high dose copper on plant growth and mineral nutrient (Zn, Fe, Mg, K, Ca) uptake in spinach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 28(28):37471–37481
Luo L, Wang B, Jiang J, Fitzgerald M, Huang Q, Yu Z, Li H, Zhang J, Wei J, Yang C, Zhang H, Dong L, Chen S (2021) Heavy metal contaminations in herbal medicines: determination, comprehensive risk assessments, and solutions. Front Pharmacol 11:595335. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.595335
Madanan MT, Shah IK, Varghese GK, Kaushal RK (2021) Application of Aztec Marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) for phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted lateritic soil. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2020.10.007
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi MK, Lahori AH, Wang Q, Li R, Zhang Z (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Malik B, Pirzadah TB, Tahir I, Hakeem KR, Rather IA, Sabir JS, Rehman RU (2021) Lead and aluminium-induced oxidative stress and alteration in the activities of antioxidant enzymes in chicory plants. Sci Hortic 278:109847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109847
Manivasagaperumal R, Vijayarengan P, Balamurugan S, Thiyagarajan G (2011) Effect of copper on growth, dry matter yield and nutrient content of vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Journal of Phytology 3(3):53–62
Marques DM, Júnior VV, da-Silva AB, Mantovani JR, Magalhães PC, de-Souza TC (2018) Copper toxicity on photosynthetic responses and root morphology of Hymenaea courbaril L. (Caesalpinioideae). Water Air Soil Pollut 229:138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3769-2
Mavrina PO, Saybel OL, Malankina EL (2021) Possibilities of using leaves cultivated chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) as a medicinal plant material (review). Veg Crops Russ 4:105–110. https://doi.org/10.18619/2072-9146 ((In Russ.))
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytostabilization of mine tailings in arid and semiarid environments—An emerging remediation technology. Environ Health Perspect 116(3):278–283. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10608
Monteoliva MI, Rizzi YS, Cecchini NM, Hajirezaei MR, Alvarez ME (2014) Context of action of proline dehydrogenase (ProDH) in the hypersensitive response of Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 14:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-21
Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 22:959–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1073-x
Mukhtar SAIMA, Bhatti HN, Khalid M, Haq MAU, Shahzad SM (2010) Potential of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) for phytoremediation of nickel (Ni) and lead (Pb) contaminated water. Pak J Bot 42(6):4017–4026
Nazir F, Hussain A, Fariduddin Q (2019) Hydrogen peroxide modulate photosynthesis and antioxidant systems in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants under copper stress. Chemosphere 230:544–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.001
Nedjimi B (2021) Phytoremediation: A sustainable environmental technology for heavy metal decontamination. SN Appl Sci 3:286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04301-4
Oniosun S, Harbottle M, Tripathy S, Cleall P (2019) Plant growth, root distribution and non-aqueous phase liquid phytoremediation at the pore-scale. J Environ Manag 249:109378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109378
Ouzounidou G, Ilias I (2005) Hormone-induced protection of sunflower photosynthetic apparatus against copper toxicity. Biol Plant 49(2):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-005-3228-y
Pandey J, Verma RK, Singh S (2019) Suitability of aromatic plants for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated areas: a review. International journal of phytoremediation 21(5):405–418
Pandey SK, Singh H (2011) A simple, cost-effective method for leaf area estimation. J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/658240
Parveen R, Abbasi AM, Shaheen N, Shah MH (2020) Accumulation of selected metals in the fruits of medicinal plants grown in urban environment of Islamabad, Pakistan. Arab J Chem 13(1):308–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.04.010
Rani J, Agarwal T, Chaudhary S (2021) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of National Capital Region, Delhi: levels and ecological risk. Curr World Environ 16(3):804–817. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.16.3.13
Rehman M, Maqbool Z, Peng D, Liu L (2019a) Morpho-physiological traits, antioxidant capacity and phytoextraction of copper by ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as fodder in copper-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5851–5861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4015-6
Rehman M, Liu L, Bashir B, Saleem MH, Chen C, Peng D, Siddique KHM (2019b) Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as forage in aged copper contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.02.021
Rehman M, Liu L, Wang Q, Saleem MH, Bashir B, Ullah S, Peng D (2019c) Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18003–18016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05073-6
Saleem MH, Ali S, Seleiman MF, Rizwan M, Rehman M, Aisha Akram N, Liu L, Alotaibi M, Al-Ashkar I, Mubushar M (2019) Assessing the correlations between different traits in copper-sensitive and copper-resistant varieties of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.). Plants 8(12):545
Saleem MH, Kamran M, Zhou Y, Parveen A, Rehman M, Ahmar S, Malik Z, Mustafa A, Anjum RMA, Wang B, Liu L (2020a) Appraising growth, oxidative stress and copper phytoextraction potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) grown in soil differentially spiked with copper. J Environ Manag 257:109994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109994
Saleem MH, Fahad S, Khan SU, Din M, Ullah A, Sabagh AEL, Hossain A, Llans A, Liu L (2020b) Copper-induced oxidative stress, initiation of antioxidants and phytoremediation potential of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) seedlings grown under the mixing of two different soils of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:5211–5221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07264-7
Saleem MH, Fahad S, Khan SU, Ahmar S, Khan MHU, Rehman M, Maqbool Z, Liu L (2020c) Morpho-physiological traits, gaseous exchange attributes, and phytoremediation potential of jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) grown in different concentrations of copper-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:109915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109915
Saleem MH, Ali S, Hussain S, Kamran M, Chattha MS, Ahmad S, Aqeel M, Rizwan M, Aljarba NH, Alkahtani S, Abdel-Daim MM (2020d) Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.): A potential candidate for phytoremediation? Biological and economical points of view. Plants 9(4):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9040496
Sanchez-Pardo B, Fernandez-Pascual M, Zornoza P (2014) Copper microlocalisation and changes in leaf morphology, chloroplast ultrastructure and antioxidative response in white lupin and soybean grown in copper excess. J Plant Res 127:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-013-0583-1
Sêkara A, Poniedzialek M, Ciura J, Jêdrszczyk E (2005) Zinc and copper accumulation and distribution in the tissues of nine crops: Implications for phytoremediation. Pol J Environ Stud 14(6):829–835
Shah A, Niaz A, Ullah N, Rehman A, Akhlaq M, Zakir M, Khan MS (2013) Comparative study of heavy metals in soil and selected medicinal plants. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/621265
Siebert SJ, Schutte NC, Bester SP, Komape DM, Rajakaruna N (2018) Senecio conrathii NE Br.(Asteraceae), a new hyperaccumulator of nickel from serpentinite outcrops of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Ecol Res 33(3):651–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-017-1541-5
Souza VL, Almeida AAF, Souza JS, Mangabeira PAO, Jesus RM, Pirovani CP, Ahnert D, Baligar VC, Loguercio LL (2014) Altered physiology, cell structure, and gene expression of Theobroma cacao seedlings subjected to Cu toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:1217–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1983-4
Street R, Sidana A, Prinsloo G (2013) Cichorium intybus: Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/579319
Tanhan P, Kruatrachue M, Pokethitiyook P (2007) Uptake and accumulation of cadmium, lead and zinc by Siam weed [Chromol aenaodorata (L.) King & Robinson]. Chemosphere 68(2):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.064
Tripathi BN, Singh V, Ezaki B, Sharma V, Gaur JP (2013) Mechanism of Cu- and Cd-induced proline hyperaccumulation in Triticum aestivum (Wheat). J Plant Growth Regul 32:799–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9343-7
Vinit-Dunand F, Epron D, Alaoui-Sossé B, Badot PM (2002) Effects of copper on growth and on photosynthesis of mature and expanding leaves in cucumber plants. Plant science 163(1):53–58
Wang R, Shafi M, Ma J, Zhong B, Guo J, Hu X, Xu W, Yang Y, Ruan Z, Wang Y, Ye Z, Liu D (2018) Effect of amendments on contaminated soil of multiple heavy metals and accumulation of heavy metals in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:28695–28704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2918-x
Wen JF, Gong M, Liu Y, Hu JL, Deng MH (2013) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on growth and activity of some enzymes involved in proline metabolism of sweet corn seedlings under copper stress. Sci Hortic 164:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.09.031
Xu J, Yang L, Wang Z, Dong G, Huang J, Wang Y (2006) Toxicity of copper on rice growth and accumulation of copper in rice grain in copper contaminated soil. Chemosphere 62(4):602–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.050
Xu Q, Qiu H, Chu W, Fu Y, Cai S, Min H, Sha S (2013) Copper ultrastructural localization, subcellular distribution, and phytotoxicity in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8672–8679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1828-1
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ 368(2–3):456–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.01.016
Zhang W, Cai Y, Tu C, Ma LQ (2002) Arsenic speciation and distribution in an arsenic hyperaccumulating plant. Sci Total Environ 300(1–3):167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(02)00165-1
Zehra A, Choudhary S, Mukarram M, Naeem M, Khan MMA, Aftab T (2020) Impact of long-term copper exposure on growth, photosynthesis, antioxidant defence system and artemisinin biosynthesis in soil-grown Artemisia annua genotypes. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 104(5):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02812-1
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Chairperson, Department of Botany, Aligarh Muslim University (A.M.U.), Aligarh for providing research experiment facilities and technical support for sample analysis.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi, for funding this research by providing a non-NET fellowship to the corresponding author (Adnan khan) for Ph.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Adnan Khan: conceptualization, methodology, writing, original data preparation. Athar Ali Khan: supervision, reviewing and editing. Sayma Samreen: Table and graph preparation. Mohammad Irfan: statistical analysis of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Khan, A. A. Khan, S. Samreen and M. Irfan declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Novelty Statement
This manuscript evaluates the effect of different concentrations of Cu on the growth and yield of chicory plants and bioaccumulation of Cu in the root, shoot and leaves of chicory plants and also assesses the risk posed to consumer health in a food chain. This study also provides insight to assess the extraction efficiency and soil remediation potential of Cichorium intybus L. against Cu contamination in soil.
The original online version of this article was revised: In table 2 of this article, the legend was incorrectly given as “Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 3). Mean values within a column followed by different letters are statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05 by Duncan’s multiple range test.”, but should have been “Data are presented as treatments mean ± SE (n = 3). Mean values within a row followed by different letters are statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05 by Duncan’s multiple range test.”
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Khan, A.A., Samreen, S. et al. Effect of Copper (Cu) Induced Toxicity on Growth and Yield of Cichorium intybus L. and its Soil Remediation Potential. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 2133–2144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00828-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00828-1