Abstract
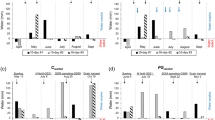
In this study, effects of different sowing dates and seeding rates on N uptake efficiency (NUE), N translocation efficiency (NTE), agronomic efficiency (AE), physiological efficiency (PE), water use efficiency for grain yield (WUEg) and water use efficiency for biomass (WUEb) of facultative wheat were investigated. As the average of cropping year, sowing dates and seeding rates, N uptake efficiency (NUE), N translocation efficiency (NTE), agronomic efficiency (AE), physiological efficiency (PE), water use efficiency for grain yield (WUEg) and water use efficiency for biomass (WUEb) values were respectively obtained as 1.17 kg Nuptake/kg Napplied, 68.5%, 36.9 kg grain/kg Napplied, 31.2 kg grain/kg Nuptake, 5.19 kg ha−1 mm−1 and 18.04 kg ha−1 mm−1.
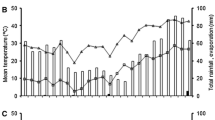
Nitrogen and water use efficiencies decreased with delayed sowing dates and increased with increasing seeding rates. It is possible to maintain a high wheat yield, nitrogen and water use efficiency by increasing plant density through winter sowing. It was concluded based on present findings that sowing date and seeding rates had significant effects on nitrogen and water use efficiencies and winter sowing should be practiced as not to cause yield losses and high seeding rates (575 seeds m−2) yielded greater nitrogen-water use efficiencies.
Zusammenfassung
In dieser Studie wurden die Auswirkungen verschiedener Aussaattermine und Aussaatmengen auf die N‑Aufnahmeeffizienz (NUE), die N‑Umsetzungseffizienz (NTE), die agronomische Effizienz (AE), die physiologische Effizienz (PE), die Wassernutzungseffizienz für den Kornertrag (WUEg) und die Wassernutzungseffizienz für die Biomasse (WUEb) von Wechselweizen untersucht. Als Durchschnittswerte für das Anbaujahr, die Aussaattermine und die Aussaatmengen wurden die Werte für die N‑Aufnahmeeffizienz (NUE), die N‑Translokationseffizienz (NTE), die agronomische Effizienz (AE), die physiologische Effizienz (PE), die Wassernutzungseffizienz für den Kornertrag (WUEg) und die Wassernutzungseffizienz für die Biomasse (WUEb) jeweils mit 1,17 kg Nuptake/kg Napplied, 68,5 %, 36,9 kg Korn/kg Napplied, 31,2 kg Korn/kg Nuptake, 5,19 kg ha−1 mm−1 und 18,04 kg ha−1 mm−1 angenommen.
Die Stickstoff- und Wassernutzungseffizienz verringerte sich mit späteren Aussaatterminen und erhöhte sich mit steigenden Aussaatmengen. Es ist möglich, einen hohen Weizenertrag sowie eine hohe Stickstoff- und Wassernutzungseffizienz aufrechtzuerhalten, indem die Pflanzdichte durch Wintersaat erhöht wird. Die vorliegenden Ergebnisse lassen den Schluss zu, dass Aussaattermin und Aussaatstärke signifikante Auswirkungen auf die Stickstoff- und Wassernutzungseffizienz haben und dass die Winteraussaat praktiziert werden sollte, um Ertragseinbußen zu vermeiden, und dass hohe Aussaatstärken (575 Samen m−2) eine höhere Stickstoff- und Wassernutzungseffizienz bewirken.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 April 2022
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00662-x
References
Abbate PE, Dardanelli JL, Cantarero MG, Maturano M, Melchiori RJM, Suero EE (2004) Climatic and water availability effects on water-use efficiency in wheat. Crop Sci 44:474–483
Ahmed S, Humphrey E, Salim M, Chauhan BS (2016) Growth, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of dry-seeded rice as influenced by nitrogen and seed rates in Bangladesh. Field Crop Res 186:18–31
Alignan M, Roche J, Bouniols A, Cerny M, Mouloungui Z, Merah O (2009) Effects of genotype and sowing date on phytostanol-phytosterol content and agronomic traits in wheat under organic agriculture. Food Chem 117:219–225
Anderson WK, Sharma DL, Shackley DL, Antuono MFD (2004) Rainfall, sowing time, soil type, and cultivar influence optimum plant population for wheat in Western Australia. Aust J Agric Res 55:921–930
Angus JF, Herwaarden AF (2001) Increasing water use and water use efficiency in dryland wheat. Agron J 93:290–298
Asseng S, Turner NC, Keating BA (2001) Analysis of water- and nitrogen-use efficiency of wheat in a Mediterranean climate. Plant Soil 233:127–143. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010381602223
Baenziger PS, Salah I, Little RS, Santra DK, Regassa T, Wang MY (2011) Structuring an efficient organic wheat breeding program. Sustainability 3:1190–1205
Barker AV, Bryson GM (2016) Nitrogen. In: Barker AV, Pilbeam DJ (eds) Handbook of plant nutrition. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 37–66
Barraclough PB, Howarth JR, Jones J, Lopezbellido RJ, Parmar S, Shepherd CE, Hawkesford MJ (2010) Nitrogen efficiency of wheat: genotypic and environmental variation and prospects for improvement. Eur J Agron 33:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2010.01.005
Belete F, Dechassa N, Molla A, Tana T (2018) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer rates on grain yield and nitrogen uptake and use efficiency of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties on the Vertisols of central highlands of Ethiopia. Agric Food Secur 7:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-018-0231-z
Blum A (2005) Drought resistance, water-use efficiency, and yield potential: Are they compatible, dissonant or mutually exclusive? Aust J Agric Res 56:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR05069
Borojevic S, Williams WA (1982) Genotype x environment interactions for leaf area parameters and yield components and their effects on wheat yields. Crop Sci 22:1020–1025
Cassman KG, Dobermann A, Walters DT (2002) Agroecosys-tems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. Ambio 31:132–140
Cayci G, Heng LK, Ozturk HS, Surek D, Kutuk C, Saglam M (2009) Crop yield and water use efficiency in semi-arid region of Turkey. Soil Tillage Res 103(1):65–72
Chen C, Payne WA, Smiley RW, Stoltz MA (2003) Yield and water-use efficiency of eight wheat cultivars planted on seven dates in Northeastern Oregon. Agron J 95:836–843. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.8360
Clarke JM, Campbell CA, Cutforth HW, DePauw RM, Winkleman GE (1990) Nitrogen and phosphorus uptake, translocation, and utilization efficiency of wheat in relation to environment and cultivar yield and protein levels. Can J Plant Sci 70:965–977
Corbeels M, Hofman G, Cleemput OV (1998) Analysis of water use by wheat grown on a cracking clay soil in a semi-arid Mediterranean environment: weather and nitrogen effects. Agr Water Manag 38:147–167
Cox MC, Qualset CO, Rains DW (1986) Genetic variation for nitrogen assimilation and translocation in wheat III Nitrogen translocation in relation to grain yield and protein. Crop Sci J 26:737–740
Dai X, Wang Y, Dong X, Qian T, Yin L, Dong S, Chu J, He M (2017) Delayed sowing can increase lodging resistance while maintaining grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat. Crop J 5:541–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2017.05.003
Dai XL, Xiao LL, Jia DY, Kong HB, Wang YC, Li CX, Zhang Y, He M (2014) Increased plant density of winter wheat can enhance nitrogen–uptake from deep soil. Plant Soil 384:141–152
Dai XL, Zhou XH, Jia DY, Xiao LL, Kong HB, He M (2013) Managing the seeding rate to improve nitrogen–use efficiency of winter wheat. Field Crop Res 154:100–109
Delogu G, Cattivelli L, Pecchioni N, Falcis DD, Maggiore T, Stanca AM (1998) Uptake and agronomic efficiency of nitrogen in winter barley and winter wheat. Eur J Agron 9:11–20
Dobermann A, Cassman KG (2005) Cereal area and nitrogen use efficiency are drivers of future nitrogen fertilizer consump-tion. Sci China Ser C 48(C):745–758
Dong S, Zhang J, Zha T, Dai X, He M (2020) Increased plant density with reduced nitrogen input can improve nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat while maintaining grain yield. Arch Agron Soil Sci 66(12):1707–1720. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2019.1690139
Du Y, Niu W, Zhang Q, Cui B, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Sun J (2021) A synthetic analysis of the effect of water and nitrogen inputs on wheat yield and water- and nitrogen-use efficiencies in China. Field Crop Res 265:108105
Duchemin BT, Fieuzal R, Rivera MA, Ezzahar J, Jarlan L, Rodriguez JC, Hagolle O, Watts C (2015) Impact of sowing date on yield and water use efficiency of wheat analyzed through spatial modeling and formosat‑2 images. Remote Sens 7(5):5951–5979. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70505951
Fageria NK (2014) Nitrogen Management in Crop Production, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton https://doi.org/10.1201/b17101
Fang Y, Xu BC, Turner NC, Li FM (2010) Grain yield, dry matter accumulation and remobilization: and root respiration in winter wheat as affected by seeding rate and root pruning. Eur J Agron 33:257–266
FAO (2020) Food and Agricultural Organization database (FAO). http://www.fao.org. Accessed 21.07.2021
Gebeyehou G, Knott DR, Baker RJ (1982) Relationships among durations of vegetative and grain filling phases, yield components, and grain yield in durum wheat cultivars. Crop Sci 22:287–290
Gomez-Macpherson H, Richards RA (1995) Effect of sowing time on yield and agronomic characteristics of wheat in South-eastern Australia. Aust J Agric Res 46:1381–1399
Hatfield JL, Dold C (2019) Water-use efficiency: advances and challenges in a changing climate. Front Plant Sci 10:103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00103
Hiltbrunner J, Streit B, Liedgens M (2007) Are seeding densities an opportunity to increase grain yield of winter wheat in a living mulch of white clover? Field Crop Res 102:163–171
Hirel B, Lemaire G (2006) From agronomy and ecophysiology to molecular genetics for improving nitrogen use efficiency in crops. J Crop Improv 15(2):213–257. https://doi.org/10.1300/J411v15n02_07
Karasahin M (2014) Nitrogen uptake efficiency in plant production and negative effects of reactive nitrogen on environment. Academic Platform J Eng Sci 2(3):15–21
Khan A (2017) Nitrogen translocation efficiency in wheat depends on N sources and tillage practices. Doing More with Less, Proceedings of the 18th Australian Agronomy Conference 2017, Ballarat, 24–28 September 2017, pp 1–4
Khan S, Anwar S, Shaobo Y, Gao Z, Sun M, Ashraf MY, Ren A, Yang Z (2020) Soil water consumption, water use efficiency and winter wheat production in response to nitrogen fertilizer and tillage. PeerJ 8:e8892
Laghari GM, Oad FC, Tunio S, Chachar Q, Ghandahi AW, Siddiqui MH, Hassan SW, Ali A (2010) Growth and yield attributes of wheat at different seed rates. Sarhad J Agric 27(2):177–183
Liang YF, Khan S, Ren A‑X, Lin W, Anwar S, Sun M, Gao Z (2019) Subsoiling and sowing time influence soil water content, nitrogen translocation and yield of dryland winter wheat. Agronomy 9(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9010037
Ma SC, Wang TC, Guan XK, Zhang X (2018) Effect of sowing time and seeding rate on yield components and water use efficiency of winter wheat by regulating the growth redundancy and physiological traits of root and shoot. Field Crop Res 221:166–174
Mandic V, Krnjaja V, Tomic Z, Bijelic Z, Simic A, Ruzic-Muslic D, Gogic M (2015) Nitrogen fertilizer influence on wheat yield and use efficiency under different environmental conditions. Chil J Agric Res 75(1):92–97. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-58392015000100013
Moll RH, Kamprath EJ, Jackson WA (1982) Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron J 74:562–564
MSTAT‑C (1991) A software program for the design, management, and analysis of agronomic research experiments. Michigan State University, East Lansing
Muchow RC (1994) Effect of nitrogen on yield determination in irrigated maize in tropical and subtropical environments. Field Crop Res 38(1):1–13
Muurinen S, Slafer GA, Peltonen-Sainio P (2006) Breeding effects on nitrogen use efficiency of spring cereals under northern conditions. Crop Sci 46:561–568
Ortiz-MonasterioR JI, Sayre KD, Rajaram S, McMahon M (1997) Genetic progress in wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency under four N rates. Crop Sci 37(3):898–904
Othmani A, Ayed S, Rezgui M, Melki M, Teixeira da Silva JA (2021) Water regimes and seeding rates influence grain yield and water use efficiency of three durum wheat varieties. Asian J Res Biosci 2(2):30–39 (https://globalpresshub.com/index.php/AJORIB/article/view/951)
Raun WR, Johnson GV (1999) Improving nitrogen use efficiency for cereal production. (Review & Interpretation). Agronomy J 91:357–363. https://doi.org/10.2134/AGRONJ2002.8150
Roberts LT (2008) Improving nutrient use efficiency. Turk J Agric For 32(3):177–182
Salim N, Raza A (2020) Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) for sustainable wheat production: a review. J of Plant Nutrition 43(2):297–315. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1676907
Sheng CF (1990) Growth tediousness as an explanation of over-compensation of crops for insect feeding. Chin J Appl Ecol 1:26–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Spink J, Semere T, Sparkes DL, Whaley JM, Foulkes MJ, Clare RW, Scott RK (2000) Effect of sowing date on the optimum plant density of winter wheat. Ann Appl Biol 137:179–188
Srivastava RK, Pandab RK, Chakrabortyc A, Halderd D (2018) Enhancing grain yield, biomass and nitrogen use efficiency of maize by varying sowing dates and nitrogen rate under rainfed and irrigated condition. Field Crop Res 221:339–349
Staley TE, Perry HD (1995) Maize silage utilization of fertilizer and soil nitrogen on a Hill-land Ultisol relative to tillage method. Agronj 87:835–842
Tambussi EA, Bort J, Araus JL (2007) Water use efficiency in C3 cereals under Mediterranean conditions: a review of physiological aspects. Ann Appl Biol 150(3):307–321
TUIK (2020) Turkish Statistical Institute, plant production data for the year 2020. http://www.tuik.gov.tr. Accessed 10 Feb 2021
USDA (2021) The 2021 U.S. Agricultural Export Yearbook provides a statistical summary of U.S. Agricultural Commodity Exports to the World and the United States’ primary trading partners. https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/2021-united-states-agricultural-export-yearbook. Accessed 5 Jan 2021
Walsh OS, Walsh WL (2020) Seeding rate and nitrogen fertilizer rate effect on dryland no-till hard red spring wheat yield and quality. Agrosyst Geosci Environ 3:e20001
Wang B, Zhang Y, Hao B, Xu X, Zhao Z, Wang Z (2016) Grain yield and water use efficiency in extremely-late sown winter wheat cultivars under two irrigation regimes in the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 11(4):e153695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0153695
Wang X, Hu X, Sun ZF, Du KM, Song GS, Ren DC (2011) Effect of different sowing dates and planting density on group characters and yield of wheat. Chin Agric Sci Bull 27:170–176 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Widdowson FV, Penny A, Darby RJ, Bird E, Hewitt MV (1987) Amount of NO3-N and NH4-N in soil, from autumn to spring, under winter wheat and their relationship to soil type, sowing date, previous crop and N uptake at Rothamsted, Woburn and Saxmundham, 1979–1985. J Agric Sci 108:73–95
Yang DQ, Cai T, Luo YL, Wang ZL (2019) Optimizing plant density and nitrogen application to manipulate tiller growth and increase grain yield and nitrogen-use efficiency in winter wheat. PeerJ 7:e6484
Yilmaz F, Hamurcu M, Gezgin S (2020) Determination of nitrogen use efficiencies of some bread wheat grown in the Central Anatolia Region. Yuzuncu Yil Univ J Agric Sci 30(4):689–695. https://doi.org/10.29133/yyutbd.764028
Yunusa AM, Sedgley RH (1992) Reduced tillering spring wheats for heavy textured soils in a semi-arid Mediterranean environment. J Agron Crop Sci 168:159–168
Zhang J, Dong S, Dai X, Wu T, Wang X, Bai H, Wang L, He M (2016a) Combined effect of plant density and nitrogen input on grain yield, nitrogen uptake and utilization of winter wheat. Vegetos 29:2. https://doi.org/10.5958/2229-4473.2016.00023.9
Zhang MM, Dong BD, Qiao YZ, Zhao H, Liu MY, Chen Q, Yang H, Zheng X (2016b) Effects of sowing date and seeding density on growth, yield and water use efficiency of ‘Xiaoyan 60’ wheat under rainfed condition. Chin J Eco Agric 24(8):1095–1102 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou X, Wang H, Chen Q, Ren J (2007) Coupling effects of depth of film-bottomed tillage and amount of irrigation and nitrogen fertilizer on spring wheat yield. Soil Tillage Res 94:251–261
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Atatürk University for supplying research fields for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised: In this article Özcan Çağlar at affiliation “Department of Organic Farming Business Management, School of Applied Sciences Igdir University, Igdir, TURKEY” and Ali Öztürk at affiliation “Department of Field Crops, Faculty of Agriculture, Ataturk University, Erzurum, Turkey” were missing from the author list.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulut, S., Çağlar, Ö. & Öztürk, A. Effects of Sowing Dates and Seeding Rates on Nitrogen and Water Use Efficiency of Facultative Wheat. Gesunde Pflanzen 74, 291–301 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-021-00608-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-021-00608-9