Abstract
Objective
To analyze the association of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values measured by readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (rs-EPI) using different simultaneous multislice (SMS) acceleration factors and the differentiation of rectal cancer grade.
Materials and methods
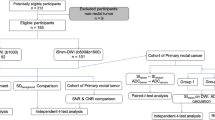
Patients with non-mucinous rectal adenocarcinoma diagnosed by biopsy (endoscope-guided biopsy or surgical resection) were retrospectively collected, and each patient underwent an MRI examination. ADC values of rs-EPI, 2 × SMS rs-EPI, and 3 × SMS rs-EPI were recorded as ADC1, ADC2, and ADC3, respectively.
Results
The scanning time of 2 × SMS rs-EPI was 60 s, 56.2% shorter than 137 s of rs-EPI sequence, while that of 3 × SMS rs-EPI was 51 s, 72.8% less than that of rs-EPI time. The ADC value of the three groups dropped with the decrease in cancer grade (p < 0.05). The AUC values of ADC1, ADC2, and ADC3 in predicting highly differentiated rectal cancer were 0.74, 0.729, and 0.687, respectively. The difference in AUC values between ADC1 and ADC2 was not statistically significant (p = 0.889).
Discussion
SMS technology with an acceleration factor of 2 could be applied clinically to evaluate the pathological differentiation of rectal cancer grade.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30
Zhu L, Pan Z, Ma Q, Yang W, Shi H, Fu C, Yan X, Du L, Yan F, Zhang H (2017) Diffusion kurtosis imaging study of rectal adenocarcinoma associated with histopathologic prognostic factors: preliminary findings. Radiology 284:66–76
Tang C, Lin MB, Xu JL, Zhang LH, Zuo XM, Zhang ZS, Liu MX, Xu JM (2018) Are ADC values of readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging (RESOLVE) correlated with pathological prognostic factors in rectal adenocarcinoma? World J Surg Oncol 16:138
Tang L, Zhou XJ (2019) Diffusion MRI of cancer: From low to high b-values. J Magn Reson Imaging 49:23–40
Geng Z, Zhang Y, Yin S, Lian S, He H, Li H, Xie C, Dai Y (2020) Preoperatively grading rectal cancer with the combination of intravoxel incoherent motions imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2020:2164509
Porter DA, Heidemann RM (2009) High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med 62:468–475
Xu XQ, Liu J, Hu H, Su GY, Zhang YD, Shi HB, Wu FY (2016) Improve the image quality of orbital 3 T diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with readout-segmented echo-planar imaging. Clin Imaging 40:793–796
Barth M, Breuer F, Koopmans PJ, Norris DG, Poser BA (2016) Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging techniques. Magn Reson Med 75:63–81
Boca Petresc B, Caraiani C, Popa L, Lebovici A, Feier DS, Bodale C, Buruian MM (2022) The utility of ADC first-order histogram features for the prediction of metachronous metastases in rectal cancer: a preliminary study. Biology (Basel) 11:1
Yuan Y, Chen XL, Li ZL, Chen GW, Liu H, Liu YS, Pang MH, Liu SY, Pu H, Li H (2022) The application of apparent diffusion coefficients derived from intratumoral and peritumoral zones for assessing pathologic prognostic factors in rectal cancer. Eur Radiol 1:1
Xia CC, Pu J, Zhang JG, Peng WL, Li L, Zhao F, Zhang K, Li YM, Liu KL, Meng WJ, Deng XB, Zhou XY, Li ZL (2018) Readout-segmented echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR for the evaluation of aggressive characteristics of rectal cancer. Sci Rep 8:12554
Song SE, Woo OH, Cho KR, Seo BK, Son YH, Grimm R, Liu W, Moon WK (2021) Simultaneous multislice readout-segmented echo planar imaging for diffusion-weighted mri in patients with invasive breast cancers. J Magn Reson Imaging 53:1108–1115
Tu C, Shen H, Liu D, Chen Q, Yuan X, Li X, Wang X, Liu R, Wang X, Li Q, Liu W, Zhang J (2021) Simultaneous multi-slice readout-segmentation of long variable echo-trains for accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a feasibility and optimization study. Clin Imaging 79:119–124
Jiang JS, Zhu LN, Wu Q, Sun Y, Liu W, Xu XQ, Wu FY (2020) Feasibility study of using simultaneous multi-slice RESOLVE diffusion weighted imaging to assess parotid gland tumors: comparison with conventional RESOLVE diffusion weighted imaging. BMC Med Imaging 20:93
Taron J, Martirosian P, Kuestner T, Schwenzer NF, Othman A, Weiss J, Notohamiprodjo M, Nikolaou K, Schraml C (2018) Scan time reduction in diffusion-weighted imaging of the pancreas using a simultaneous multislice technique with different acceleration factors: How fast can we go? Eur Radiol 28:1504–1511
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J Chiropr Med 15:155–163
Attenberger UI, Pilz LR, Morelli JN, Hausmann D, Doyon F, Hofheinz R, Kienle P, Post S, Michaely HJ, Schoenberg SO, Dinter DJ (2014) Multi-parametric MRI of rectal cancer—Do quantitative functional MR measurements correlate with radiologic and pathologic tumor stages? Eur J Radiol 83:1036–1043
Youden WJ (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3:32–35
Cho EY, Kim SH, Yoon JH, Lee Y, Lim YJ, Kim SJ, Baek HJ, Eun CK (2013) Apparent diffusion coefficient for discriminating metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes in primary rectal cancer. Eur J Radiol 82:e662-668
Curvo-Semedo L, Lambregts DM, Maas M, Beets GL, Caseiro-Alves F, Beets-Tan RG (2012) Diffusion-weighted MRI in rectal cancer: apparent diffusion coefficient as a potential noninvasive marker of tumor aggressiveness. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:1365–1371
Yang L, Qiu M, Xia C, Li Z, Wang Z, Zhou X, Wu B (2019) Value of high-resolution DWI in combination with texture analysis for the evaluation of tumor response after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1:1–8
Xia CC, Liu X, Peng WL, Li L, Zhang JG, Meng WJ, Deng XB, Zuo PL, Li ZL (2016) Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the image quality of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in rectal cancer: comparison with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences. Eur J Radiol 85:1818–1823
Park JH, Seo N, Lim JS, Hahm J, Kim MJ (2020) Feasibility of simultaneous multislice acceleration technique in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the rectum. Korean J Radiol 21:77–87
White NS, McDonald C, Farid N, Kuperman J, Karow D, Schenker-Ahmed NM, Bartsch H, Rakow-Penner R, Holland D, Shabaik A, Bjørnerud A, Hope T, Hattangadi-Gluth J, Liss M, Parsons JK, Chen CC, Raman S, Margolis D, Reiter RE, Marks L, Kesari S, Mundt AJ, Kane CJ, Carter BS, Bradley WG, Dale AM (2014) Diffusion-weighted imaging in cancer: physical foundations and applications of restriction spectrum imaging. Can Res 74:4638–4652
Akashi M, Nakahusa Y, Yakabe T, Egashira Y, Koga Y, Sumi K, Noshiro H, Irie H, Tokunaga O, Miyazaki K (1987) (2014) Assessment of aggressiveness of rectal cancer using 3-T MRI: correlation between the apparent diffusion coefficient as a potential imaging biomarker and histologic prognostic factors. Acta Radiol (Stockholm Sweden) 55:524–531
Holdsworth SJ, Yeom K, Skare S, Gentles AJ, Barnes PD, Bammer R (2011) Clinical application of readout-segmented-echo-planar imaging for diffusion-weighted imaging in pediatric brain, AJNR. Am J Neuroradiol 32:1274–1279
Hosonuma T, Tozaki M, Ichiba N, Sakuma T, Hayashi D, Yanaga K, Fukuda K (2006) Clinical usefulness of diffusion-weighted imaging using low and high b-values to detect rectal cancer. Magn Reson Med Sci MRMS Off J Jpn Soc Magn Reson Med 5:173–177
Liu J, Li Q, Tang L, Huang Z, Lin Q (2021) Correlations of mean and mimimum apparent diffusion coefficient values with the clinicopathological features in rectal cancer. Acad Radiol 28(Suppl 1):S105–S111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Huang, H., Li, H. et al. Application value of simultaneous multislice readout-segmented echo-planar imaging for diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiation of rectal cancer grade. Magn Reson Mater Phy 36, 621–629 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-022-01054-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-022-01054-y