Abstract
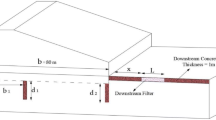
Reservoir dam erosion caused by an increased seepage velocity on downstream slopes is a major concern, and zoned-type dams are commonly used to mitigate this issue. However, previous methods for calculating filter spacing have been overly conservative, focusing on short-term stability and neglecting long-term erosion risk. This study proposes a determining equation for the horizontal filter spacing in reservoir dams, considering material property variability and diverse dam construction conditions. Through comprehensive three-dimensional seepage simulations, the lateral drainage range (LDR) and hydraulic gradient were investigated as separate factors. The proposed equation aims to optimize the filter design while balancing the safety and cost considerations. Validation using a multi-horizontal filter model confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed spacing in mitigating erosion hazards. This study contributes to the improvement in dam design practices by providing a less conservative approach. These findings offer valuable insights for designing horizontal filters in reservoir dams, ensuring both short- and long-term erosion stability. Ultimately, these advancements in filter design will enhance dam stability and reduce the risk of failure.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins RE (1961) Flow of fluids through porous material. Reinhold, New York
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) (2011) "Filter for embankment dams: Best practice for design and construction." U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Fell R, Wan CF, Cyganiewicz J, Foster M (2003) Time for development of internal erosion and piping in embankment dams. J Geotech Geo-Environ Eng 129(4):307–310. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2003)129:4(307)
Korean Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA). (2002). "Design standards of agricultural production infrastructure improvement project (Fill Dam)" (in Korean).
Foster M, Fell R, Spannagle M (2000) The statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents. Can Geotech J 37(5):1000–1024. https://doi.org/10.1139/t00-030
Javier FS, Luis AG, Adrián MT, Ignacio EB (2018) Climate change impacts on dam safety. Nat Hazard 18(9):2471–2488. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-2471-2018
Ke L, Takahashi A (2012) Strength reduction of cohesionless soil due to internal erosion induced by one-dimensional upward seepage flow. Soils Found 52(4):698–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2012.07.010
Korean Ministry of Environment (ME) (2017) “Guidelines for Design and Construction of Reservoirs” (in Korean)
Lambe TW, Whitman RV (1969) "Soil mechanics." Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Lee YH, Park SY, Tokida K, Lee DW (2018) Three-dimensional seepage characteristics of reservoir embankment considering interval of horizontal filter. Int J Offshore Polar Eng 28(1):80–86. https://doi.org/10.17736/ijope.2018.cl08
Lee YH, Lee D, Park J, Fujisawa K, Murakami A, Lee DW (2019) Experimental study on seepage characteristics of reservoir embankment considering interval of horizontal filter. Paddy Water Environ 17(2019):273–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00720-7
MIDAS Information Technology Corporation LTD (2015) "Midas geotechnical and tunnel analysis system (Midas GTS)" (in Korean).
Ministry of agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (2020) "Statistical yearbook of land and water development for agriculture 2020. Korea Rural Community Corporation (KRC). (accessed on 25 May: http://rims.ekr.or.kr/stastics/pdf/2020.pdf)
Pörtner H-O, Roberts D, Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Tignor M, Poloczanska E, Mintenbeck K, Nicolai M, Okem A, Petzold J et al. (2022) "Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change."
Ren X, Santamarina JC (2018) The hydraulic conductivity of sediments: a pore size perspective. Eng Geol 233:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.022
Korean Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs (MLTM) (2011) "Guidelines for dam design" (in Korean).
United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR). (2007). "Design standards No. 13: Embankment dams." U.S. Department of Interior, Technical Service Center, Denver, CO.
Ziyang L, Wei Y, Miroslav M, Jeremy DB (2018) Unsteady seepage behavior of an earthfill dam during drought-flood cycles. Geosciences (switzerland) 9(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9010017
Acknowledgement
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the the Korea Rural Community Corporation(KRCC) for their generous support of our research. Their support in the form of data, administrative assistance, and design information was essential to the success of our project.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea (Grant No. 2019R1C1C1007100) and the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A1A01058373).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, HK., Tobita, T., Lee, YH. et al. Determining Optimal Horizontal Spacing for Sand Filter in Reservoir Dams. Paddy Water Environ 22, 99–108 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-023-00955-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-023-00955-5