Abstract
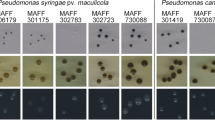
Bacterial black node, a disease of barley and wheat, is caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae (synonym pv. japonica, hereafter Psj). Here a selective medium, serine-potassium tellurite-based Psj-selective agar (SPTPsjA) was developed to isolate and detect Psj. After 5–7 days on SPTPsjA at 25 °C, characteristic black Psj colonies formed with an efficiency equal to that on potato–peptone–glucose agar. Except for P. viridiflava, P. cichorii, and some strains of P. syringae group bacteria, SPTPsjA either inhibited growth of other phytopathogenic bacteria or enabled their discrimination. To facilitate diagnosis of Psj, we prepared three antisera against three strains; in a slide agglutination test, the antisera reacted to all tested strains of Psj and failed to react to P. viridiflava and P. cichorii although some strains of other P. syringae group bacteria were indistinguishable from Psj with SPTPsjA and antisera. When barley and wheat seeds from fields in which bacterial black node had occurred were placed on SPTPsjA in the dark at 25 °C for 7 days, black colonies grew on the medium around the seeds. Among these strains, only those responsive to the above antisera were pathogenic on barley. These results show that the combination of SPTPsjA and antisera can isolate Psj from seeds of barley and wheat.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyagi K, Sakai T, Iwata K (1980) Occurrence and damage of the barley ear-burn in Niigata Prefecture (in Japanese). Proc Assoc Plant Prot Hokuriku 28:84–86
Fieldhouse DJ, Sasser M (1982) A medium highly selective for Pseudomonas syringae. pv. glycinea. Phytopathology 72:706
Fukuda T, Azegami K, Tabei H (1990) Histological studies on bacterial black node of barley and wheat caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. japonica (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 56:252–256
Goto K, Nakanishi I (1951) Ear burn, a new bacterial disease of barley (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 15:117–120
Hasebe M, Hino K, Kondo A, Tsuchiya K (1998) Examination of selective isolation medium of bacterial black node of barley and wheat caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. japonica. Ann Rept Kansai Plant Prot 40:87–88
Ikata S, Hori M (1950) Showa 24 nendo shukaku mugi ni gekihatsu shita shin saikinbyo ni tsuite (in Japanese). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 15:32–33
Inoue Y, Takikawa Y (2006) The hrpZ and hrpA genes are variable, and useful for grouping Pseudomonas syringae bacteria. J Gen Plant Pathol 72:26–33
Kan M (1978) Mugirui kurofushibyo no hassei seitai to shuryo heno eikyo (in Japanese). Kongetsuno Nouyaku 22:14–18
Kawaguchi A, Tanina K, Takehara T (2017) Molecular epidemiology of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae strains isolated from barley and wheat infected with bacterial black node. J Gen Plant Pathol 83:162–168
Kawaguchi A, Yoshioka R, Mori M, Nishimura F, Kawata K, Tomioka K, Takehara T (2018) Spatiotemporal distribution of barley and wheat plants naturally infected with bacterial black node in fields in western Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 84:35–43
Maeda T, Tsuchiya K (1993) Kokessei sakuseiho (in Japanese). In: Wakimoto S (ed) Laboratory guide for plant pathology and microbiology. Soft Science Publications, Tokyo, pp 249–263
Matsuzawa K (1987) Occurrence of bacterial black node of barley in Toyama Prefecture in 1987 (in Japanese). Proc Assoc Plant Prot Hokuriku 35:57–60
Miyoshi T, Tachibana Y (1994) A selective medium for isolation of Pseudomonas syringae, the pathogen of bacterial blossom blight of kiwifruit (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 60:729–734
Mori M, Sogou K, Kanegae Y (1999) Detection of Pseudomonas syringae pv. japonica from barley seeds by selective medium and antiserum (in Japanese). Ann Phytopathol Soc Japan 65:362–363
Mukoo H, Tsuchiya Y (1950) Mugirui no saikinbyo ni tsuite (in Japanese). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 15:44–45
Nishiyama K (1978) Shokubutsu byogen saikin kan-i doteiho no shian (in Japanese). Plant Prot 32:283–288
Oba S, Saito S, Sato M, Ishigaki H, Tanaka T, Uzuki T (1990) On the occurrence of bacterial black node of wheat in Shonai region of Yamagata Prefecture (in Japanese). Ann Rept Plant Prot North Jpn 41:50–52
Sato M, Takahashi K, Uematsu T, Ohata K (1981) Selective media for isolation of Pseudomonas syringae pv. mori, the pathogen of bacterial blight of mulberry (in Japanese with English summary). J Seric Sci Jpn 50:409–414
Senba T, Kaneko M, Kondo A, Takashi S (1994) Occurrence and its yield loss, control effects of some methods of bacterial black node of wheat and tow-lowed barley (in Japanese). Ann Rept Kansai Plant Prot 36:63–64
Shimizu S, Yanagihara Y, Asaka S (1981) Occurrence of barley bacterial node in Nagano Prefecture (in Japanese). Ann Rep Kanto-Tosan Plant Prot Soc 28:23–24
Takamatsu S (1983) New occurrence of bacterial black node of barley in Fukui Prefecture, in 1979 (in Japanese). Proc Assoc Plant Prot Hokuriku 31:77–78
Tsao PH (1970) Selective media for isolation of pathogenic fungi. Ann Rev Phytopathol 8:157–186
Tsushima S, Wakimoto S, Mogi S (1986) Selective medium for detecting Pseudomonas glumae Kurita et Tabei, the causal bacterium of grain rot of rice (in Japanese with English summary). Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 52:253–259
Uematsu T, Takatsu A, Ohata K (1982) A medium for the selective isolation of Pseudomonas cichorii. Ann Phytopathol Soc Japan 48:425–432
Wakimoto S, Uematsu T (1993) Bunri-baiyoho (in Japanese). In: Wakimoto S (ed) Laboratory guide for plant pathology and microbiology. Soft Science Publications, Tokyo, pp 51–77
Yokoyama S (1976) Fukuoka-ken ni toppatsu shita mugirui kurofushibyo (in Japanese). Plant Prot 30:7–10
Yoshioka R, Uematsu H, Takikawa Y, Kajihara H, Inoue Y (2014) Development of PCR primer sets for detection of Pseudomonas syringae. pv. syringae, the causal agent of bacterial black node (in Japanese). Jpn J Phytopathol 80:322–323
Young JM (1992) Pseudomonas syringae pv. japonica (Mukoo 1955) Dye et al. 1980 is a junior synonym of Ps. syringae pv. syringae van Hall 1902. Lett Appl Microbiol 15:129–130
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Dr. Kenichi Tsuchiya (professor emeritus at Kyushu University) and Dr. Jun-Ichirou Yamaguchi for providing valuable strains, and to Drs. Koji Nishiyama and Takanori Miyoshi for helpful advice. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Science and Technology Research Promotion Program for Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries and Food Industry from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan (Grant number 25063C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Kazuhiro Sogou: Retired.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, M., Sogou, K. & Inoue, Y. Development of a selective medium and antisera for Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae from seeds of barley and wheat. J Gen Plant Pathol 85, 211–220 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-019-00838-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-019-00838-w