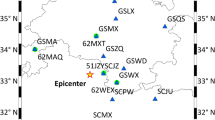
Abstract
Retrieving the coseismic displacement in real time is essential when the high-rate Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is used for the real-time earthquake source description. In 2020, the third generation of the BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) initiated a real-time precise point positioning service through the B2b signal (PPP-B2b), which provides a new possibility for real-time earthquake source description. In this study, the performance of the PPP-B2b on the real-time retrieval of coseismic displacement was first validated with GNSS observations collected during the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo earthquake. Then, the warning magnitude, focal mechanism and fault slip distribution were inverted with the derived PPP-B2b displacement in a simulated real-time model. Our results indicate that the accuracies of the coseismic displacements in the north, east and up components are 0.8 cm, 0.5 cm, and 1.4 cm for the single GPS PPP-B2b, 0.5 cm, 0.6 cm, and 0.9 cm for the single BDS-3 PPP-B2b and 0.4 cm, 0.3 cm, and 0.4 cm for the combined GPS/BDS-3 PPP-B2b, respectively, when compared with the coseismic displacements of the post-processing precise point positioning (PPP). Moreover, the warning magnitude, focal mechanism and fault slip distribution inverted with the PPP-B2b displacements are all in good agreement with those inverted with the PPP displacements. This study highlights the great possibility of the PPP-B2b to be used for earthquake early warning and rapid emergency responses.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The final precise orbit and clock products from the Wuhan University can be obtained at ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn/pub/. The GNSS observations from the CMONOC, the CORS and the China Mobile Communications Group Co., Ltd. can be obtained under permission.
References
Allen R, Alon Z (2011) Application of real-time GPS to earthquake early warning. Geophys Res Lett 38(16):L16310. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047947
Chen K, Avouac J, Geng J, Liang C, Zhang Z, Li Z, Zhang S (2022) The 2021 Mw 7.4 Madoi earthquake: an archetype bilateral slip-pulse rupture arrested at a splay fault. Geophys Res Lett 49(2):e2021GL095243. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GL095243
Crowell BW, Melgar D, Bock Y, Haase JS, Geng J (2013) Earthquake magnitude scaling using seismogeodetic data. Geophys Res Lett 40(23):6089–6094. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058391
CSNO (2020) BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal In: Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0)
Fang R, Lv H, Hu Z, Wang G, Zheng J, Zhou R, Xiao K, Li M, Liu J (2022) GPS/BDS precise point positioning with B2b products for high-rate seismogeodesy: application to the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo earthquake. Geophys J Int 231(3):2079–2090. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggac311
Ge Y, Cao X, Lyu D, He Z, Ye F, Xiao G, Shen F (2023) An investigation of PPP time transfer via BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. GPS Solut 27:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01402-y
Geng J, Jiang P, Liu J (2017) Integrating GPS with GLONASS for high-rate seismogeodesy. Geophys Res Lett 44(7):3139–3146. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL072808
Geng T, Li Z, Xie X, Liu W, Li Y, Zhao Q (2022) Real-time ocean precise point positioning with BDS-3 service signal PPP-B2b. Measurement 203:111911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111911
Goldberg D, Melgar D, Sahakian V, Thomas A, Xu X, Crowell B, Geng J (2020) Complex rupture of an immature fault zone: a simultaneous kinematic model of the 2019 Ridgecrest CA earthquakes. Geophys Res Lett 47:e2019GL086382. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL086382
Hadas T, Bosy J (2015) IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut 19(1):93–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0369-5
Larson K, Bodin P, Gomberg J (2003) Using 1 Hz GPS data to measure deformations caused by the Denali fault earthquake. Science 300(5624):1421–1424. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084531
Leick A, Rapoport L, Tatarnikov D (2015) GPS satellite surveying. Wiley, Hoboken
Li X, Zheng K, Li X, Liu G, Ge M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2019) Real-time capturing of seismic waveforms using high-rate BDS, GPS and GLONASS observations: the 2017 Mw 6.5 Jiuzhaigou earthquake in China. GPS Solut 23(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0808-9
Melgar D, Bock Y, Crowell BW (2012) Real-time centroid moment tensor determination for large earthquakes from local and regional displacement records. Geophys J Int 188(2):703–718. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05297.x
Melgar D, Crowell BW, Geng J, Allen RM, Bock Y, Riquelme S, Hill EM, Protti M, Ganas A (2015) Earthquake magnitude calculation without saturation from the scaling of peak ground displacement. Geophys Res Lett 42(13):5197–5205. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL064278
Meng G, Su X, Wu W, Nikolay S, Takahashi H, Ohzono M, Gerasimenko M (2019) Crustal deformation of the Northeastern China after the 2011 Tohoku, Japan Mw 9.0 earthquake estimated from GPS observations: strain heterogeneity and seismicity. Remote Sens 11(24):3029. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243029
Minson S, Murray JR, Langbein JO, Gomberg JS (2014) Real-time inversions for finite fault slip models and rupture geometry based on high-rate GPS data. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 119(4):3201–3231. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013JB010622
Miyazaki S, Larson K, Choi K, Hikima K, Koketsu K, Bodin P, Haase J, Emore G, Yamagiwa A (2004) Modeling the rupture process of the 2003 September 25 Tokachi-Oki (Hokkaido) earthquake using 1-Hz GPS data. Geophys Res Lett 31:L21603. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021457
Nie Z, Xu X, Wang Z, Du J (2021) Initial assessment of BDS PPP-B2b service: precision of orbit and clock corrections, and PPP performance. Remote Sens 13(11):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13112050
Okada Y (1985) Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull Seismol Soc Am 75(4):1135–1154. https://doi.org/10.1785/BSSA0750041135
Pan J, Bai M, Li C, Liu F, Li H, Liu D, Chevalier ML, Wu K, Wang P, Lu H, Chen P, Li C (2021) Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021–05–22 Maduo (Qinghai) Ms 7.4 earthquake. Acta Geol Sin 95(6):1655–1670. https://doi.org/10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2021166
Ren Z, Gong H, Peng J, Tang C, Huang X, Sun G (2021) Performance assessment of real-time precise point positioning using BDS PPP-B2b service signal. Adv Space Res 68(8):3242–3254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.06.006
Ren J, Xu X, Zhang G, Wang Q, Zhang Z, Gai H, Kang W (2022) Coseismic surface ruptures, slip distribution, and 3D seismogenic fault for the 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo earthquake, central Tibetan Plateau, and its tectonic implications. Tectonophysics 827:229275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2022.229275
Sun S, Wang M, Liu C, Meng X, Ji R (2023) Long-term performance analysis of BDS-3 precise point positioning (PPP-B2b) service. GPS Solut 27:69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01409-5
Tang C, Hu X, Chen J, Liu L, Zhou S, Guo R, Li X, He F, Liu J, Yang J (2022) Orbit determination, clock estimation and performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. J Geod 96:60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01642-9
Tao J, Liu J, Hu Z, Zhao Q, Chen G, Ju B (2021) Initial assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solut 25(4):131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01168-1
Wang R, Martin F, Roth F (2003) Computation of deformation induced by earthquakes in a multi-layered elastic crust: FORTRAN programs EDGRN/EDCMP. Comput Geosci 29(2):195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-3004(02)00111-5
Wang W, Fang L, Wu J, Tu H, Chen L, Lai G, Zhang L (2021) Aftershock sequence relocation of the 2021 Ms7.4 Maduo Earthquake. Qinghai China Sci China Earth Sci 64:1371–1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-021-9803-3
Wells B, Coppersmith K (1994) New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(4):974–1002
Wen Y, Xiao Z, He P, Zang J, Liu Y, Xu C (2021) Source characteristics of the 2020 Mw 7.4 Oaxaca, Mexico, earthquake estimated from GPS, InSAR, and teleseismic waveforms. Seismol Res Lett 92(3):1900–1912. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220200313
Xu P, Shi C, Fang R, Liu J, Niu X, Zhang Q, Yanagidani T (2013) High-rate precise point positioning (PPP) to measure seismic wave motions: an experimental comparison of GPS PPP with inertial measurement units. J Geod 87(4):361–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-012-0606-z
Xu Y, Yang Y, Li J (2021) Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut 25(4):142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-021-01175-2
Xu X, Nie Z, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Dong L (2023) An improved BDS-3 PPP-B2b positioning approach by estimating signal in space range errors. GPS Solut 27:110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01455-z
Yang Y, Liu L, Li J, Yang Y, Zhang T, Mao Y, Sun B, Ren X (2021) Featured services and performance of BDS-3. Sci Bull 66(20):2135–2143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2021.06.013
Yang Y, Ding Q, Gao W, Li J, Xu Y, Sun B (2022) Principle and performance of BDSBAS and PPP-B2b of BDS-3. Satell Navig 3:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43020-022-00066-2
Yang H, He X, Ferreira V, Ji S, Xu Y, Song S (2023) Assessment of precipitable water vapor retrieved from precise point positioning with PPP-B2b service. Earth Sci Inform 16:315–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-00939-3
Zang J, Xu C, Li X (2020) Scaling earthquake magnitude in real time with high-rate GNSS peak ground displacement from variometric approach. GPS Solut 24:101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01013-x
Zang J, Wen Y, Li Z, Xu C, He K, Zhang P, Wen G, Fan S (2022) Rapid source models of the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo, China, earthquake inferred from high-rate BDS3/2, GPS, Galileo and GLONASS observations. J Geod 96:58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-022-01641-w
Zhang Z, Xu L (2021) The centroid moment tensor solution of the 2021 Mw7.5 Maduo, Qinghai, earthquake. Acta Seismol Sin 43(3):387–391. https://doi.org/10.11939/jass.20210079
Zhang W, Lou Y, Song W, Sun W, Zou X, Gong X (2022) Initial assessment of BDS-3 precise point positioning service on GEO B2b signal. Adv Space Res 69(1):690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.09.006
Acknowledgements
This work is co-supported by the Qingdao Natural Science Foundation (23-2-1-70-zyyd-jch), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR202211210055), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22CX06034A) and the key project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42130101). The authors acknowledge the Crustal Movement Observation Network Of China (CMONOC), the Continuously Operating Reference Stations of Qinghai Province in China (CORS) and the China Mobile Communications Group Co., Ltd. for providing GNSS observations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ performed the data processing and wrote the manuscript. SF contributed to the experimental design, analysis and proof-read the manuscript. CX provided the advice and guidance for the results analysis. ZL contributed to the GNSS data collection and processing. RF and YL contributed to the recovery of the precise satellite orbit and clock offsets with the PPP-B2b corrections.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (AVI 23195 kb)
Supplementary file2 (AVI 23473 kb)
Supplementary file3 (AVI 23491 kb)
Supplementary file4 (AVI 23403 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zang, J., Fan, S., Xu, C. et al. Performance assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b service for real-time earthquake source description: a case study for the 2021 Mw 7.4 Maduo earthquake. GPS Solut 28, 26 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01570-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01570-x