Abstract
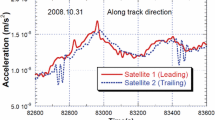
As a crucial payload on dedicated gravity satellites, the accelerometer (ACC) measures the non-gravitational force acting on the satellite. The unknown scale and bias contaminate the raw ACC data, preventing the direct use in precise orbit determination (POD) and gravity recovery, and thus ACC data need to be calibrated. We analyze the performance of GRACE-FO ACC and calibrate the ACC data from 2018 to 2021 based on a step-by-step calibration method. First, we give an overview of temperature records and ACC operational modes, which reflect the operational status of the ACC. The calibration method consists of four steps: pre-calibration, two POD processes with different parameterizations, and bias fitting. Low-degree/order (10 × 10) spherical harmonic coefficients (SHCs) are estimated with scale, bias, and other dynamic parameters in POD. As an assessment, we compare the calibrated ACC data and the modeled non-gravitational force products. The average differences between them are less than 5 nm/s2 in the SRF-X direction and 6 nm/s2 in other directions. The obtained orbits based on ACC data and GPS observations are compared with precise science orbits. Furthermore, six tests show that introducing low-order/degree SHCs could effectively improve the consistency of the calibrated ACC data with non-gravitational force models and enhance orbit determination. Otherwise, empirical accelerations should be estimated with loose constraints to ensure POD results.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All original data in this study are publicly available. GPS ephemeris, precise clock offset are available from the CODE (ftp.aiub.unibe.ch), and the GRACE-FO L1B dataset from JPL at https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/GRACE-FO or GFZ via ftp://rz-vm152.gfz-potsdam.de/. The Jacchia-Bowman 2008 empirical thermospheric density model can be found at https://sol.spacenvironment.net/jb2008/introduction.html. CERES earth radiation data were obtained from https://ceres.larc.nasa.gov/. Non-gravitational force products were provided by the Institute of Geodesy (IfG) at Graz University of Technology via https://ftp.tugraz.at/outgoing/ITSG/satelliteOrbitProducts/.
References
Bandikova T, McCullough C, Kruizinga GL, Save H, Christophe B (2019) GRACE accelerometer data transplant. Adv Space Res 64(3):623–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.05.021
Behzadpour S, Mayer-Gürr T, Krauss S (2021) GRACE follow-on accelerometer data recovery. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 126(5):e2020JB021297. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB021297
Bettadpur S (2009) Recommendation for a-priori bias & scale parameters for level-1B ACC Data (Version 2)
Bezděk A (2010) Calibration of accelerometers aboard GRACE satellites by comparison with POD-based nongravitational accelerations. J Geodyn 50(5):410–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2010.05.001
Bezděk A, Sebera J, Klokočník J (2017) Validation of swarm accelerometer data by modelled nongravitational forces. Adv Space Res 59(10):2512–2521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2017.02.037
Bowman B, Tobiska WK, Marcos F, Huang C, Lin C, Burke W (2008) A new empirical thermospheric density model JB2008 using new solar and geomagnetic indices. In: AIAA/AAS astrodynamics specialist conference and exhibit, August 18–21 2008, Honolulu. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2008-6438
Calabia A, Jin S, Tenzer R (2015) A new GPS-based calibration of GRACE accelerometers using the arc-to-chord threshold uncovered sinusoidal disturbing signal. Aerosp Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2015.05.013
Christophe B, Boulanger D, Foulon B, Huynh P-A, Lebat V, Liorzou F, Perrot E (2015) A new generation of ultra-sensitive electrostatic accelerometers for GRACE follow-on and towards the next generation gravity missions. Acta Astronaut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.06.021
Doornbos EN (2011) Thermospheric density and wind determination from satellite dynamics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Drinkwater MR, Haagmans R, Muzi D, Popescu A, Floberghagen R, Kern M, Fehringer M (2006) The GOCE gravity mission: ESA’s first core Earth explorer. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international GOCE User Workshop, Frascati
Folkner WM, Williams JG, Boggs DH (2009) The planetary and lunar ephemeris DE 421. IPN Prog Rep 42(178):1–34
Forootan E, Farzaneh S, Kosary M, Schmidt M, Schumacher M (2020) A simultaneous calibration and data assimilation (C/DA) to improve NRLMSISE00 using thermospheric neutral density (TND) from space-borne accelerometer measurements. Geophys J Int 224(2):1096–1115. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggaa507
Fulcher RC (2016) Temperature fluctuation analysis for GRACE twin satellites. Master Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin
Girardin V (2016) Impact of non-gravitational forces on GPS-based precise orbit determination of low Earth orbiters. Master Thesis, the Delft University of Technology
Harvey N, McCullough CM, Save H (2022) Modeling GRACE-FO accelerometer data for the version 04 release. Adv Space Res 69(3):1393–1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.10.056
Helleputte TV, Doornbos E, Visser P (2009) CHAMP and GRACE accelerometer calibration by GPS-based orbit determination. Adv Space Res 43(12):1890–1896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2009.02.017
Jäggi A, Dach R, Montenbruck O, Hugentobler U, Bock H, Beutler G (2009) Phase center modeling for LEO GPS receiver antennas and its impact on precise orbit determination. J Geodesy 83(12):1145–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-009-0333-2
Kalimeris G, Pail R, Gruber T (2022) Impact of GRACE Follow-On LRI and the updated accelerometer transplant product (ACH1B) on the estimated static earth gravity field. In: 2022 GRACE-FO science team meeting, Potsdam. https://doi.org/10.5194/gstm2022-54
Kang Z, Tapley B, Bettadpur S, Ries J, Nagel P (2006) Precise orbit determination for GRACE using accelerometer data. Adv Space Res 38(9):2131–2136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2006.02.021
Klinger B, Mayer-Gürr T (2016) The role of accelerometer data calibration within GRACE gravity field recovery: results from ITSG-Grace2016. Adv Space Res 58(9):1597–1609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2016.08.007
Klinger B (2018) A contribution to GRACE time-variable gravity field recovery: improved Level-1B data pre-processing methodologies. Ph.D. Thesis, Graz University of Technology
Knocke P, Ries J, Tapley B (1988) Earth radiation pressure effects on satellites. In: Astrodynamics conference, Minneapolis. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.1988-4292
Kornfeld RP, Arnold BW, Gross MA, Dahya NT, Klipstein WM, Gath PF, Bettadpur S (2019) GRACE-FO: the gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on mission. J Spacecr Rocket 56(3):931–951. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A34326
Krauss S, Behzadpour S, Temmer M, Lhotka C (2020) Exploring thermospheric variations triggered by severe geomagnetic storm on 26 august 2018 using GRACE follow-on data. J Geophys Res Space Phys 125(5):e2019JA027731. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JA027731
Kvas A, Behzadpour S, Ellmer M, Klinger B, Strasser S, Zehentner N, Mayer-Gürr T (2019) ITSG-grace 2018: overview and evaluation of a new GRACE-only gravity field time series. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 124(8):9332–9344. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB017415
Landerer FW et al (2020) Extending the global mass change data record: GRACE follow-on instrument and science data performance. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL088306
Landerer F, Flechtner F, Save H, Dahle C (2022) GRACE follow-on science data system newsletter report: Jan–Mar 2022 (No. 20)
Li M, Lei Z, Li W, Jiang K, Wang Y, Zhao Q (2022) Calibration of GRACE on-board accelerometers for thermosphere density derivation. Geo Spat Inf Sci 25(1):74–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2021.2010506
McCullough CM, Harvey N, Save H, Bandikova T (2019) Description of calibrated GRACE-FO accelerometer data products (ACT). Level-1 Product Version 4.
McCullough CM (2017) Gravity field estimation for next generation satellite missions. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin
McGirr R, Tregoning P, Allgeyer S, McQueen H, Purcell A (2022) Mitigation of thermal noise in GRACE accelerometer observations. Adv Space Res 69(1):386–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2021.10.055
Montenbruck O, Gill E (2000) Satellite orbits: models, methods, and applications. Springer, Heidelberg
Papanikolaou T (2022) Precise orbit determination and accelerometer data modelling of the GRACE follow-on mission. In: GRACE/GRACE-FO science team meeting 2022, 18–20 Oct 2022, Potsdam. https://doi.org/10.5194/gstm2022-90
Rebischung P, Schmid R, Herring T (2016) Upcoming switch to IGS14/igs14.atx. IGSMAIL-7399.
Reigber C, Lühr H, Schwintzer P (2002) CHAMP mission status. Adv Space Res 30(2):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00276-4
Rievers B, Kato T, van der Ha J, Lämmerzahl C (2012) Numerical prediction of satellite surface forces with application to Rosetta. Adv Astronaut Sci 143:1123–1142
Steigenberger P, Thölert S, Montenbruck O (2019) Flex power on GPS block IIR-M and IIF. GPS Solut 23(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-018-0797-8
Tapley BD, Bettadpur S, Watkins M, Reigber C (2004) The gravity recovery and climate experiment: mission overview and early results. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL019920
Teixeira da Encarnação J, Save H, Tapley B, Rim H-J (2020) Accelerometer parameterization and the quality of gravity recovery and climate experiment solutions. J Spacecr Rocket 57(4):740–752. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A34639
Van Helleputte T, Visser P (2008) GPS based orbit determination using accelerometer data. Aerosp Sci Technol 12(6):478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2007.11.002
Vielberg K, Forootan E, Lück C, Löcher A, Kusche J, Börger K (2018) Comparison of accelerometer data calibration methods used in thermospheric neutral density estimation. Ann Geophys 36(3):761–779. https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-36-761-2018
Visser PNAM, Jvd I (2003) Verification of champ accelerometer observations. Adv Space Res 31(8):1905–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1177(03)00165-0
Wen HY, Kruizinga G, Paik M, Landerer F, Bertiger W, Sakumura C, Bandikova T, Mccullough C (2019) Gravity recovery and climate experiment follow-on (GRACE-FO) level-1 data product user handbook. JPL D-56935 (URS270772) 11.
Wielicki BA, Barkstrom BR, Harrison EF, Lee RB III, Smith GL, Cooper JE (1996) Clouds and the earth’s radiant energy system (CERES): an earth observing system experiment. Bull Am Meteor Soc 77(5):853–868. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077%3C0853:CATERE%3E2.0.CO;2
Wöske F, Kato T, Rievers B, List M (2019) GRACE accelerometer calibration by high precision non-gravitational force modeling. Adv Space Res 63(3):1318–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.10.025
Wu S-C, Kruizinga G, Bertiger W (2006) Algorithm theoretical basis document for GRACE level-1B data processing V1.2. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology, Pasadena
Yang X, Liu W, Huang J, Xiao W, Wang F (2022) Real-time monitoring of GPS flex power based on machine learning. GPS Solut 26(3):73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01257-9
Yu B, You W, Fan D-M, Su Y, Nigatu ZM (2021) A comparison of GRACE temporal gravity field models recovered with different processing details. Geophys J Int 227(2):1392–1417. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggab279
Acknowledgements
This study is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41974013, 42174014). We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their comments, which greatly improved our original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, WY, and BY devised the main conceptual ideas; JZ performed the calculations for the experiments; BY and DF helped to analyze the results and data; JZ and BY prepared figures; JZ and WY wrote the manuscript; WY, BY, and DF modified the manuscript; all authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., You, W., Yu, B. et al. GRACE-FO accelerometer performance analysis and calibration. GPS Solut 27, 158 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01487-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-023-01487-5