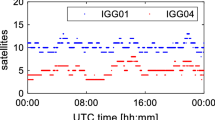
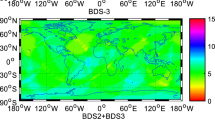
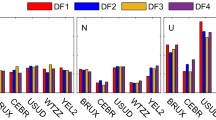
Abstract
BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) began to provide global services of positioning, navigation, and timing on July 31, 2020. The Real-time Kinematic (RTK) is one of the essential services for BDS’ precise applications. In this contribution, a BDS-3 RTK model based on the constraint of the Wet component of Zenith Tropospheric Delay (WZTD) and the partial ambiguity resolution methods is provided, in which the impact of WZTD residuals caused by both horizontal distance and height is restrained. To evaluate the performance of such a BDS-3 RTK model, a set of triple-frequency multi-constellation Global Navigation Satellite Systems vehicle-borne data is collected and processed. Results demonstrate that (1) the positioning accuracy of BDS-3 is decimeter-level to centimeter-level in terms of root mean square value while using single, dual, and triple frequency observations, which is generally close to that of GPS; (2) the positioning accuracy of BDS-3 RTK based on the new signals (B1C, B1C + B2a, and B1C + B2a + B3I) are higher than that using B1I and B3I signals; (3) the ambiguity resolution fixed rate of BDS-3 RTK is improved after applying the partial ambiguity resolution methods and WZTD constraint.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of the zero baseline and vehicle kinematic experiment can be provided by contacting the corresponding author for reasonable reasons.
References
Böhm J, Niell A, Tregoning P, Schuh H (2006) Global Mapping Function (GMF): a new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025546
Brack A (2016) Reliable GPS+BDS RTK positioning with partial ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 21(3):1083–1092
CSNO (2019a) Development of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version 4.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/2019a12/P02019a1227430565455478.pdf
CSNO (2019b) The Application service architecture of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (Version1.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/2019b12/P02019b1227333024390305.pdf
CSNO (2021) BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Open Service Performance Standard (Version3.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202105/P020210526216231136238.pdf
Deng J, Zhang A, Zhu N, Ke F (2020) Extra-wide lane ambiguity resolution and validation for a single epoch based on the triple-frequency BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. Sensors 20(5):1534
Deng C, Qi S, Li Y, Wang Y, Zou X, Tang W, Guo C (2021) A comparative analysis of navigation signals in BDS-2 and BDS-3 using zero-baseline experiments. GPS Solut 25:143
Forssell B, Martin-Neira M, Harrisz RA (1997) Carrier phase ambiguity resolution in GNSS-2. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 1997, Institute of Navigation, Kansas City, Missouri, USA, September 16–19, pp 1727–1736
Hadas T, Teferle FN, Kazmierski K, Hordyniec P, Bosy J (2017) Optimum stochastic modeling for GNSS tropospheric delay estimation in real-time. GPS Solut 21:1069–1081
Hatch R, Jung J, Enge P, Pervan B (2000) Civilian GPS: the benefits of three frequencies. GPS Solut 3(4):1–9
Han S (1997) Quality-control issues relating to instantaneous ambiguity resolution for real-time GPS kinematic positioning. J Geodesy 71(6):351–361
He H, Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, Guo H, Wang A (2014) Performance assessment of single-and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut 18(3):393–403
Janes HW, Langley RB, Newby SP (1991) Analysis of tropospheric delay prediction models: comparisons with ray-tracing and implications for GPS relative positioning. Bull Géod 65(3):151–161
Jung J (1999). High integrity carrier phase navigation for future LAAS using multiple civilian GPS signals. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 1999, Institute of Navigation, Nashville, Tennessee, USA, September 14–17, pp 727–736
Landau H, Vollath U, Chen X (2003) Virtual reference stations versus broadcast solutions in network RTK—advantages and limitations. In: Proceedings of ION GPS 2003, Institute of Navigation, Graz, Austria, pp 22–25
Li B, Shen Y, Feng Y, Gao W, Yang L (2014) GNSS ambiguity resolution with controllable failure rate for long baseline network RTK. J Geodesy 88(2):99–112
Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, He H, Guo H (2015) GNSS multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy tested with real BDS/GPS dual-and triple-frequency observations. GPS Solut 19(1):5–13
Lu M, Li W, Yao Z, Cui X (2019a) Overview of BDS III new signals. Navigation 66(1):19–35
Lu L, Ma L, Liu W, Wu T, Chen B (2019b) A triple checked partial ambiguity resolution for GPS/BDS RTK positioning. Sensors 19(22):5034
Li Y, Zou X, Tang W, Deng C, Wang Y (2020) Regional modeling of tropospheric delay considering vertically and horizontally separation of station for regional augmented PPP. Adv Space Res 66(10):2338–2348
Odijk D, Arora BS, Teunissen PJG (2014) Predicting the success rate of long-baseline GPS+ Galileo (partial) ambiguity resolution. J Navig 67(3):385–401
Parkins A (2011) Increasing GNSS RTK availability with a new single-epoch batch partial ambiguity resolution algorithm. GPS Solut 15(4):391–402
Shu B, Liu H, Xu L, Qian C, Gong X, An X (2018) Performance analysis of BDS medium-long baseline RTK positioning using an empirical troposphere model. Sensors 18(4):1199
Takasu T, Yasuda A (2010) Kalman-filter-based integer ambiguity resolution strategy for long-baseline RTK with ionosphere and troposphere estimation. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2010, Institute of Navigation, Portland, Oregon, USA, September 21–24, pp 161–171
Teunissen PJG (1998) Success probability of integer GPS ambiguity rounding and bootstrapping. J Geodesy 72(10):606–612
Teunissen PJG (2003) Integer aperture GNSS ambiguity resolution. Artif Satell 38(3):79–88
Teunissen PJG, Verhagen S (2004) On the foundation of the popular ratio test for GNSS ambiguity resolution. In: Proc. ION GNSS 2004, Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, California, USA, September 21–24, pp 2529–2540
Teunissen PJG (2005) Integer aperture bootstrapping: a new GNSS ambiguity estimator with controllable fail-rate. J Geodesy 79(6):389–397
Teunissen PJG, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2014) Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geodesy 88(4):335–350
Verhagen S (2002) On the approximation of the integer least-squares success rate: which lower or upper bound to use. Positioning 1(05)
Verhagen S, Teunissen PJG (2013) The ratio test for future GNSS ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 17(4):535–548
Wang K, Rothacher M (2013) Ambiguity resolution for triple-frequency geometry-free and ionosphere-free combination tested with real data. J Geodesy 87(6):539–553
Wen Z, Henkel P, Günther C (2015) Precise point positioning with partial ambiguity fixing and optimal subset selection. Springer, Berlin
Xu Y, Wu C, Li L, Yan L, Liu M, Wang S (2018) GPS/BDS medium/long-range RTK constrained with tropospheric delay parameters from NWP model. Remote Sens 10(7):1113
Yang Y, Gao W, Guo S, Mao Y, Yang Y (2019) Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 66(1):7–18
Yuan Y, Mi X, Zhang B (2020) Initial assessment of single-and dual-frequency BDS-3 RTK positioning. Satell Navig 1(1):1–7
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhu F (2020) A method of improving ambiguity fixing rate for post-processing kinematic GNSS data. Satell Navig 1(1):1–13
Zhang Y, Kubo N, Chen J, Wang J, Wang H (2019a) Initial positioning assessment of BDS new satellites and new signals. Remote Sens 11(11):1320
Zhang Z, Li B, Nie L, Wei C, Jia S, Jiang S (2019b) Initial assessment of BeiDou-3 global navigation satellite system: signal quality, RTK and PPP. GPS Solut 23(4):1–12
Zhu H, Xu A, Gao M, Yang Q (2016) The algorithm of single-epoch integer ambiguity resolution between middle-range BDS network RTK reference stations. Acta Geod Cartogr Sin 45(1):50
Acknowledgements
This work was partially funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFB0505802), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (Grant No. YESS20200308), the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2021M690192), and Beijing Postdoctoral Research Foundation (Grant No. 2021-ZZ-088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Gao, Z., Xu, Q. et al. Assessing partial ambiguity resolution and WZTD-constraint multi-frequency RTK in an urban environment using new BDS signals. GPS Solut 26, 88 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01274-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01274-8